Marketing Management - 12th Edition
... 34. In ________ pricing, the company decides how to price its products to different customers in different locations and countries. a. specialty b. geographical c. offset d. regional e. none of the above Answer: b Page: 450 Level of difficulty: Easy 35. A ________ is offered by a manufacturer to tra ...
... 34. In ________ pricing, the company decides how to price its products to different customers in different locations and countries. a. specialty b. geographical c. offset d. regional e. none of the above Answer: b Page: 450 Level of difficulty: Easy 35. A ________ is offered by a manufacturer to tra ...
Managing the influence of internal and external determinants on
... positive impact on cost-based pricing strategies in the short run. For instance, organizations operating at full capacity are able to spread fixed costs over more units, thereby achieving greater flexibility in developing pricing strategies. This route to pricing flexibility is equally available to ...
... positive impact on cost-based pricing strategies in the short run. For instance, organizations operating at full capacity are able to spread fixed costs over more units, thereby achieving greater flexibility in developing pricing strategies. This route to pricing flexibility is equally available to ...
MSF Marketing – 2017 Shared Pool Terms
... that are not able to be made due to reductions in supply. (ii) If the supply of raw sugar falls below the quantity that has been priced and/or sold in the Default Pool, which is currently the 2017 Late Season Pool, then, depending on the circumstances, there may be costs to correct the sales program ...
... that are not able to be made due to reductions in supply. (ii) If the supply of raw sugar falls below the quantity that has been priced and/or sold in the Default Pool, which is currently the 2017 Late Season Pool, then, depending on the circumstances, there may be costs to correct the sales program ...
PPT Chapter 15
... Contribution Margin Pricing Pricing is used to help cover fixed costs Very useful for hotels in soft periods of demand ...
... Contribution Margin Pricing Pricing is used to help cover fixed costs Very useful for hotels in soft periods of demand ...
In the previous chapter, attention ... element of the Four P
... sensitive when they cannot easily compare the quality of substitutes. Total expenditure effect - Buyers are less price sensitive the lower the expenditure is as a ratio to ...
... sensitive when they cannot easily compare the quality of substitutes. Total expenditure effect - Buyers are less price sensitive the lower the expenditure is as a ratio to ...
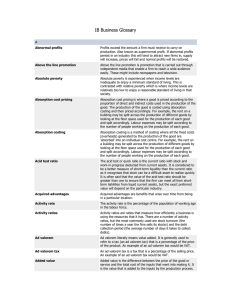
IB Business Glossary - Business-TES
... proportion of direct and indirect costs used in the production of the good. The production of the good is costed using absorption costing and then priced accordingly. For example, the rent on a building may be split across the production of different goods by looking at the floor space used for the ...
... proportion of direct and indirect costs used in the production of the good. The production of the good is costed using absorption costing and then priced accordingly. For example, the rent on a building may be split across the production of different goods by looking at the floor space used for the ...
PPT 5
... • Single-zone pricing- the seller receives a different net return when transportation costs for customers vary • Multiple-zone pricing- delivered prices are uniform within two or more zones McGraw-Hill/Irwin ...
... • Single-zone pricing- the seller receives a different net return when transportation costs for customers vary • Multiple-zone pricing- delivered prices are uniform within two or more zones McGraw-Hill/Irwin ...
2000 WILR 941 - University of Baltimore
... The classic understanding of collusion is that firms collude in order to mimic the actions of a monopoly. [FN14] The monopoly outcome arises as the cartel members agree [FN15] either to restrict output, [FN16] to raise prices, or to divide markets. [FN17] This agreement allows cartel members to maxi ...
... The classic understanding of collusion is that firms collude in order to mimic the actions of a monopoly. [FN14] The monopoly outcome arises as the cartel members agree [FN15] either to restrict output, [FN16] to raise prices, or to divide markets. [FN17] This agreement allows cartel members to maxi ...
Fixing Prices, Rivals, and Rules
... For a discussion of straightforward price-fixing arrangements see ABA Section Of Antitrust Law, Antitrust Law Developments 78–87 4th ed. 1997). The vitamin cartel provides a recent example of a large price-fixing cartel. See Price Fixing: Hoffman-LaRoche, BASF Plead Guilty, Agree to Pay Over $700 Mill ...
... For a discussion of straightforward price-fixing arrangements see ABA Section Of Antitrust Law, Antitrust Law Developments 78–87 4th ed. 1997). The vitamin cartel provides a recent example of a large price-fixing cartel. See Price Fixing: Hoffman-LaRoche, BASF Plead Guilty, Agree to Pay Over $700 Mill ...
Monopolistic Competition
... Price competition, which is where a company tries to distinguish its product or service from competing products on the basis of low price. Firms will engage in non-price competition, in spite of the additional costs involved, because it is usually more profitable than selling for a lower price, and ...
... Price competition, which is where a company tries to distinguish its product or service from competing products on the basis of low price. Firms will engage in non-price competition, in spite of the additional costs involved, because it is usually more profitable than selling for a lower price, and ...
4.5 service marketing triangle - KV Institute of Management and
... procedure should be based on the environmental, engineering, and economic considerations described above. National or local governments new to the air quality management process should focus on obvious sources of air pollution and the quickest means of control - more sophisticated and comprehensive ...
... procedure should be based on the environmental, engineering, and economic considerations described above. National or local governments new to the air quality management process should focus on obvious sources of air pollution and the quickest means of control - more sophisticated and comprehensive ...
Chapter 9 Strategic Brand Management BESPLATNI SEMINARSKI
... initiatives designed to build strong brands and a powerful portfolio. It is important to distinguish between the terms product and brand. In practice they are often used interchangeably, although there are differences in meaning. A product is intended to meet the needs ofbuyers in the product-market ...
... initiatives designed to build strong brands and a powerful portfolio. It is important to distinguish between the terms product and brand. In practice they are often used interchangeably, although there are differences in meaning. A product is intended to meet the needs ofbuyers in the product-market ...
Section 1.5 Theory of the firm and market structures (HL
... Price competition, which is where a company tries to distinguish its product or service from competing products on the basis of low price. Firms will engage in non-price competition, in spite of the additional costs involved, because it is usually more profitable than selling for a lower price, and ...
... Price competition, which is where a company tries to distinguish its product or service from competing products on the basis of low price. Firms will engage in non-price competition, in spite of the additional costs involved, because it is usually more profitable than selling for a lower price, and ...
Cornerstones of cost management, 3e
... • With all else equal, customers will buy more at lower prices and less at higher prices • Factors other than price that influence demand include consumer income, quality of goods offered for sale, availability of substitutes, demand for complementary goods, whether or not the good is a necessity or ...
... • With all else equal, customers will buy more at lower prices and less at higher prices • Factors other than price that influence demand include consumer income, quality of goods offered for sale, availability of substitutes, demand for complementary goods, whether or not the good is a necessity or ...
Ch-12
... • Yield management, used regularly in travel industry, links price to availability – Importance of fixed, perishable capacity – Low incremental cost vs. average cost – Cost-sensitive vs. most loyal customers – Analyzing and predicting demand uncertainty ...
... • Yield management, used regularly in travel industry, links price to availability – Importance of fixed, perishable capacity – Low incremental cost vs. average cost – Cost-sensitive vs. most loyal customers – Analyzing and predicting demand uncertainty ...
Chapter 14
... large companies, division and product line managers do. Even here, top management sets general pricing objectives and policies and often approves lower management’s proposals. Where pricing is a key factor (aerospace, railroads, oil companies), companies often establish a pricing department to set o ...
... large companies, division and product line managers do. Even here, top management sets general pricing objectives and policies and often approves lower management’s proposals. Where pricing is a key factor (aerospace, railroads, oil companies), companies often establish a pricing department to set o ...
Pricing Strategies
... Marketers who use demand-oriented pricing attempt to determine what consumers are willing to pay for given goods and services. The key to this method of pricing is the consumer’s perceived value of the item. The price set must be in line with this perception or the item will be priced too high or to ...
... Marketers who use demand-oriented pricing attempt to determine what consumers are willing to pay for given goods and services. The key to this method of pricing is the consumer’s perceived value of the item. The price set must be in line with this perception or the item will be priced too high or to ...
Application of the Price Discrimination in Marketing
... seat location in a plane or train and etc.). Moreover, in such cases, production costs are either the same or slightly different, but the degree of the difference is not as great as the difference in the price. Pigou (1920) identifies three degrees of price discrimination. Price discrimination of fi ...
... seat location in a plane or train and etc.). Moreover, in such cases, production costs are either the same or slightly different, but the degree of the difference is not as great as the difference in the price. Pigou (1920) identifies three degrees of price discrimination. Price discrimination of fi ...
MARKETING MIX
... Marketing involves a number of activities. To begin with, an organisation may decide on its target group of customers to be served. Once the target group is decided, the product is to be placed in the market by providing the appropriate product, price, distribution and promotional efforts. These are ...
... Marketing involves a number of activities. To begin with, an organisation may decide on its target group of customers to be served. Once the target group is decided, the product is to be placed in the market by providing the appropriate product, price, distribution and promotional efforts. These are ...
I. Chapter Overview
... is, increases in price result in increases in total revenue, while decreases in price result in decreases in total revenue. Elasticity of demand for a product often differs for different price levels and with different percentages of change. As a rule, businesses can determine the actual price elast ...
... is, increases in price result in increases in total revenue, while decreases in price result in decreases in total revenue. Elasticity of demand for a product often differs for different price levels and with different percentages of change. As a rule, businesses can determine the actual price elast ...
Pricing methods
... over price is one of main problems that companies may encounter, many companies cannot solve this problem in an excellent manner. As the quality of goods from different companies become more equal, the price factor changes to one of the most important factors for attracting and retaining customers a ...
... over price is one of main problems that companies may encounter, many companies cannot solve this problem in an excellent manner. As the quality of goods from different companies become more equal, the price factor changes to one of the most important factors for attracting and retaining customers a ...
Chapter 11
... • These examples highlight the many varied ways that price plays a part in our daily lives. • From a marketing viewpoint, price is the money or other considerations, including other goods and services, exchanged for the ownership or use of a product. • The practice of exchanging goods and services f ...
... • These examples highlight the many varied ways that price plays a part in our daily lives. • From a marketing viewpoint, price is the money or other considerations, including other goods and services, exchanged for the ownership or use of a product. • The practice of exchanging goods and services f ...
implementation of a complex of marketing pricing strategies based
... carefully the complex strategies of their own company – their corporate, business and functional levels. However, the basis of the successful implementation of Marketing Pricing Strategy (hereinafter – MPS), as one of the Functional Strategies, is its integration into the overall Decision-Making Sys ...
... carefully the complex strategies of their own company – their corporate, business and functional levels. However, the basis of the successful implementation of Marketing Pricing Strategy (hereinafter – MPS), as one of the Functional Strategies, is its integration into the overall Decision-Making Sys ...
Strategic Online and Offline Retail Pricing: A Review and Research
... –Because the marginal cost of another digital product is close to zero, many consumers believe that a “fair price” is much lower than that for traditional versions of products How can firms set optimal pricing strategies? Can firms' price discriminate among customers and extract any surplus? How can ...
... –Because the marginal cost of another digital product is close to zero, many consumers believe that a “fair price” is much lower than that for traditional versions of products How can firms set optimal pricing strategies? Can firms' price discriminate among customers and extract any surplus? How can ...