OPAx835 Ultra-Low-Power, Rail-to-Rail Out, Negative Rail In, VFB
... single and dual ultralow-power, rail-to-rail output, negative-rail input, voltage-feedback (VFB) operational amplifiers designed to operate over a power supply range of 2.5-V to 5.5-V with a single supply, or ±1.25-V to ±2.75-V with a dual supply. Consuming only 250 µA per channel and with a unity g ...
... single and dual ultralow-power, rail-to-rail output, negative-rail input, voltage-feedback (VFB) operational amplifiers designed to operate over a power supply range of 2.5-V to 5.5-V with a single supply, or ±1.25-V to ±2.75-V with a dual supply. Consuming only 250 µA per channel and with a unity g ...
laboratory module
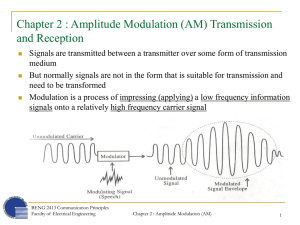
... a. Apart from the observation of waveform of an input signal, one can measure its amplitude because the Y-axis is calibrated in volts. One can also measure various time parameter of the signal waveform because the X-axis is calibrated in unit of time. b. We first introduce the following parameters: ...
... a. Apart from the observation of waveform of an input signal, one can measure its amplitude because the Y-axis is calibrated in volts. One can also measure various time parameter of the signal waveform because the X-axis is calibrated in unit of time. b. We first introduce the following parameters: ...
SRM UNIVERSITY Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering
... drift. The wide bandwidth allows the LF198 to be included inside the feedback loop of 1 MHz op amps without having stability problems. Input impedance of 1010(Ohm) allows high source impedance to be used without degrading accuracy. P-channel junction FET’s are combined with bipolar devices in the ou ...
... drift. The wide bandwidth allows the LF198 to be included inside the feedback loop of 1 MHz op amps without having stability problems. Input impedance of 1010(Ohm) allows high source impedance to be used without degrading accuracy. P-channel junction FET’s are combined with bipolar devices in the ou ...
Comparison of CMOS Current Conveyor Circuits for Non
... [2]. Current conveyors have found use in current-mode and mixed-mode filter design, instrumentation and wideband amplifiers, and non-Foster circuits [3]-[5], [7]-[8]. Although current conveyors have been used for more than four decades, there is renewed interest in their use in a variety of analog s ...
... [2]. Current conveyors have found use in current-mode and mixed-mode filter design, instrumentation and wideband amplifiers, and non-Foster circuits [3]-[5], [7]-[8]. Although current conveyors have been used for more than four decades, there is renewed interest in their use in a variety of analog s ...
DC Circuits–Series, Parallel, and Combination Circuits
... our original bulb circuit (b). The larger current will discharge the battery more quickly. Since the battery chemistry limits the total amount of charge that it can provide, the larger current will use up this charge in a shorter time (q = It) in circuit (b). Hopefully you observed that the current ...
... our original bulb circuit (b). The larger current will discharge the battery more quickly. Since the battery chemistry limits the total amount of charge that it can provide, the larger current will use up this charge in a shorter time (q = It) in circuit (b). Hopefully you observed that the current ...
Series and Parallel Circuits
... Although the connection may not immediately be clear to you, a mountain river can be used to model an electric circuit. From its source high in the mountains, the river flows downhill to the plains below. No matter which path the river takes, its change in elevation, from the mountaintop to the plai ...
... Although the connection may not immediately be clear to you, a mountain river can be used to model an electric circuit. From its source high in the mountains, the river flows downhill to the plains below. No matter which path the river takes, its change in elevation, from the mountaintop to the plai ...
FT-991 o M perATing
... Note that other manufacturers may use the same type of DC power connections as does your FT-991 transceiver, however, the wiring configuration may be different from that specified for your transceiver. Serious damage can be caused if improper DC connections are made; consult with a qualified service ...
... Note that other manufacturers may use the same type of DC power connections as does your FT-991 transceiver, however, the wiring configuration may be different from that specified for your transceiver. Serious damage can be caused if improper DC connections are made; consult with a qualified service ...
NI PXIe-5171R Specifications
... information about cooling, refer to the Maintain Forced-Air Cooling Note to Users available at ni.com/manuals. ...
... information about cooling, refer to the Maintain Forced-Air Cooling Note to Users available at ni.com/manuals. ...
Hand-Drawn Circuit Diagrams for all circuits that are to
... Inductors and Transformers Purpose: Partly as preparation for the next project and partly to help develop a more complete picture of voltage sources, we will return to considering inductors. The extension we are primarily concerned with is the mutual inductor or transformer. The transformer has thre ...
... Inductors and Transformers Purpose: Partly as preparation for the next project and partly to help develop a more complete picture of voltage sources, we will return to considering inductors. The extension we are primarily concerned with is the mutual inductor or transformer. The transformer has thre ...
4.5-V-18-V Input, High Current, Synchronous Step Down 3-DC
... All converters have peak current mode control which simplifies external frequency compensation. The device has a built-in slope compensation ramp. The slope compensation can prevent sub harmonic oscillations in peak current mode control. A traditional type II compensation network can stabilize the s ...
... All converters have peak current mode control which simplifies external frequency compensation. The device has a built-in slope compensation ramp. The slope compensation can prevent sub harmonic oscillations in peak current mode control. A traditional type II compensation network can stabilize the s ...
V - Chi K. Tse
... number of nodes of the circuit minus 1. One important point: The nodal method is over-complex when applied to circuits with voltage source(s). WHY? We don’t need N equations for circuits with voltage source(s) because the node voltages are partly known! ...
... number of nodes of the circuit minus 1. One important point: The nodal method is over-complex when applied to circuits with voltage source(s). WHY? We don’t need N equations for circuits with voltage source(s) because the node voltages are partly known! ...
Experiment 3 Inductors and Transformers Pre-Lab
... Inductors and Transformers Purpose: Partly as preparation for the next project and partly to help develop a more complete picture of voltage sources, we will return to considering inductors. The extension we are primarily concerned with is the mutual inductor or transformer. The transformer has thre ...
... Inductors and Transformers Purpose: Partly as preparation for the next project and partly to help develop a more complete picture of voltage sources, we will return to considering inductors. The extension we are primarily concerned with is the mutual inductor or transformer. The transformer has thre ...
lesson3-student-answers 2483KB Apr 09 2015 10:22:46 AM
... The current in the branch circuits will stay the same. They are unaffected by the other branches. C) the brightness of the remaining bulbs? The brightness of the remaining bulbs will stay the same because the current stays the same. 12) Is there ever any parallel circuit where one branch gets all t ...
... The current in the branch circuits will stay the same. They are unaffected by the other branches. C) the brightness of the remaining bulbs? The brightness of the remaining bulbs will stay the same because the current stays the same. 12) Is there ever any parallel circuit where one branch gets all t ...
Regenerative circuit
The regenerative circuit (or regen) allows an electronic signal to be amplified many times by the same active device. It consists of an amplifying vacuum tube or transistor with its output connected to its input through a feedback loop, providing positive feedback. This circuit was widely used in radio receivers, called regenerative receivers, between 1915 and World War II. The regenerative receiver was invented in 1912 and patented in 1914 by American electrical engineer Edwin Armstrong when he was an undergraduate at Columbia University. Due partly to its tendency to radiate interference, by the 1930s the regenerative receiver was superseded by other receiver designs, the TRF and superheterodyne receivers and became obsolete, but regeneration (now called positive feedback) is widely used in other areas of electronics, such as in oscillators and active filters. A receiver circuit that used regeneration in a more complicated way to achieve even higher amplification, the superregenerative receiver, was invented by Armstrong in 1922. It was never widely used in general receivers, but due to its small parts count is used in a few specialized low data rate applications, such as garage door openers, wireless networking devices, walkie-talkies and toys.