
Notes LM1036 Dual DC Operated Tone/Volume/Balance Circuit
... The volume control function of the LM1036 is carried out in two stages, controlled by the DC voltage on pin 12, to improve signal handling capability and provide a reduction of output noise level at reduced gain. The first stage is before the tone control processing and provides an initial 15 dB of ...
... The volume control function of the LM1036 is carried out in two stages, controlled by the DC voltage on pin 12, to improve signal handling capability and provide a reduction of output noise level at reduced gain. The first stage is before the tone control processing and provides an initial 15 dB of ...
AD781
... rms sum of the first six harmonic components to the rms value of the measured input signal and is expressed as a percentage or in decibels. ...
... rms sum of the first six harmonic components to the rms value of the measured input signal and is expressed as a percentage or in decibels. ...
DA: Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor Introduction - Ford
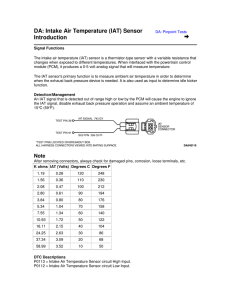
... The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is a thermistor-type sensor with a variable resistance that changes when exposed to different temperatures. When interfaced with the powertrain control module (PCM), it produces a 0-5 volt analog signal that will measure temperature. The IAT sensor's primary f ...
... The intake air temperature (IAT) sensor is a thermistor-type sensor with a variable resistance that changes when exposed to different temperatures. When interfaced with the powertrain control module (PCM), it produces a 0-5 volt analog signal that will measure temperature. The IAT sensor's primary f ...
TPA2000D2 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... The main reason that the traditional class-D amplifier needs an output filter is that the switching waveform results in maximum current flow. This causes more loss in the load, which causes lower efficiency. The ripple current is large for the traditional modulation scheme because the ripple current ...
... The main reason that the traditional class-D amplifier needs an output filter is that the switching waveform results in maximum current flow. This causes more loss in the load, which causes lower efficiency. The ripple current is large for the traditional modulation scheme because the ripple current ...
Quartet II ME Tube Recording Channel Features · The tube Mic/DI
... The GAIN Control is an 11 position rotary switch that adjusts the gain of the tube stage from +33dB to +63dB (Full) or +40dB to +70dB (Focused) in 3dB steps. The 1% metalfilm resistors that determine gain are selected for precise 3dB increments. At low gain settings, there is more global feedback in ...
... The GAIN Control is an 11 position rotary switch that adjusts the gain of the tube stage from +33dB to +63dB (Full) or +40dB to +70dB (Focused) in 3dB steps. The 1% metalfilm resistors that determine gain are selected for precise 3dB increments. At low gain settings, there is more global feedback in ...
EC2205
... CE, CB and CC amplifiers - Method of drawing small-signal equivalent circuit - Midband analysis of various types of single stage amplifiers to obtain gain, input impedance and output impedance - Miller’s theorem - Comparison of CB, CE and CC amplifiers and their uses - Methods of increasing input im ...
... CE, CB and CC amplifiers - Method of drawing small-signal equivalent circuit - Midband analysis of various types of single stage amplifiers to obtain gain, input impedance and output impedance - Miller’s theorem - Comparison of CB, CE and CC amplifiers and their uses - Methods of increasing input im ...
LECT7V23_printvers
... the noise that the circuit can tolerate in the "low" state, is the difference between the maximum voltage that it can tolerate at the input, and the maximum that it will get from the output of the previous gate. 2. Fanout - The fanout is defined as the number of gates that can be "driven" by the out ...
... the noise that the circuit can tolerate in the "low" state, is the difference between the maximum voltage that it can tolerate at the input, and the maximum that it will get from the output of the previous gate. 2. Fanout - The fanout is defined as the number of gates that can be "driven" by the out ...
Author Guidelines for ACES Journal Paper (16 pt bold)
... in this study to have better and more accurate results. As mentioned in [17], the result will be more accurate with more number of sections but from specific number of section like 10 the results will not change significantly. Utilizing the distributed parameter model developed in this paper, as sho ...
... in this study to have better and more accurate results. As mentioned in [17], the result will be more accurate with more number of sections but from specific number of section like 10 the results will not change significantly. Utilizing the distributed parameter model developed in this paper, as sho ...
Leakage describes an unwanted loss, or leak, of something which
... or thousands of milliamperes while in full operation. These leakage currents are becoming a significant factor to portable device manufacturers because of their undesirable effect on battery run time for the consumer. Referred from Microelectronic circuits by Sedra Smith, IV Edition. For reducing th ...
... or thousands of milliamperes while in full operation. These leakage currents are becoming a significant factor to portable device manufacturers because of their undesirable effect on battery run time for the consumer. Referred from Microelectronic circuits by Sedra Smith, IV Edition. For reducing th ...
Reduction of coupling capacitance, using a capacitor
... In analog designs, two circuits with different common mode DC voltages can be connected together through a coupling capacitor. Therefore, the ac signal from the first stage can pass toward the next stage while DC is blocked. However, using the capacitive coupling method degrades the low frequency be ...
... In analog designs, two circuits with different common mode DC voltages can be connected together through a coupling capacitor. Therefore, the ac signal from the first stage can pass toward the next stage while DC is blocked. However, using the capacitive coupling method degrades the low frequency be ...
Document
... Second, the solutions to the differential equations we obtained were exponential in time, being characterized by a single time constant which is equal to the product of an equivalent resistance and an equivalent capacitance. For example, for a circuit that charges a single capacitor C through a sing ...
... Second, the solutions to the differential equations we obtained were exponential in time, being characterized by a single time constant which is equal to the product of an equivalent resistance and an equivalent capacitance. For example, for a circuit that charges a single capacitor C through a sing ...
fets_alsari
... system need to be applied in order to make possible to detect the phase deference and give enough time to the stepper motor to respond to the output to maintain the RF frequency. Suggested scenario is to expand the RF pulse signal throughout the “no pulse time” to give a continuous output to the p ...
... system need to be applied in order to make possible to detect the phase deference and give enough time to the stepper motor to respond to the output to maintain the RF frequency. Suggested scenario is to expand the RF pulse signal throughout the “no pulse time” to give a continuous output to the p ...
Regenerative circuit
The regenerative circuit (or regen) allows an electronic signal to be amplified many times by the same active device. It consists of an amplifying vacuum tube or transistor with its output connected to its input through a feedback loop, providing positive feedback. This circuit was widely used in radio receivers, called regenerative receivers, between 1915 and World War II. The regenerative receiver was invented in 1912 and patented in 1914 by American electrical engineer Edwin Armstrong when he was an undergraduate at Columbia University. Due partly to its tendency to radiate interference, by the 1930s the regenerative receiver was superseded by other receiver designs, the TRF and superheterodyne receivers and became obsolete, but regeneration (now called positive feedback) is widely used in other areas of electronics, such as in oscillators and active filters. A receiver circuit that used regeneration in a more complicated way to achieve even higher amplification, the superregenerative receiver, was invented by Armstrong in 1922. It was never widely used in general receivers, but due to its small parts count is used in a few specialized low data rate applications, such as garage door openers, wireless networking devices, walkie-talkies and toys.


















![been investigated [7] - [9]. ... extremely low coupling capacitance require ultra-high input Abstract](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008415826_1-b2d6ab6bf6b67f7918778c5674407c67-300x300.png)
