Logic Demo Board Kit Compact, easy-to-use boards for fast, www.nxp.com
... and switched to nY pins or vice versa with minimal loss. The maximum input frequency for each of the two channels can be as high as 60 MHz at a load of 50 Ω. By default, to avoid floating enable pins, 1 kΩ pull-down resistors are connected between the 1E, 2E lines and GND, and both switches are OFF/ ...
... and switched to nY pins or vice versa with minimal loss. The maximum input frequency for each of the two channels can be as high as 60 MHz at a load of 50 Ω. By default, to avoid floating enable pins, 1 kΩ pull-down resistors are connected between the 1E, 2E lines and GND, and both switches are OFF/ ...
Appendix A Decibels
... in dB will be different; the three values will only be the same when the circuit resistance is constant. For example, if the input and output load resistances of an amplifier are equal, then its power gain, voltage gain., and current gain (calculated in dB) will be the same. If the resistances are d ...
... in dB will be different; the three values will only be the same when the circuit resistance is constant. For example, if the input and output load resistances of an amplifier are equal, then its power gain, voltage gain., and current gain (calculated in dB) will be the same. If the resistances are d ...
Microwave Oven Signal Interference And
... frequency of the AM-FM signal is a random variable Fc that is uniformly distributed between frequencies fa and fb. During any given period, Fc is fixed, but it varies from one ON cycle to the next. Using the model, any MWO signal can be represented by appropriately choosing a set of 13 independent p ...
... frequency of the AM-FM signal is a random variable Fc that is uniformly distributed between frequencies fa and fb. During any given period, Fc is fixed, but it varies from one ON cycle to the next. Using the model, any MWO signal can be represented by appropriately choosing a set of 13 independent p ...
Introduction to Power Management
... the magnetic material of our inductor; these are called Core Losses if we switch faster we will have higher core losses ...
... the magnetic material of our inductor; these are called Core Losses if we switch faster we will have higher core losses ...
MAX2370 Complete 450MHz Quadrature Transmitter General Description Features
... Complete 450MHz Quadrature Transmitter (MAX2370 EV kit, VCC = +2.7V to +3.3V, SHDN = IDLE = TXGATE = high, VGC = 2.5V, RBIAS = 10kΩ, 50Ω system, TA = -40°C to +85°C. Typical values are at VCC_ = SHDN = IDLE = TXGATE = CS = 3.0V, fREF = 19.2MHz, LO input power = -15dBm, fLO = 575MHz, f RFOUT = 455MH ...
... Complete 450MHz Quadrature Transmitter (MAX2370 EV kit, VCC = +2.7V to +3.3V, SHDN = IDLE = TXGATE = high, VGC = 2.5V, RBIAS = 10kΩ, 50Ω system, TA = -40°C to +85°C. Typical values are at VCC_ = SHDN = IDLE = TXGATE = CS = 3.0V, fREF = 19.2MHz, LO input power = -15dBm, fLO = 575MHz, f RFOUT = 455MH ...
Evaluates: MAX17020 MAX17020 Evaluation Kit General Description Features
... The MAX17020 provides a fixed 1.05V output (VOUT2) when REFIN2 is connected to RTC (R12 = 0Ω, R11 = open), or a fixed 3.3V output when REFIN2 is connected to VCC (R11 = 0). VOUT2 can also be adjusted from 0 to 2V using a resistive voltage-divider formed by R13 and R15. REFIN2 sets the feedback-regul ...
... The MAX17020 provides a fixed 1.05V output (VOUT2) when REFIN2 is connected to RTC (R12 = 0Ω, R11 = open), or a fixed 3.3V output when REFIN2 is connected to VCC (R11 = 0). VOUT2 can also be adjusted from 0 to 2V using a resistive voltage-divider formed by R13 and R15. REFIN2 sets the feedback-regul ...
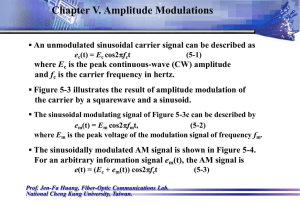
Chap05--Amplitude Mo..
... Indeed, many use a second down conversion and second IF amplifier system following the first IF. Such a superheterodyne receiver is called a double-conversion receiver. The LO frequency is almost always higher than the RF carrier frequency, a characteristic referred to as high-side injection to ...
... Indeed, many use a second down conversion and second IF amplifier system following the first IF. Such a superheterodyne receiver is called a double-conversion receiver. The LO frequency is almost always higher than the RF carrier frequency, a characteristic referred to as high-side injection to ...
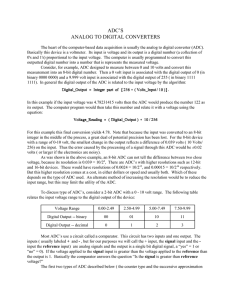
ADC`S ANALOG TO DIGITAL CONVERTERS
... 16) in which after each guess the one making the guesses is told if her last guess is high or low. If a young child were playing the game, he might just make random guesses. A slightly older child would start at the lowest number and just start counting name all of the numbers until they hit the cho ...
... 16) in which after each guess the one making the guesses is told if her last guess is high or low. If a young child were playing the game, he might just make random guesses. A slightly older child would start at the lowest number and just start counting name all of the numbers until they hit the cho ...
Exp.1: Linear Variable Differential Transformer (LVDT) Transducers
... change in the voltage at VO. Full-bridge and half bridge strain gauges are designed to maximize sensitivity by arranging the strain gauge elements in opposing directions. For example, the half-bridge strain gauge in Figure 5 includes an element RG1, which is installed so that its resistance increase ...
... change in the voltage at VO. Full-bridge and half bridge strain gauges are designed to maximize sensitivity by arranging the strain gauge elements in opposing directions. For example, the half-bridge strain gauge in Figure 5 includes an element RG1, which is installed so that its resistance increase ...
AD2s1205
... programmable sinusoidal oscillator that provides sine wave excitation for resolvers. An external crystal is recommended to provide a precision time reference. ...
... programmable sinusoidal oscillator that provides sine wave excitation for resolvers. An external crystal is recommended to provide a precision time reference. ...
A Closer Look at LVDS Technology
... through differential signaling. Differential signaling offers enormous advantages over single-ended technologies because it is less susceptible to noise. In using differential signaling, two-balanced signals are transmitted through the line in opposite direction. Because the signals are of the same ...
... through differential signaling. Differential signaling offers enormous advantages over single-ended technologies because it is less susceptible to noise. In using differential signaling, two-balanced signals are transmitted through the line in opposite direction. Because the signals are of the same ...
Shielded twisted-pair cable
... Describe the type of connectors and equipment used with fiber-optic cable. Explain how fiber is tested to ensure that it will function properly. Discuss safety issues dealing with fiber-optics. ...
... Describe the type of connectors and equipment used with fiber-optic cable. Explain how fiber is tested to ensure that it will function properly. Discuss safety issues dealing with fiber-optics. ...
NI USB-6001/6002/6003 User Guide
... This product was tested and complies with the regulatory requirements and limits for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) stated in the product specifications. These requirements and limits provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the product is operated in the intended operati ...
... This product was tested and complies with the regulatory requirements and limits for electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) stated in the product specifications. These requirements and limits provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the product is operated in the intended operati ...
Differential Input, Dual, Simultaneous Sampling, 4.2 MSPS, 14-Bit, SAR ADC AD7357
... The AD7357 uses advanced design techniques to achieve very low power dissipation at high throughput rates. With a 2.5 V supply and a 4.2 MSPS throughput rate, the part consumes 14 mA typically. The part also offers flexible power/throughput rate management options. The analog input range for the par ...
... The AD7357 uses advanced design techniques to achieve very low power dissipation at high throughput rates. With a 2.5 V supply and a 4.2 MSPS throughput rate, the part consumes 14 mA typically. The part also offers flexible power/throughput rate management options. The analog input range for the par ...
1100_T1_13-4_lab3_electronicsII_manual
... measure them. On the other hand, circuits may contain time varying signals that change with time; we then need an oscilloscope to observe these signals. The oscilloscope is a widely used instrument. In this Lab session, you will learn how to use such equipment. The lab exercises also show you how to ...
... measure them. On the other hand, circuits may contain time varying signals that change with time; we then need an oscilloscope to observe these signals. The oscilloscope is a widely used instrument. In this Lab session, you will learn how to use such equipment. The lab exercises also show you how to ...
Instructions for Authors of Papers Submitted for - Atlas Japan
... measurement in individual channel buffers. The time of both leading and trailing edge of the hit signal (or leading edge time and pulse width) can be stored. Each channel has a 4-word buffer where measurements are stored until they can be written into the common level 1 (L1) buffer. The L1 buffer is ...
... measurement in individual channel buffers. The time of both leading and trailing edge of the hit signal (or leading edge time and pulse width) can be stored. Each channel has a 4-word buffer where measurements are stored until they can be written into the common level 1 (L1) buffer. The L1 buffer is ...
Efficiently Amplified
... with fixed supply voltage, the dc supply is controlled appropriately to amplify the signal, and the dissipated power of the PA is minimized. In this article, we briefly introduce supply modulated PAs, including the conventional EER, H-EER, and ET transmitters [1]–[17]. Much research on the supply mo ...
... with fixed supply voltage, the dc supply is controlled appropriately to amplify the signal, and the dissipated power of the PA is minimized. In this article, we briefly introduce supply modulated PAs, including the conventional EER, H-EER, and ET transmitters [1]–[17]. Much research on the supply mo ...
MAX3280E/MAX3281E/ MAX3283E/MAX3284E ±15kV ESD-Protected 52Mbps, 3V to 5.5V, SOT23 RS-485/RS-422 True Fail-Safe Receivers
... single, true fail-safe receivers designed to operate at data rates up to 52Mbps. The fail-safe architecture guarantees a high output signal if both input terminals are open or shorted together. See the True Fail-Safe section. This feature assures a stable and predictable output logic state with any ...
... single, true fail-safe receivers designed to operate at data rates up to 52Mbps. The fail-safe architecture guarantees a high output signal if both input terminals are open or shorted together. See the True Fail-Safe section. This feature assures a stable and predictable output logic state with any ...
BFQ790 for 433 MHz Smart Metering Applications
... smart meters and the power grid should be guaranteed in terms of quality, time, and security. As a result, more than one technology is adopted at the same time to fulfill the requirements. The function block diagram of a smart meter is shown in Figure 2. Among all the communication standards, sub-GH ...
... smart meters and the power grid should be guaranteed in terms of quality, time, and security. As a result, more than one technology is adopted at the same time to fulfill the requirements. The function block diagram of a smart meter is shown in Figure 2. Among all the communication standards, sub-GH ...
Heterodyne
Heterodyning is a radio signal processing technique invented in 1901 by Canadian inventor-engineer Reginald Fessenden, in which new frequencies are created by combining or mixing two frequencies. Heterodyning is used to shift one frequency range into another, new one, and is also involved in the processes of modulation and demodulation. The two frequencies are combined in a nonlinear signal-processing device such as a vacuum tube, transistor, or diode, usually called a mixer. In the most common application, two signals at frequencies f1 and f2 are mixed, creating two new signals, one at the sum f1 + f2 of the two frequencies, and the other at the difference f1 − f2. These new frequencies are called heterodynes. Typically only one of the new frequencies is desired, and the other signal is filtered out of the output of the mixer. Heterodynes are related to the phenomenon of ""beats"" in acoustics.A major application of the heterodyne process is in the superheterodyne radio receiver circuit, which is used in virtually all modern radio receivers.