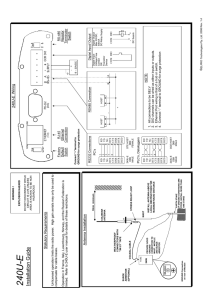
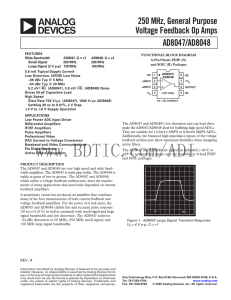
Sampling Theory and Analog-to-Digital Conversion Basic
... • “One common form of aliasing, which most people have observed, is the 'wagon wheels' effect in films. Since the rate of the film is usually much lower than the frequency at which the spokes of a wheel pass any one point, aliasing takes place and the wheels appear to turn either much more slowly th ...
... • “One common form of aliasing, which most people have observed, is the 'wagon wheels' effect in films. Since the rate of the film is usually much lower than the frequency at which the spokes of a wheel pass any one point, aliasing takes place and the wheels appear to turn either much more slowly th ...
here - Sonic Farm
... versions of their circuits. This is a world which Sonic Farm seeks to steer clear from. They believe that focusing on yesterday’s designs limits tomorrow’s possibilities. One of their founding premises is to come up with pro audio equipment that the world market is not already saturated with. Furthe ...
... versions of their circuits. This is a world which Sonic Farm seeks to steer clear from. They believe that focusing on yesterday’s designs limits tomorrow’s possibilities. One of their founding premises is to come up with pro audio equipment that the world market is not already saturated with. Furthe ...
model sr540 optical chopper
... signals. The unit can chop light sources at rates from 4 Hz to 3.7 kHz. Versatile, low jitter reference outputs provide the synchronizing signals required for several operating modes: single or dual beam; sum & difference frequency; and synthesized chopping to 20 kHz. ...
... signals. The unit can chop light sources at rates from 4 Hz to 3.7 kHz. Versatile, low jitter reference outputs provide the synchronizing signals required for several operating modes: single or dual beam; sum & difference frequency; and synthesized chopping to 20 kHz. ...
PS-EP-2test - Edquest Science
... A. short circuit B. short pathway C. incomplete pathway D. incomplete circuit 3. Which of the following is most likely enough electricity to kill you… A. .01A B. .01V C. 10A D. 10V 4. Evan was inspecting the wiring in a new house and found that the green wire had not been connected properly in the e ...
... A. short circuit B. short pathway C. incomplete pathway D. incomplete circuit 3. Which of the following is most likely enough electricity to kill you… A. .01A B. .01V C. 10A D. 10V 4. Evan was inspecting the wiring in a new house and found that the green wire had not been connected properly in the e ...
Sinusoidal Steady
... circuits for steady-state sinusoidal circuits 5. Be able to write mesh, node, KVL, and KCL equations for sinusoidal steady-state circuit 6. Be able to conduct steady-state sinusoidal analysis of circuits with transformers ...
... circuits for steady-state sinusoidal circuits 5. Be able to write mesh, node, KVL, and KCL equations for sinusoidal steady-state circuit 6. Be able to conduct steady-state sinusoidal analysis of circuits with transformers ...
verberator.pdf
... Ok, here's the bypass cap deal. Yes it negates the effect of the 10k resistor if you were looking to reduce the gain of the stage. When you bypass the cathode you get the total possible gain of the tube down to the -3dB break point of the RC pair. The equation I like to use to calculate AC gain of a ...
... Ok, here's the bypass cap deal. Yes it negates the effect of the 10k resistor if you were looking to reduce the gain of the stage. When you bypass the cathode you get the total possible gain of the tube down to the -3dB break point of the RC pair. The equation I like to use to calculate AC gain of a ...
Introduction to switched-capacitor circuits
... • Integrator gain depends upon ratio of capacitor values • Operation is analogous to a continuous-time active RC integrator with respect to input frequencies >> fs ...
... • Integrator gain depends upon ratio of capacitor values • Operation is analogous to a continuous-time active RC integrator with respect to input frequencies >> fs ...
SSB Mic Filter
... selects voltage gains of 1 or 2 (0 dB or 6 dB). LOW CUT switch S4 selects between 1, 2, and 3 which corresponds to F-3dB frequencies of 6 Hz, 150 Hz, and 325 Hz, respectively. DX switch S2 adds 8 dB of high frequency boost centered around 4.8 KHz and a low cut F-3dB at 450 Hz. In the bandwidth limit ...
... selects voltage gains of 1 or 2 (0 dB or 6 dB). LOW CUT switch S4 selects between 1, 2, and 3 which corresponds to F-3dB frequencies of 6 Hz, 150 Hz, and 325 Hz, respectively. DX switch S2 adds 8 dB of high frequency boost centered around 4.8 KHz and a low cut F-3dB at 450 Hz. In the bandwidth limit ...
q1 q2 1/r V TEST – XII ( Physics ) 1 r
... What are the two possible faults in this circuit? If the galvanometer deflection at B is: (i) more than that at A (ii) less than that at A, which of the two faults, listed by you, would be there in the circuit? Give reasons in support of your ...
... What are the two possible faults in this circuit? If the galvanometer deflection at B is: (i) more than that at A (ii) less than that at A, which of the two faults, listed by you, would be there in the circuit? Give reasons in support of your ...
San Jose State University
... Not all of these devices are necessary for the task. The usage of these parts can be found in the VEX component documentation (hard copies on the lab) (www.vexlabs.com). If you want to use any other sensors or parts that are not included in the basic kit, you will need to request the additional part ...
... Not all of these devices are necessary for the task. The usage of these parts can be found in the VEX component documentation (hard copies on the lab) (www.vexlabs.com). If you want to use any other sensors or parts that are not included in the basic kit, you will need to request the additional part ...
A Numerical Solution to an Analog Problem
... warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Except where mandated by government requirements, testing of all parameters of each product is not necessarily performed. TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or ...
... warranty. Testing and other quality control techniques are used to the extent TI deems necessary to support this warranty. Except where mandated by government requirements, testing of all parameters of each product is not necessarily performed. TI assumes no liability for applications assistance or ...
MT-071: Analog Isolation Amplifiers
... systems. Operating power is of course, essential. Both the input and the output circuitry must be powered, and unless there is a battery on the isolated side of the isolation barrier (which is possible, but rarely convenient), some form of isolated power must be provided. Systems using transformer i ...
... systems. Operating power is of course, essential. Both the input and the output circuitry must be powered, and unless there is a battery on the isolated side of the isolation barrier (which is possible, but rarely convenient), some form of isolated power must be provided. Systems using transformer i ...
Chapter 1 - Answers - Pearson Schools and FE Colleges
... 1. Define what effect a capacitor and inductor will have on an a.c. circuit. A capacitor will cause a current to lead voltage and an inductor will make current lag voltage in an a.c. circuit. 2. What is impedance? This is the combined effect of capacitors, inductors and resistance in an a.c. circuit ...
... 1. Define what effect a capacitor and inductor will have on an a.c. circuit. A capacitor will cause a current to lead voltage and an inductor will make current lag voltage in an a.c. circuit. 2. What is impedance? This is the combined effect of capacitors, inductors and resistance in an a.c. circuit ...
Regenerative circuit
The regenerative circuit (or regen) allows an electronic signal to be amplified many times by the same active device. It consists of an amplifying vacuum tube or transistor with its output connected to its input through a feedback loop, providing positive feedback. This circuit was widely used in radio receivers, called regenerative receivers, between 1915 and World War II. The regenerative receiver was invented in 1912 and patented in 1914 by American electrical engineer Edwin Armstrong when he was an undergraduate at Columbia University. Due partly to its tendency to radiate interference, by the 1930s the regenerative receiver was superseded by other receiver designs, the TRF and superheterodyne receivers and became obsolete, but regeneration (now called positive feedback) is widely used in other areas of electronics, such as in oscillators and active filters. A receiver circuit that used regeneration in a more complicated way to achieve even higher amplification, the superregenerative receiver, was invented by Armstrong in 1922. It was never widely used in general receivers, but due to its small parts count is used in a few specialized low data rate applications, such as garage door openers, wireless networking devices, walkie-talkies and toys.