Answers
... Exploration 5: If the number of cells in the circuit increases, what happens to the amount of electric current in the circuit? Remember (from the video): Electric Current (Amps) = Flow of electricity (how much or many negative charges or electrons in motion) Voltage (Volts) = The amount of electric ...
... Exploration 5: If the number of cells in the circuit increases, what happens to the amount of electric current in the circuit? Remember (from the video): Electric Current (Amps) = Flow of electricity (how much or many negative charges or electrons in motion) Voltage (Volts) = The amount of electric ...
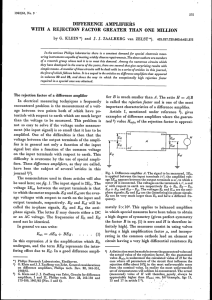
difference amplifiers with a rejection factor greater than one
... with an even higher rejection factor. The problem concerned a set-up for measuring the Hall effect on test bars of various materials. The set-up is shown schematically infig. 2 and explained in the caption. The Hall voltage to be measured, which varied in frequency from 50 to 200 cIs, was extremely ...
... with an even higher rejection factor. The problem concerned a set-up for measuring the Hall effect on test bars of various materials. The set-up is shown schematically infig. 2 and explained in the caption. The Hall voltage to be measured, which varied in frequency from 50 to 200 cIs, was extremely ...
electronic_pc2181-09_lec1
... RC High-pass filter High pass filter acts as a differentiator at low frequency ...
... RC High-pass filter High pass filter acts as a differentiator at low frequency ...
ML145170 - Lansdale Semiconductor
... 5 MΩ is required across the OSCin and OSCout pins in the AC–coupled case (see Figure 8a or alternate circuit 8b). OSCout is an internal node on the device and should not be used to drive any loads (i.e. OSCout is unbuffered). However, the buffered REFout is available to drive external loads. The ext ...
... 5 MΩ is required across the OSCin and OSCout pins in the AC–coupled case (see Figure 8a or alternate circuit 8b). OSCout is an internal node on the device and should not be used to drive any loads (i.e. OSCout is unbuffered). However, the buffered REFout is available to drive external loads. The ext ...
velodyne ULD15 manual from Velodyne
... Sender board: The sender board is the board that resides within the subwoofer cabinet at the point where the servo and speaker wires from the servo controller connect. This board is responsible for amplifying the accelerometer signal from the driver and transmitting it to the amplifier via the servo ...
... Sender board: The sender board is the board that resides within the subwoofer cabinet at the point where the servo and speaker wires from the servo controller connect. This board is responsible for amplifying the accelerometer signal from the driver and transmitting it to the amplifier via the servo ...
Instruction Manual SSQ-2F Controller Board for the v3.22
... The SSQ-2F v1.41 was designed to provide a +5 volt or a +12 volt square wave output. This signal can be used to drive an external RF amplifier or it may be used as a low voltage contact device driver. The SSQ-2F v3.22 differs from the SSQ-2F v3.10 in that the v3.22 has provision for a digital duty c ...
... The SSQ-2F v1.41 was designed to provide a +5 volt or a +12 volt square wave output. This signal can be used to drive an external RF amplifier or it may be used as a low voltage contact device driver. The SSQ-2F v3.22 differs from the SSQ-2F v3.10 in that the v3.22 has provision for a digital duty c ...
Circuits
... C. A real emf device, such as any real battery, has internal resistance to the internal movement of charge. When a real emf device is not connected to a circuit, and thus does not have current through it, the potential difference between its terminals is equal to its emf. However, when that devi ...
... C. A real emf device, such as any real battery, has internal resistance to the internal movement of charge. When a real emf device is not connected to a circuit, and thus does not have current through it, the potential difference between its terminals is equal to its emf. However, when that devi ...
0.05 uV/C max, Single-Supply CMOS
... Some applications require output voltage swing from 0 V to a positive full-scale voltage (such as 2.5 V) with excellent accuracy. With most single-supply op amps, problems arise when the output signal approaches 0 V, near the lower output swing limit of a single-supply op amp. A good single-supply o ...
... Some applications require output voltage swing from 0 V to a positive full-scale voltage (such as 2.5 V) with excellent accuracy. With most single-supply op amps, problems arise when the output signal approaches 0 V, near the lower output swing limit of a single-supply op amp. A good single-supply o ...
Lecture 2. Transistors
... Forward biasing makes the depletion region smaller so that it is easier for the current to flow through the device. ...
... Forward biasing makes the depletion region smaller so that it is easier for the current to flow through the device. ...
Design Considerations for an LLC Resonant Converter
... The resonant inductor (Lr) and resonant capacitor (Cr) are in series The resonant capacitor is in series with the load 9 The resonant tank and the load act as a voltage dividerÆ DC gain is always lower than 1 (maximum gain happens at the resonant frequency) 9 The impedance of resonant tank can b ...
... The resonant inductor (Lr) and resonant capacitor (Cr) are in series The resonant capacitor is in series with the load 9 The resonant tank and the load act as a voltage dividerÆ DC gain is always lower than 1 (maximum gain happens at the resonant frequency) 9 The impedance of resonant tank can b ...
10. Diodes – Basic Diode Concepts
... 10.3.2 Zener-Diode Voltage-Regulator Circuits * Sometimes, a circuit that produces constant output voltage while operating from a variable supply voltage is needed. Such circuits are called voltage regulator. * The Zener diode has a breakdown voltage equal to the desired output voltage. * The resist ...
... 10.3.2 Zener-Diode Voltage-Regulator Circuits * Sometimes, a circuit that produces constant output voltage while operating from a variable supply voltage is needed. Such circuits are called voltage regulator. * The Zener diode has a breakdown voltage equal to the desired output voltage. * The resist ...
Detector Selection for Spectrum analyzer Measurements
... Figure B is a graph of the highest sample amplitude versus the signal frequency. It repeats with a period of the frequency width of a bucket. This is a scallop shape. Scalloping error is the difference between the highest sample result and the peak result. The term “scalloping error” is not commonly ...
... Figure B is a graph of the highest sample amplitude versus the signal frequency. It repeats with a period of the frequency width of a bucket. This is a scallop shape. Scalloping error is the difference between the highest sample result and the peak result. The term “scalloping error” is not commonly ...
TDA7052A/AT
... The total gain can be controlled from 35.5 dB to −44 dB. If the DC volume control voltage is below 0.3 V, the device switches to the mute mode. The amplifier is short-circuit proof to ground, VP and across the load. Also a thermal protection circuit is implemented. If the crystal temperature rises a ...
... The total gain can be controlled from 35.5 dB to −44 dB. If the DC volume control voltage is below 0.3 V, the device switches to the mute mode. The amplifier is short-circuit proof to ground, VP and across the load. Also a thermal protection circuit is implemented. If the crystal temperature rises a ...
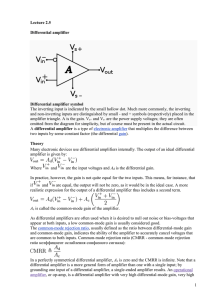
Differential amplifier
... proved its value by being liberally used in the M9 artillery director designed at Bell Labs. This artillery director worked with the SCR584 radar system to achieve extraordinary hit rates (near 90%) that would not have been possible otherwise.[3] 1947: First op-amp with an explicit non-inverting inp ...
... proved its value by being liberally used in the M9 artillery director designed at Bell Labs. This artillery director worked with the SCR584 radar system to achieve extraordinary hit rates (near 90%) that would not have been possible otherwise.[3] 1947: First op-amp with an explicit non-inverting inp ...
eriii20_control_navigation3
... o MCUs have limited speed and memory. This inadequacy is normally not a problem for entry level ROVs. o Their power output is minimal, normally around 20 mA at 3 – 5 volts. This limitation can be overcome with the use of transistors which amplify the microcontroller output to drive higher powered de ...
... o MCUs have limited speed and memory. This inadequacy is normally not a problem for entry level ROVs. o Their power output is minimal, normally around 20 mA at 3 – 5 volts. This limitation can be overcome with the use of transistors which amplify the microcontroller output to drive higher powered de ...
Regenerative circuit
The regenerative circuit (or regen) allows an electronic signal to be amplified many times by the same active device. It consists of an amplifying vacuum tube or transistor with its output connected to its input through a feedback loop, providing positive feedback. This circuit was widely used in radio receivers, called regenerative receivers, between 1915 and World War II. The regenerative receiver was invented in 1912 and patented in 1914 by American electrical engineer Edwin Armstrong when he was an undergraduate at Columbia University. Due partly to its tendency to radiate interference, by the 1930s the regenerative receiver was superseded by other receiver designs, the TRF and superheterodyne receivers and became obsolete, but regeneration (now called positive feedback) is widely used in other areas of electronics, such as in oscillators and active filters. A receiver circuit that used regeneration in a more complicated way to achieve even higher amplification, the superregenerative receiver, was invented by Armstrong in 1922. It was never widely used in general receivers, but due to its small parts count is used in a few specialized low data rate applications, such as garage door openers, wireless networking devices, walkie-talkies and toys.