The sella turcica in children with lumbosacral myelomeningocele
... patients. In a wider perspective, prenatal accounts of the occurrence and extent of other malformations should form the basis for interdisciplinary studies of children with congenital malformations. Studies of growth in the normal craniofacial skeleton have revealed that the contour of the perpendic ...
... patients. In a wider perspective, prenatal accounts of the occurrence and extent of other malformations should form the basis for interdisciplinary studies of children with congenital malformations. Studies of growth in the normal craniofacial skeleton have revealed that the contour of the perpendic ...
Multiple Exostoses
... Exostoses continue to grow during the period of the affected individual's growth. That is, exostoses may continue to appear and grow throughout childhood, tend to show a spurt of activity during adolescence and become dormant following completion of puberty. Indeed, any increase in size of an exosto ...
... Exostoses continue to grow during the period of the affected individual's growth. That is, exostoses may continue to appear and grow throughout childhood, tend to show a spurt of activity during adolescence and become dormant following completion of puberty. Indeed, any increase in size of an exosto ...
GROWTH/GROWTH DISORDER
... heterogeneous population of children gathered by the National Center for Health Statistics in 1979, updated in 2000. Using the charts, a child's growth pattern can be tracked from birth to age 18. The charts show the mean and 5th percentile and 95th percentile limits (Figure 1). Because of subtle di ...
... heterogeneous population of children gathered by the National Center for Health Statistics in 1979, updated in 2000. Using the charts, a child's growth pattern can be tracked from birth to age 18. The charts show the mean and 5th percentile and 95th percentile limits (Figure 1). Because of subtle di ...
Achondroplasia: pathogenesis and implications for future treatment
... 1040-8703 ß 2010 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
... 1040-8703 ß 2010 Wolters Kluwer Health | Lippincott Williams & Wilkins ...
Case Report: Achondroplasia
... 15000. It is inherited as autosomal dominant trait with complete penetrance. Approximately 80% of cases are due to de novo dominant mutations with a mutation rate estimated to be 0.000014 per gamete per generation[1]. It occurs as a result of mutations in one copy of the fibro-blast growth factor re ...
... 15000. It is inherited as autosomal dominant trait with complete penetrance. Approximately 80% of cases are due to de novo dominant mutations with a mutation rate estimated to be 0.000014 per gamete per generation[1]. It occurs as a result of mutations in one copy of the fibro-blast growth factor re ...
Growth & Development
... • Is a visible display of the child`s physical growth and development.It is designed primarily for the longitudinal follow-up (growth monitoring ) of a child ,so changes can be interpreted . How is it used? • The successive weights are plotted on the growth chart . • The plotting produces a line or ...
... • Is a visible display of the child`s physical growth and development.It is designed primarily for the longitudinal follow-up (growth monitoring ) of a child ,so changes can be interpreted . How is it used? • The successive weights are plotted on the growth chart . • The plotting produces a line or ...
shprintzen goldberg syndrome
... What causes Shprintzen-Goldberg syndrome? Most cases of Shprintzen-Goldberg syndrome are caused by a change (mutation) in the SKI gene. This gene affects many cell types throughout the body and appears to play a role in the development of many tissues, including the skull, other bones, skin, and brai ...
... What causes Shprintzen-Goldberg syndrome? Most cases of Shprintzen-Goldberg syndrome are caused by a change (mutation) in the SKI gene. This gene affects many cell types throughout the body and appears to play a role in the development of many tissues, including the skull, other bones, skin, and brai ...
Case Conference
... Signs of URI infection anywhere from 2 days to 14 days Low grade fever 38-38.5C ...
... Signs of URI infection anywhere from 2 days to 14 days Low grade fever 38-38.5C ...
Morquio Syndrome
... syndrome. High cervical myelopathy and/or sudden respiratory deaths may arise if not appropriately cared for. There appear to be three contributing factors to C-spine problems – odontoid hypoplasia, ligamentous laxity causing instability of C1-C2, and thickening of the soft tissues anterior to the u ...
... syndrome. High cervical myelopathy and/or sudden respiratory deaths may arise if not appropriately cared for. There appear to be three contributing factors to C-spine problems – odontoid hypoplasia, ligamentous laxity causing instability of C1-C2, and thickening of the soft tissues anterior to the u ...
115KB - NZQA
... events – any changes in mtDNA are the diseases that they would be exposed to by result of (gene) mutation only. mtDNA is migrating out of Africa. Offspring carry inherited from the mother only and passes this advantage enabling them to further through the maternal (female) line of the disperse into ...
... events – any changes in mtDNA are the diseases that they would be exposed to by result of (gene) mutation only. mtDNA is migrating out of Africa. Offspring carry inherited from the mother only and passes this advantage enabling them to further through the maternal (female) line of the disperse into ...
Read PDF - Hormones
... However, following the description of pycnodysostosis as a new genetic skeletal dysplasia, Maroteaux and Lamy5 concluded that this was Toulouse-Lautrecs affliction (Figure1). He, in fact, presented all the clinical features suggestive of this diagnosis, in addition to parental consanguinity. Toulou ...
... However, following the description of pycnodysostosis as a new genetic skeletal dysplasia, Maroteaux and Lamy5 concluded that this was Toulouse-Lautrecs affliction (Figure1). He, in fact, presented all the clinical features suggestive of this diagnosis, in addition to parental consanguinity. Toulou ...
Microcephaly
... “Microcephaly vera” or true microcephaly has been defined as genetic conditions in which the brain is abnormally small because of reduce number of neurons , but is keeping normal Gyral pattern and being uncomplicated by other anomalies present at birth, with normal pregnancy, delivery, and postnatal ...
... “Microcephaly vera” or true microcephaly has been defined as genetic conditions in which the brain is abnormally small because of reduce number of neurons , but is keeping normal Gyral pattern and being uncomplicated by other anomalies present at birth, with normal pregnancy, delivery, and postnatal ...
Richard M - Little People of America Medical Resource Center
... Expectations: There is marked variability of growth potential with ultimate adult height ranging from about 3 feet 10 inches to 5 feet 5 inches (118-165 cm). Note that growth in the first 1-3 years may be near normal and, in relatively mildly affected individuals, this may result in delay in diagnos ...
... Expectations: There is marked variability of growth potential with ultimate adult height ranging from about 3 feet 10 inches to 5 feet 5 inches (118-165 cm). Note that growth in the first 1-3 years may be near normal and, in relatively mildly affected individuals, this may result in delay in diagnos ...
Chromosomal Syndromes: Cri du Chat Syndrome
... Caused by mutations in a specific gene (FGFR2) located on Chromosome 10. The gene is associated with growth factors in face and skull. Identified by Crouzon in 1912 (French neurosurgeon). ...
... Caused by mutations in a specific gene (FGFR2) located on Chromosome 10. The gene is associated with growth factors in face and skull. Identified by Crouzon in 1912 (French neurosurgeon). ...
File
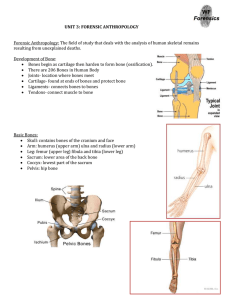
... Determining Age: You can determine the approximate age of a victim by looking at certain bones for any cartilage still remaining. Age: Infant or Not? Look at fusion! Babies bones are not Fused together, such as the skull. Also look to see if teeth have fallen out. ...
... Determining Age: You can determine the approximate age of a victim by looking at certain bones for any cartilage still remaining. Age: Infant or Not? Look at fusion! Babies bones are not Fused together, such as the skull. Also look to see if teeth have fallen out. ...
Craniosynostosis

Craniosynostosis (from cranio, cranium; + syn, together; + ostosis relating to bone) is a condition in which one or more of the fibrous sutures in an infant skull prematurely fuses by turning into bone (ossification), thereby changing the growth pattern of the skull. Because the skull cannot expand perpendicular to the fused suture, it compensates by growing more in the direction parallel to the closed sutures. Sometimes the resulting growth pattern provides the necessary space for the growing brain, but results in an abnormal head shape and abnormal facial features. In cases in which the compensation does not effectively provide enough space for the growing brain, craniosynostosis results in increased intracranial pressure leading possibly to visual impairment, sleeping impairment, eating difficulties, or an impairment of mental development combined with a significant reduction in IQ.Craniosynostosis occurs in one in 2000 births. Craniosynostosis is part of a syndrome in 15 to 40% of the patients, but it usually occurs as an isolated condition.