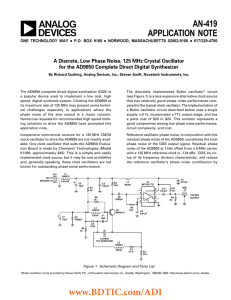
A 6-to-18 GHz Tunable Concurrent Dual-Band Receiver
... separates it into its low-band and high-band components. Both the high-band and the low-band have their own down-conversion signal paths. If the second LO frequency is chosen to be half of the first LO frequency, image signals will always fall out of the 6-18GHz frequency range; thus they can be fil ...
... separates it into its low-band and high-band components. Both the high-band and the low-band have their own down-conversion signal paths. If the second LO frequency is chosen to be half of the first LO frequency, image signals will always fall out of the 6-18GHz frequency range; thus they can be fil ...
Copyright © 2004 IEEE. Reprinted from IEEE International Symposium on
... Keywords: RFI, Pin direct injection method, Power reflection coefficient, Pulsed modulated RF, Clock network ...
... Keywords: RFI, Pin direct injection method, Power reflection coefficient, Pulsed modulated RF, Clock network ...
T4500 Auto Synchronizer
... generator against reverse power, the generator should come in at a slightly higher frequency than the frequency of the busbar. When the voltage and frequency difference are within limits, the closing signal will be activated just before the next phase accordance, anticipating the circuit breaker ma ...
... generator against reverse power, the generator should come in at a slightly higher frequency than the frequency of the busbar. When the voltage and frequency difference are within limits, the closing signal will be activated just before the next phase accordance, anticipating the circuit breaker ma ...
lecture1429901112
... The RF input to be analyzed is applied to the input attenuator. After attenuating, the signal is fed to low pass filter. The low pass filter suppresses high frequency components and allows low frequency components to pass through it. The output of the low pass filter is given to the mixer, where th ...
... The RF input to be analyzed is applied to the input attenuator. After attenuating, the signal is fed to low pass filter. The low pass filter suppresses high frequency components and allows low frequency components to pass through it. The output of the low pass filter is given to the mixer, where th ...
File
... Objectives • State the purpose and general principles of motor control • Discuss the differences between manual and automatic motor control • Discuss considerations when installing motors or control equipment ...
... Objectives • State the purpose and general principles of motor control • Discuss the differences between manual and automatic motor control • Discuss considerations when installing motors or control equipment ...
11111-HWS516 Data Sheet產品規格-E1
... • Isolation: 23 dB @ 2.5 GHz • Low DC Power Consumption • Miniature USON6L (1.5x1.5x0.4 mm) ...
... • Isolation: 23 dB @ 2.5 GHz • Low DC Power Consumption • Miniature USON6L (1.5x1.5x0.4 mm) ...
3.2 Electrical conversion system
... designed for the purpose of extracting significant power from the wind and converting it to rotary motion. The rotor is connected to the main shaft (low-speed or rotor shaft), which is the principal rotating element, thereby providing for the transfer of torque from the rotor to the rest of the driv ...
... designed for the purpose of extracting significant power from the wind and converting it to rotary motion. The rotor is connected to the main shaft (low-speed or rotor shaft), which is the principal rotating element, thereby providing for the transfer of torque from the rotor to the rest of the driv ...
UPM310 - Isotron Systems
... powerful capabilities offered by the instruments make it ideal for stand-alone metering or energy management systems. UPM310 offers a compact unit together with a variety of mounting combinations making it suitable for new installations as well as retrofit applications. The power meter fits in DIN96 ...
... powerful capabilities offered by the instruments make it ideal for stand-alone metering or energy management systems. UPM310 offers a compact unit together with a variety of mounting combinations making it suitable for new installations as well as retrofit applications. The power meter fits in DIN96 ...
Versa-Pac as Forward Converter
... primarily, for low voltage applications typically 3.3V, 5V and 12V. With the addition of the VPH products to the range the Versa-Pac can now be used for 24V, 48V and, at higher frequencies, even 120V applications. Each transformer has six identical windings that can be configured in series and paral ...
... primarily, for low voltage applications typically 3.3V, 5V and 12V. With the addition of the VPH products to the range the Versa-Pac can now be used for 24V, 48V and, at higher frequencies, even 120V applications. Each transformer has six identical windings that can be configured in series and paral ...
ME 461 Laboratory #2
... Timer A for PWM generation on channel 1. That is, set the CCR1 OUTMOD bits appropriately; set/reset or reset/set should work for our application (but one is better). Output the TA1 signal to pin 1.2 by setting that pin to its alternative function with the P1SEL register and by setting its direction ...
... Timer A for PWM generation on channel 1. That is, set the CCR1 OUTMOD bits appropriately; set/reset or reset/set should work for our application (but one is better). Output the TA1 signal to pin 1.2 by setting that pin to its alternative function with the P1SEL register and by setting its direction ...
A 6-to-18 GHz Tunable Concurrent Dual-Band Receiver Front End
... separates it into its low-band and high-band components. Both the high-band and the low-band have their own down-conversion signal paths. If the second LO frequency is chosen to be half of the first LO frequency, image signals will always fall out of the 6-18GHz frequency range; thus they can be fil ...
... separates it into its low-band and high-band components. Both the high-band and the low-band have their own down-conversion signal paths. If the second LO frequency is chosen to be half of the first LO frequency, image signals will always fall out of the 6-18GHz frequency range; thus they can be fil ...
Utility frequency
The utility frequency, (power) line frequency (American English) or mains frequency (British English) is the frequency of the oscillations of alternating current (AC) in an electric power grid transmitted from a power plant to the end-user. In large parts of the world this is 50 Hz, although in the Americas and parts of Asia it is typically 60 Hz. Current usage by country or region is given in the list of mains power around the world.During the development of commercial electric power systems in the late 19th and early 20th centuries, many different frequencies (and voltages) had been used. Large investment in equipment at one frequency made standardization a slow process. However, as of the turn of the 21st century, places that now use the 50 Hz frequency tend to use 220–240 V, and those that now use 60 Hz tend to use 100–127 V. Both frequencies coexist today (Japan uses both) with no great technical reason to prefer one over the other and no apparent desire for complete worldwide standardization.Unless specified by the manufacturer to operate on both 50 and 60 Hz, appliances may not operate efficiently or even safely if used on anything other than the intended frequency.