Syntax and semantics of the prefix-scale interplay I argue for
... The question arises, why the direct objects have different thematic roles (agent in (1-a) and patient in (1-b) ), though the syntactic structure looks identical on the surface. I explain this inconsistency through different syntactic structures for the sentences. In the tripartite event decompositio ...
... The question arises, why the direct objects have different thematic roles (agent in (1-a) and patient in (1-b) ), though the syntactic structure looks identical on the surface. I explain this inconsistency through different syntactic structures for the sentences. In the tripartite event decompositio ...
Peer Revision Checklist
... Preposition—In front of the class, Mrs. Lane waited patiently for her students to become quiet. Participle—Waiting patiently for her students to become quiet, Mrs. Lane stood in front of the class. ...
... Preposition—In front of the class, Mrs. Lane waited patiently for her students to become quiet. Participle—Waiting patiently for her students to become quiet, Mrs. Lane stood in front of the class. ...
What is subject-verb agreement?
... 1. (Was, Were) both of the meetings canceled? 2. Some of the plants (require, requires) full sun. 3. Each of the children (want, wants) a new toy. ...
... 1. (Was, Were) both of the meetings canceled? 2. Some of the plants (require, requires) full sun. 3. Each of the children (want, wants) a new toy. ...
Daily Edit-Parts of Speech and Agreement
... Tall woman, steep mountain, exciting story Which one? This year, last answer, middle row How much or how many? Less time, many mistakes, few marbles ...
... Tall woman, steep mountain, exciting story Which one? This year, last answer, middle row How much or how many? Less time, many mistakes, few marbles ...
Using Subject-Verb Agreement
... 1. (Was, Were) both of the meetings canceled? 2. Some of the plants (require, requires) full sun. 3. Each of the children (want, wants) a new toy. ...
... 1. (Was, Were) both of the meetings canceled? 2. Some of the plants (require, requires) full sun. 3. Each of the children (want, wants) a new toy. ...
For staff, students and parents.
... something done to it by someone or something. For example: "The mouse was being chased by the cat." Past continuous (or progressive) The past continuous is the verb tense we use to describe actions that continued for a period of time in the past (I was walking / I was singing). Past perfect The past ...
... something done to it by someone or something. For example: "The mouse was being chased by the cat." Past continuous (or progressive) The past continuous is the verb tense we use to describe actions that continued for a period of time in the past (I was walking / I was singing). Past perfect The past ...
Understanding Verbs:
... • A gerund is a verbal that ends in –ing and functions as a noun. • Since they are derived from verbs and have an –ing ending, they express action. • Gerunds can be used as a subject, direct object, subject complement, and object of preposition because it functions as a noun. • Gerunds may occur as ...
... • A gerund is a verbal that ends in –ing and functions as a noun. • Since they are derived from verbs and have an –ing ending, they express action. • Gerunds can be used as a subject, direct object, subject complement, and object of preposition because it functions as a noun. • Gerunds may occur as ...
Complement clauses in Canela
... analogous to the object of the main clause (word-order OV). The kind of nominalization found in the examples above can be described on the basis of the proposal by Comrie and Thompson (1985) regarding clausal nominalization (a nominalization without a lexically derived noun). The characteristic feat ...
... analogous to the object of the main clause (word-order OV). The kind of nominalization found in the examples above can be described on the basis of the proposal by Comrie and Thompson (1985) regarding clausal nominalization (a nominalization without a lexically derived noun). The characteristic feat ...
Document
... Subject Complements: Direct and Indirect Objects Most sentences need words beyond a subject and a verb to complete their meaning. Direct objects and indirect objects complete ideas and make sentences more specific. A direct object is a noun or pronoun that receives the action of the verb and answe ...
... Subject Complements: Direct and Indirect Objects Most sentences need words beyond a subject and a verb to complete their meaning. Direct objects and indirect objects complete ideas and make sentences more specific. A direct object is a noun or pronoun that receives the action of the verb and answe ...
Grammar Diagnostic and Definitions - Linn
... In Japan, during the last war and just before the armistice. This sentence accomplishes a great deal in terms of placing the reader in time and place, but there is no subject, no verb. b. It describes something, but there is no subject-verb relationship: Working far into the night in an effort to sa ...
... In Japan, during the last war and just before the armistice. This sentence accomplishes a great deal in terms of placing the reader in time and place, but there is no subject, no verb. b. It describes something, but there is no subject-verb relationship: Working far into the night in an effort to sa ...
Phrases and Appositives Handout
... A phrase is a group of words without a subject or a verb that functions in a sentence as one part of speech. The different types of phrases include; prepositional, adjectival, adverbial, verbal, participle, gerund, infinitive, and appositive phrases. ➔ A prepositional phrase is a group of words that ...
... A phrase is a group of words without a subject or a verb that functions in a sentence as one part of speech. The different types of phrases include; prepositional, adjectival, adverbial, verbal, participle, gerund, infinitive, and appositive phrases. ➔ A prepositional phrase is a group of words that ...
(Verbs 2)
... because Kelly was not sensing or touching something. In Sentence A, Dawn is again not feeling or sensing anything on her skin, and yet “felt” in this sentence is still an action verb. Again, as we did earlier with the verb “turn,” we are using a metaphorical sense of the verb in saying that Dawn “fe ...
... because Kelly was not sensing or touching something. In Sentence A, Dawn is again not feeling or sensing anything on her skin, and yet “felt” in this sentence is still an action verb. Again, as we did earlier with the verb “turn,” we are using a metaphorical sense of the verb in saying that Dawn “fe ...
Cultivating the Right On the Job Attitude
... Qualified: The numbers show, I think, that we can expect a further increase in sales. Qualified: You will, in my opinion, be satisfied with the service that you receive from our company. In both of these sentences, the author has qualified the statements by adding “I think” and “in my opinion.” Thes ...
... Qualified: The numbers show, I think, that we can expect a further increase in sales. Qualified: You will, in my opinion, be satisfied with the service that you receive from our company. In both of these sentences, the author has qualified the statements by adding “I think” and “in my opinion.” Thes ...
Learning Punctuation through Pattern Recognition
... Choose 1-3 full pages of a transcribed report (or a magazine article if a report is not available). Use different-colored highlighting pens to highlight the subjects, verbs (predicates), and conjunctions of compound sentences. Identify the conjunctions as coordinating conjunctions, conjunctive adver ...
... Choose 1-3 full pages of a transcribed report (or a magazine article if a report is not available). Use different-colored highlighting pens to highlight the subjects, verbs (predicates), and conjunctions of compound sentences. Identify the conjunctions as coordinating conjunctions, conjunctive adver ...
1 Effects of Verb Bias and Syntactic Ambiguity on Reading in People
... to the Lexical Bias Hypothesis, these impairments emerge when a verb’s argument structure biases conflict with the sentence structure (Gahl, 2002). For example, PWA had more trouble understanding sentences in which the verb’s transitivity bias conflicted with the sentence structure (e.g., a transiti ...
... to the Lexical Bias Hypothesis, these impairments emerge when a verb’s argument structure biases conflict with the sentence structure (Gahl, 2002). For example, PWA had more trouble understanding sentences in which the verb’s transitivity bias conflicted with the sentence structure (e.g., a transiti ...
Basic sentence Transformation: Active/Passive
... advisement.” 4. We had heard nothing from her since then. ...
... advisement.” 4. We had heard nothing from her since then. ...
Ah depreciate other persons dinners you ministers give
... type (simple, compound, compound complex) and purpose (declarative, interrogative, imperative, and exclamatory) ...
... type (simple, compound, compound complex) and purpose (declarative, interrogative, imperative, and exclamatory) ...
Subject and Predicate
... different parts of speech than they’re being used as here. It depends on their purpose. Here, though, love is a noun and stinks is a verb. ...
... different parts of speech than they’re being used as here. It depends on their purpose. Here, though, love is a noun and stinks is a verb. ...
Examples - Cobb Learning
... 1. Swimming is my favorite thing to do in the summer. 2. Washing the dishes is my daily chore. ...
... 1. Swimming is my favorite thing to do in the summer. 2. Washing the dishes is my daily chore. ...
sport
... Prepositions work in combination with a noun or pronoun to create phrases that modify verbs, nouns/pronouns, or adjectives. Prepositional phrases convey a spatial, temporal, or directional meaning. 1. Prepositions of Place and location 2. Prepositions of Time 3. Prepositions of Direction / Movement ...
... Prepositions work in combination with a noun or pronoun to create phrases that modify verbs, nouns/pronouns, or adjectives. Prepositional phrases convey a spatial, temporal, or directional meaning. 1. Prepositions of Place and location 2. Prepositions of Time 3. Prepositions of Direction / Movement ...
Exploring Affixation in English
... Inflectional categories such as tense, voice and number play important role in syntax and are called morphosyntactic categories, since they affect both the words around them and the words within which they occur. They are very productive and are semantically more regular than the derivational ones; ...
... Inflectional categories such as tense, voice and number play important role in syntax and are called morphosyntactic categories, since they affect both the words around them and the words within which they occur. They are very productive and are semantically more regular than the derivational ones; ...
singular - Washington Latin Grade 8
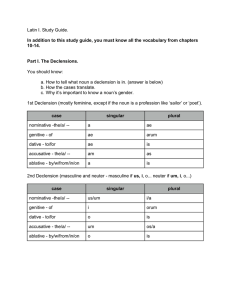
... Latin I. Study Guide. In addition to this study guide, you must know all the vocabulary from chapters ...
... Latin I. Study Guide. In addition to this study guide, you must know all the vocabulary from chapters ...
18.7 Talking about what HAD happened Language
... How far can you go up? 1000 feet? 3000 feet? What about 10000 feet?? Even after taking precautions, there is one thing that can still get you: altitude sickness. This happens due to the low oxygen levels in high altitude places, which can decrease mental and physical alert levels. Great destinations ...
... How far can you go up? 1000 feet? 3000 feet? What about 10000 feet?? Even after taking precautions, there is one thing that can still get you: altitude sickness. This happens due to the low oxygen levels in high altitude places, which can decrease mental and physical alert levels. Great destinations ...
Gerunds - Old Tappan School
... Gerunds- Subject Gerunds end in –ing Gerunds are nouns. To find out how they function as a subject, Isolate the gerund or gerund phrase Locate the main verb in the sentence and the main ...
... Gerunds- Subject Gerunds end in –ing Gerunds are nouns. To find out how they function as a subject, Isolate the gerund or gerund phrase Locate the main verb in the sentence and the main ...
Chapter 7 Reference Sheet
... decl.: -a, -am; -ae, -ās, etc.), so that you can recognize them, and we can add new caseendings to these categories as we learn them. ...
... decl.: -a, -am; -ae, -ās, etc.), so that you can recognize them, and we can add new caseendings to these categories as we learn them. ...