Mineral Grain–Complete
... growth-type-2—growth where surface formation is modified by abundant inclusions; growth-type-3—growth where surface formation is modified by preexisting surfaces; growth-type-4—growth where surface formation is modified by another, simultaneous growing grain of similar bond strength (ΔH < 2); growth ...
... growth-type-2—growth where surface formation is modified by abundant inclusions; growth-type-3—growth where surface formation is modified by preexisting surfaces; growth-type-4—growth where surface formation is modified by another, simultaneous growing grain of similar bond strength (ΔH < 2); growth ...
Chapter 5: Porosity
... Fluid Displacement This method notes the displacement of fluid on a graduated scale when the rock sample is placed in a container containing the fluid. If the fluid automatically enters the pores errors will result. The method is commonly carried out with a non-wetting fluid such as mercury, or with ...
... Fluid Displacement This method notes the displacement of fluid on a graduated scale when the rock sample is placed in a container containing the fluid. If the fluid automatically enters the pores errors will result. The method is commonly carried out with a non-wetting fluid such as mercury, or with ...
Popularity of harvest bags heating up
... store well in this situation, there is a chance that the bags might not develop an insecticidal environment, and that moisture movement in the bags could lead to localised moulding. Technology trial Researchers from CSIRO Entomology will study harvest bags to determine their effectiveness in Austral ...
... store well in this situation, there is a chance that the bags might not develop an insecticidal environment, and that moisture movement in the bags could lead to localised moulding. Technology trial Researchers from CSIRO Entomology will study harvest bags to determine their effectiveness in Austral ...
I Ceramic Material Classes - Wiley-VCH
... main components (e.g., alumina, magnesia), which are applied in the field of electroceramics (insulators), or industrial refractories. Advanced ceramics require a much higher quality and purity of raw materials, as well as the careful control of processing conditions and of the materials microstru ...
... main components (e.g., alumina, magnesia), which are applied in the field of electroceramics (insulators), or industrial refractories. Advanced ceramics require a much higher quality and purity of raw materials, as well as the careful control of processing conditions and of the materials microstru ...
Siliciclastic Sedimentary Rocks.
... These two views of the Spray River siltstone illustrate lamination [parallel to green arrows], which is basically a synonym for layering. This characteristic of many sedimentary rocks is produced by discontinuities (e.g. grain size, grain type, colour) in sedimentation. Discreet units of sediment ar ...
... These two views of the Spray River siltstone illustrate lamination [parallel to green arrows], which is basically a synonym for layering. This characteristic of many sedimentary rocks is produced by discontinuities (e.g. grain size, grain type, colour) in sedimentation. Discreet units of sediment ar ...
SINTERED MATERIALS WITH HIGH POROSITY
... sintered porous materials. It presents in a synthetic way the classification, the main properties and the functional characteristics of the porous sintered sheets: behaviour to mechanical stress, permeability and technological possibilities of processing. The sintered materials with high porosity ca ...
... sintered porous materials. It presents in a synthetic way the classification, the main properties and the functional characteristics of the porous sintered sheets: behaviour to mechanical stress, permeability and technological possibilities of processing. The sintered materials with high porosity ca ...
combined effects of interstitial and laplace pressure in hot isostatic
... dissipation is shown to be compatible with the incompressibility of the matrix if and only if the material is nonlinearly viscous. Analogously, in Section 2.4 a practical way to account for the interstitial stress (that is, the gas pressure in pores) is proposed. In Section 3, the effect of the Lapl ...
... dissipation is shown to be compatible with the incompressibility of the matrix if and only if the material is nonlinearly viscous. Analogously, in Section 2.4 a practical way to account for the interstitial stress (that is, the gas pressure in pores) is proposed. In Section 3, the effect of the Lapl ...
Sandstone - Department of Geology UPRM
... C- negatively skewed finer half is better sorted than the coarser and the median and the mean are shifted toward coarser grain size. ...
... C- negatively skewed finer half is better sorted than the coarser and the median and the mean are shifted toward coarser grain size. ...
Effects of the Laplace pressure and of gas pressure on isostatic
... the seventies (see, for example, [26, 1, 6]) and many studies have given important new impulses in the nineties [19, 4, 7], even in last years several paper have been improve the knowledge of sintering processes, both from the analytical (see, among others, [21, 32, 15]) and the experimental (see, f ...
... the seventies (see, for example, [26, 1, 6]) and many studies have given important new impulses in the nineties [19, 4, 7], even in last years several paper have been improve the knowledge of sintering processes, both from the analytical (see, among others, [21, 32, 15]) and the experimental (see, f ...
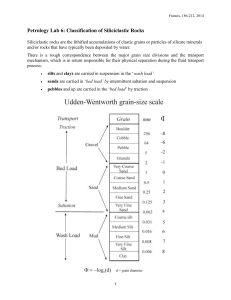
Petrology Lab 6: Siliciclastic Rocks
... Conglomerates and breccias can be distinguished by the sphericity of the clasts in the rock: if the clasts are rounded the rock is referred to as a conglomerate, if they are angular it is a breccia. With both conglomerates and breccias, grain-size, shape and orientation can be measured accurately in ...
... Conglomerates and breccias can be distinguished by the sphericity of the clasts in the rock: if the clasts are rounded the rock is referred to as a conglomerate, if they are angular it is a breccia. With both conglomerates and breccias, grain-size, shape and orientation can be measured accurately in ...
Slide #1
... Quartz is the dominant framework grain of most sandstones and is recognized primarily by its low birefringence, lack of cleavage, low positive relief, and uniaxial interference figure. A large number quartz types have been defined based mainly on the number of subcrystals in the grain and their exti ...
... Quartz is the dominant framework grain of most sandstones and is recognized primarily by its low birefringence, lack of cleavage, low positive relief, and uniaxial interference figure. A large number quartz types have been defined based mainly on the number of subcrystals in the grain and their exti ...
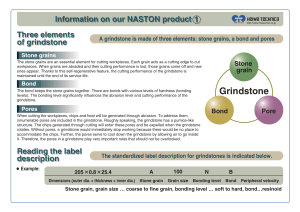
Grindstone
... It is a type of precision processing conducted with a grindstone wheel rotating at high speed. A workpiece is cut gradually by extremely hard particles (stone grains) included in the grindstone. Because it is a cutting process based on abrasion, any damage to the workpiece is kept to a minimum and a ...
... It is a type of precision processing conducted with a grindstone wheel rotating at high speed. A workpiece is cut gradually by extremely hard particles (stone grains) included in the grindstone. Because it is a cutting process based on abrasion, any damage to the workpiece is kept to a minimum and a ...
Diagenesis of Siliciclastics
... composition, pressure, temperature, grain size, porosity/permeability, and the amount of fluid flow. After deposition has taken place, diagenesis can begin almost immediately. ...
... composition, pressure, temperature, grain size, porosity/permeability, and the amount of fluid flow. After deposition has taken place, diagenesis can begin almost immediately. ...
Sandstones and other Clastic Sedimentary Rocks
... Sandstones with less than 15% mud, are called Arenites, use the front triangle ...
... Sandstones with less than 15% mud, are called Arenites, use the front triangle ...
Powerpoint: What grains can tell us
... Very poorly-sorted sediments - grains with a wide range of sizes ...
... Very poorly-sorted sediments - grains with a wide range of sizes ...
GEOS 254 Sol St Mst
... surface area (the solid space filling 3D equivalent of spheres) and – By increasing the grain size that also reduces the total area of grain-boundaries (1000 mm cubes have a surface of 60 cm2, one cm cube has the same volume and only 6 cm2 surface area). • Or by forming crystal faces that have most ...
... surface area (the solid space filling 3D equivalent of spheres) and – By increasing the grain size that also reduces the total area of grain-boundaries (1000 mm cubes have a surface of 60 cm2, one cm cube has the same volume and only 6 cm2 surface area). • Or by forming crystal faces that have most ...
Pet13Ss - West Virginia University
... pyroxene, etc. If loose sand or disaggregated sandstone is put in a heavy liquid (s.g. 2.8-3.0) "heavies" sink to the bottom ...
... pyroxene, etc. If loose sand or disaggregated sandstone is put in a heavy liquid (s.g. 2.8-3.0) "heavies" sink to the bottom ...
Grain Size Determination
... specimen is virtually identical to that of a single crystal of the same material. Bulk or Volume Defects Other defects exist in all solid materials that are much larger than those heretofore discussed. These include pores, cracks, foreign inclusions, and other phases. They are normally introduced du ...
... specimen is virtually identical to that of a single crystal of the same material. Bulk or Volume Defects Other defects exist in all solid materials that are much larger than those heretofore discussed. These include pores, cracks, foreign inclusions, and other phases. They are normally introduced du ...
Sintering

Sintering is the process of compacting and forming a solid mass of material by heat and/or pressure without melting it to the point of liquefaction.Sintering happens naturally in mineral deposits or as a manufacturing process used with metals, ceramics, plastics, and other materials. The atoms in the materials diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, fusing the particles together and creating one solid piece. Because the sintering temperature does not have to reach the melting point of the material, sintering is often chosen as the shaping process for materials with extremely high melting points such as tungsten and molybdenum. The study of sintering in metallurgy powder-related processes is known as powder metallurgy. An example of sintering can be observed when ice cubes in a glass of water adhere to each other, which is driven by the temperature difference between the water and the ice. Examples of pressure-driven sintering are the compacting of snowfall to a glacier, or the forming of a hard snowball by pressing loose snow together.The word ""sinter"" comes from the Middle High German sinter, a cognate of English ""cinder"".