CHEM - Catalog
... Detailed study of various industrial chemical manufacturing processes including underlying chemistry, reaction pathways and separation processes. Prerequisite: Chem Eng 3130 or Chem 2210, or graduate standing. (Co-listed with Chem Eng 5096). CHEM 5310 Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry (LEC 3.0) A ...
... Detailed study of various industrial chemical manufacturing processes including underlying chemistry, reaction pathways and separation processes. Prerequisite: Chem Eng 3130 or Chem 2210, or graduate standing. (Co-listed with Chem Eng 5096). CHEM 5310 Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry (LEC 3.0) A ...
CHEM - Catalog
... Detailed study of various industrial chemical manufacturing processes including underlying chemistry, reaction pathways and separation processes. Prerequisite: Chem Eng 3130 or Chem 2210, or graduate standing. (Co-listed with Chem Eng 5096). CHEM 5310 Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry (LEC 3.0) A ...
... Detailed study of various industrial chemical manufacturing processes including underlying chemistry, reaction pathways and separation processes. Prerequisite: Chem Eng 3130 or Chem 2210, or graduate standing. (Co-listed with Chem Eng 5096). CHEM 5310 Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry (LEC 3.0) A ...
Chemistry (CHEM)
... course in the elementary principles of chemistry for individuals who do not meet the criteria for enrollment in CHEM 101; required for all students without a high school chemistry background who need to take CHEM 101-102. These credits may not be used to satisfy any chemistry course requirements in ...
... course in the elementary principles of chemistry for individuals who do not meet the criteria for enrollment in CHEM 101; required for all students without a high school chemistry background who need to take CHEM 101-102. These credits may not be used to satisfy any chemistry course requirements in ...
DOI:10.1478/C1S0801002 Atti dell’Accademia Peloritana dei Pericolanti
... Interesting is that the temperature does not appear in the balances (10) to (18). Temperature is introduced into the balances by constitutive properties, here, in Clausius-Duhem theories, by Φ = (1/Θ)q. 3.3. Material axioms. Material axioms are rules restricting the arbitrariness of the constitutive ...
... Interesting is that the temperature does not appear in the balances (10) to (18). Temperature is introduced into the balances by constitutive properties, here, in Clausius-Duhem theories, by Φ = (1/Θ)q. 3.3. Material axioms. Material axioms are rules restricting the arbitrariness of the constitutive ...
Thermochemistry, thermodynamics Thermochemistry
... also called standard molar entropy. The reference state for absolute entropy is specified by the third law of thermodynamics. It is different from the reference state for ∆Hf0 The standard entropy change, ∆Sr0 , of a reaction can be determined from the absolute entropies of reactants and products: ...
... also called standard molar entropy. The reference state for absolute entropy is specified by the third law of thermodynamics. It is different from the reference state for ∆Hf0 The standard entropy change, ∆Sr0 , of a reaction can be determined from the absolute entropies of reactants and products: ...
2. Local equilibrium thermodynamics.
... consider irreversible processes, but its account in exact terms is restricted to variables that refer only to initial and final states of thermodynamic equilibrium, or to rates of input and output that do not change with time. For example, classical thermodynamics can consider time-average rates of ...
... consider irreversible processes, but its account in exact terms is restricted to variables that refer only to initial and final states of thermodynamic equilibrium, or to rates of input and output that do not change with time. For example, classical thermodynamics can consider time-average rates of ...
Thermodynamics
... An important concept in thermodynamics is the thermodynamic system, a precisely defined region of the universe under study. Everything in the universe except the system is known as the surroundings. A system is separated from the remainder of the universe by a boundary which may be notional or not, b ...
... An important concept in thermodynamics is the thermodynamic system, a precisely defined region of the universe under study. Everything in the universe except the system is known as the surroundings. A system is separated from the remainder of the universe by a boundary which may be notional or not, b ...
Thermodynamics Of Chemical Processes
... context, thermodynamics can be considered as the extension of mechanics covering all phenomena which require temperature as an additional unit. The science of applied (or engineering) thermodynamics is based on two foundations: at first, the three basic laws of thermodynamics and, at second, the pro ...
... context, thermodynamics can be considered as the extension of mechanics covering all phenomena which require temperature as an additional unit. The science of applied (or engineering) thermodynamics is based on two foundations: at first, the three basic laws of thermodynamics and, at second, the pro ...
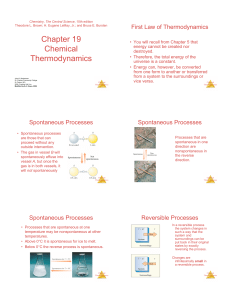
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
... – Translational: Movement of the entire molecule from one place to another. – Vibrational: Periodic motion of atoms within a molecule. – Rotational: Rotation of the molecule on about an axis or rotation about bonds. ...
... – Translational: Movement of the entire molecule from one place to another. – Vibrational: Periodic motion of atoms within a molecule. – Rotational: Rotation of the molecule on about an axis or rotation about bonds. ...
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
... – Translational: Movement of the entire molecule from one place to another. – Vibrational: Periodic motion of atoms within a molecule. – Rotational: Rotation of the molecule on about an axis or rotation about bonds. ...
... – Translational: Movement of the entire molecule from one place to another. – Vibrational: Periodic motion of atoms within a molecule. – Rotational: Rotation of the molecule on about an axis or rotation about bonds. ...
unit ii chemical thermodynamics
... Second law Entropy - entropy change for an ideal gas, reversible and irreversible processes ,entropy of phase transitions. Clausius inequality. Free energy and work function: Helmholtz and Gibbs free energy functions Criteria of spontaneity Gibbs-Helmholtz equation Clausius-Clapeyron ...
... Second law Entropy - entropy change for an ideal gas, reversible and irreversible processes ,entropy of phase transitions. Clausius inequality. Free energy and work function: Helmholtz and Gibbs free energy functions Criteria of spontaneity Gibbs-Helmholtz equation Clausius-Clapeyron ...
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
... Standard Entropies • These are molar entropy values of substances in their standard states. • Standard entropies tend to increase with increasing molar mass. Chemical Thermodynamics ...
... Standard Entropies • These are molar entropy values of substances in their standard states. • Standard entropies tend to increase with increasing molar mass. Chemical Thermodynamics ...
Spring, 2010 -- Chemistry Course Offerings
... development of complex organisms, and the development of modern humans including evidence for the various ideas presented, the scientific method used by scientists, and how the community of scientists evaluate the evidence. This course does not fulfill pre-med requirements for a lab-based chemistry ...
... development of complex organisms, and the development of modern humans including evidence for the various ideas presented, the scientific method used by scientists, and how the community of scientists evaluate the evidence. This course does not fulfill pre-med requirements for a lab-based chemistry ...
S - BEHS Science
... Translational: Movement of the entire molecule from one place to another. Vibrational: Periodic motion of atoms within a molecule. Rotational: Rotation of the molecule on about an axis or rotation about bonds. ...
... Translational: Movement of the entire molecule from one place to another. Vibrational: Periodic motion of atoms within a molecule. Rotational: Rotation of the molecule on about an axis or rotation about bonds. ...
ME 7280 Statistical Thermodynamics
... Once the basic theory is compete, we will look at cases of particular interest; ideal and non ideal gases, thermal radiation (an ideal gas of photons), lattice vibrations in a solid (an ideal gas of phonons) and the free electron theory of metals. Relevance: Because statistical thermodynamics result ...
... Once the basic theory is compete, we will look at cases of particular interest; ideal and non ideal gases, thermal radiation (an ideal gas of photons), lattice vibrations in a solid (an ideal gas of phonons) and the free electron theory of metals. Relevance: Because statistical thermodynamics result ...
GFS Chemicals Organic Manufacturing
... GFS Chemicals, Inc. Innovation and Commercialization through Chemistry Leaders in the development and commercialization of specialty alkynes and derivatives ...
... GFS Chemicals, Inc. Innovation and Commercialization through Chemistry Leaders in the development and commercialization of specialty alkynes and derivatives ...
Book review of ELISABETH CRAWFORD, Arrhenius
... techniques of the new physical chemistry under Wilhelm Ostwald, where he focussed on understanding, in a physical sense, the nature and causes of electromotive force in galvanic cells. Called to Göttingen as an assistant by Eduard Riecke, Nernst continued independent research on the theory of soluti ...
... techniques of the new physical chemistry under Wilhelm Ostwald, where he focussed on understanding, in a physical sense, the nature and causes of electromotive force in galvanic cells. Called to Göttingen as an assistant by Eduard Riecke, Nernst continued independent research on the theory of soluti ...
... Big Idea 2: Chemical and physical properties of materials can be explained by the structure and the arrangement of atoms, ions, or molecules and the forces between them. Transformations of matter can be observed in multiple ways that are generally categorized as either chemical or physical change. T ...
Chemistry 331 In Class Exercise Review for Final #1) (a) What are
... #4) What is the law of corresponding states and why it important when describing real gases in terms of cubic equations of state? ...
... #4) What is the law of corresponding states and why it important when describing real gases in terms of cubic equations of state? ...
What is Thermodynamics?
... transformations, and interaction between energy and matter. Although every body has feeling of what energy is, it is difficult to give a precise definition of it. Energy can be viewed as the ability to cause changes. The name thermodynamics is due to the Greek words therme (heat) and dynamis (power) ...
... transformations, and interaction between energy and matter. Although every body has feeling of what energy is, it is difficult to give a precise definition of it. Energy can be viewed as the ability to cause changes. The name thermodynamics is due to the Greek words therme (heat) and dynamis (power) ...
CHEM 240 Who am I?
... othe study of the macroscopic properties of systems of many atoms or molecules othe study of processes which such systems can undergo othe study of the properties of individual atoms and molecules othe study of the relationship between microscopic (atomic or molecular) properties and macroscopic pro ...
... othe study of the macroscopic properties of systems of many atoms or molecules othe study of processes which such systems can undergo othe study of the properties of individual atoms and molecules othe study of the relationship between microscopic (atomic or molecular) properties and macroscopic pro ...