Lab 6 FSK Comm Syste.. - The College of Engineering at the
... Figure 2. Transmitter Control Circuitry The receiver circuit is somewhat more complex as shown in Figure 3. It consists of the receiving monopole antenna and matching network (built during a previous lab), followed by a radio frequency (RF) amplifier. A splitter then evenly splits the input power to ...
... Figure 2. Transmitter Control Circuitry The receiver circuit is somewhat more complex as shown in Figure 3. It consists of the receiving monopole antenna and matching network (built during a previous lab), followed by a radio frequency (RF) amplifier. A splitter then evenly splits the input power to ...
AM Receiver - Profe Saul
... true, but SW broadcasts are so powerful that this receiver will work well with signals up to around 6 or 7 mhz. The 10k resistor controls the operating voltage for the ic which is critical for ...
... true, but SW broadcasts are so powerful that this receiver will work well with signals up to around 6 or 7 mhz. The 10k resistor controls the operating voltage for the ic which is critical for ...
LAB 12 AC Circuits
... At low frequencies, the reactance of a capacitor is quite high, often permitting the use of an open-circuit equivalent. At higher frequencies the reactance of a capacitor decreases in a nonlinear manner. At very high frequencies, the capacitor can be approximated by a short-circuit equivalency. PROC ...
... At low frequencies, the reactance of a capacitor is quite high, often permitting the use of an open-circuit equivalent. At higher frequencies the reactance of a capacitor decreases in a nonlinear manner. At very high frequencies, the capacitor can be approximated by a short-circuit equivalency. PROC ...
Adjustable Cable Equalizer Combines Wideband Differential Receiver with Analog Switches
... For a practical equalizer design, we prefer that an EQ be based on a single amplifier stage in order to keep its adjustability manageable and to minimize cost and complexity. The equalizer to be discussed here uses RC networks of the former type, described by Budak, with alternating poles and zeros; ...
... For a practical equalizer design, we prefer that an EQ be based on a single amplifier stage in order to keep its adjustability manageable and to minimize cost and complexity. The equalizer to be discussed here uses RC networks of the former type, described by Budak, with alternating poles and zeros; ...
Introduction to Microwave Measurements, I
... impedance, VSWR, and reflection coefficients at microwave frequencies. The measurement apparatus consists of an air-dielectric transmission line with a small probe that can be slid along the length of the transmission line to pick off a small amount of the signal (electric field), thus giving an ind ...
... impedance, VSWR, and reflection coefficients at microwave frequencies. The measurement apparatus consists of an air-dielectric transmission line with a small probe that can be slid along the length of the transmission line to pick off a small amount of the signal (electric field), thus giving an ind ...
Abstract - JPInfotech
... these noises, spread spectrum clock generators (SSCGs) are proposed to reduce the EMI at a relatively low cost and a relatively simple design. There are several devices that have the defined specifications to restrict the EMI with a SSCG, such as Display Port [2], [3], which is a digital display in ...
... these noises, spread spectrum clock generators (SSCGs) are proposed to reduce the EMI at a relatively low cost and a relatively simple design. There are several devices that have the defined specifications to restrict the EMI with a SSCG, such as Display Port [2], [3], which is a digital display in ...
Octiv Technical
... • Impedans has filed patents in a number of global regions for two novel technologies for VI probes – Octiv. ...
... • Impedans has filed patents in a number of global regions for two novel technologies for VI probes – Octiv. ...
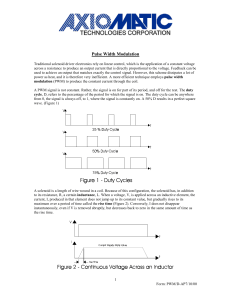
Embedded systems Pulse Width Modulation, PWM
... Class AB A class AB amplifier is a combination on the class A and class B theme. We start from the class B configuration but we make sure that the two transistors have a small bias voltage on their bases even in rest, Figure 4. In this way we make sure that the transistors work in their linear mode. ...
... Class AB A class AB amplifier is a combination on the class A and class B theme. We start from the class B configuration but we make sure that the two transistors have a small bias voltage on their bases even in rest, Figure 4. In this way we make sure that the transistors work in their linear mode. ...
Radio Merit Badge Key Word List
... Transistor – An electronic component that is used for amplification and switching. A common transistor has three leads: base, collector, and emitter. Tube – An electrical component that is used for amplification and switching. Unlike the transistor that can serve the same function, a tube consists o ...
... Transistor – An electronic component that is used for amplification and switching. A common transistor has three leads: base, collector, and emitter. Tube – An electrical component that is used for amplification and switching. Unlike the transistor that can serve the same function, a tube consists o ...
11.3.5 worksheet - Digilent Learn site
... 2. Attach, to this worksheet, analyses which support your circuit design. These analyses should include (at a minimum) your desired low frequency gain and cutoff frequency; chosen resistance and capacitance values, and how these values were chosen. (15 pts) ...
... 2. Attach, to this worksheet, analyses which support your circuit design. These analyses should include (at a minimum) your desired low frequency gain and cutoff frequency; chosen resistance and capacitance values, and how these values were chosen. (15 pts) ...
Hardware Test Plan
... Input a 3.3V, 800Hz (mid-range of BPF, will have greatest response, and thus most power) signal into the second stage of the circuit (shown in figure 3) Measure the peak voltage of power amp that is being delivered to the speaker and determine RMS power from measurement. (Help determine Amplifier Qu ...
... Input a 3.3V, 800Hz (mid-range of BPF, will have greatest response, and thus most power) signal into the second stage of the circuit (shown in figure 3) Measure the peak voltage of power amp that is being delivered to the speaker and determine RMS power from measurement. (Help determine Amplifier Qu ...
Homework 4 plus notes out: 4-22 due: 4
... Assuming the pump field is intense and coherent enough that it is in a constant coherent state, so that a0 can be replaced with a c-number. Then solve Heisenberg’s equation of motion for a1 and a2 . (Hint: you will have to solve a coupled set of two operator differential equations. It is a special c ...
... Assuming the pump field is intense and coherent enough that it is in a constant coherent state, so that a0 can be replaced with a c-number. Then solve Heisenberg’s equation of motion for a1 and a2 . (Hint: you will have to solve a coupled set of two operator differential equations. It is a special c ...
Power Sensor Theory - Herbert Dingfelder – DL5NEG
... proportional to the input level measured in dB. For every dB the input amplitude raises, the DC output raises for some millivolts. Therefore we can measure over a very wide dynamic range (from very small input signals to rather big ones) without the need for a high amplification of the DC voltage. E ...
... proportional to the input level measured in dB. For every dB the input amplitude raises, the DC output raises for some millivolts. Therefore we can measure over a very wide dynamic range (from very small input signals to rather big ones) without the need for a high amplification of the DC voltage. E ...
Optimizing the Heathkit HW-101, SB100-102 Transceivers
... If the carrier oscillator frequency is placed too far from the filter passband, the receive and transmit signals will lack “lows” but the opposite sideband rejection will be high. If the carrier oscillator frequency is placed too close to the filter center frequency, the receive and transmit signal ...
... If the carrier oscillator frequency is placed too far from the filter passband, the receive and transmit signals will lack “lows” but the opposite sideband rejection will be high. If the carrier oscillator frequency is placed too close to the filter center frequency, the receive and transmit signal ...
Receiver Design - School of Electrical Engineering and Computer
... • Radio frequency (RF) amplifiers amplify a selected band of frequencies. RF extend from about 30 KHz up to several thousand MHz. The band of frequencies is selected by a bandpass filter or a tuning circuit. • Wide band amplifiers are designed to amplify a very wide band of frequencies, say from a ...
... • Radio frequency (RF) amplifiers amplify a selected band of frequencies. RF extend from about 30 KHz up to several thousand MHz. The band of frequencies is selected by a bandpass filter or a tuning circuit. • Wide band amplifiers are designed to amplify a very wide band of frequencies, say from a ...
DC Regulated Power Supplies
... 0.05 % mV + 5 mV for no load to full load for 10% line variation ...
... 0.05 % mV + 5 mV for no load to full load for 10% line variation ...
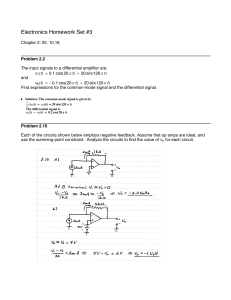
Chapter 1 Problems
... If a receiver is underselective: a. only part of the bandwidth of the AM signal is amplified, causing some of the sideband information to be lost and distortion results. b. the tank circuits within the tuned amplifiers have too high a Q. c. when the volume control is turned up to maximum, the desire ...
... If a receiver is underselective: a. only part of the bandwidth of the AM signal is amplified, causing some of the sideband information to be lost and distortion results. b. the tank circuits within the tuned amplifiers have too high a Q. c. when the volume control is turned up to maximum, the desire ...
Heterodyne
Heterodyning is a radio signal processing technique invented in 1901 by Canadian inventor-engineer Reginald Fessenden, in which new frequencies are created by combining or mixing two frequencies. Heterodyning is used to shift one frequency range into another, new one, and is also involved in the processes of modulation and demodulation. The two frequencies are combined in a nonlinear signal-processing device such as a vacuum tube, transistor, or diode, usually called a mixer. In the most common application, two signals at frequencies f1 and f2 are mixed, creating two new signals, one at the sum f1 + f2 of the two frequencies, and the other at the difference f1 − f2. These new frequencies are called heterodynes. Typically only one of the new frequencies is desired, and the other signal is filtered out of the output of the mixer. Heterodynes are related to the phenomenon of ""beats"" in acoustics.A major application of the heterodyne process is in the superheterodyne radio receiver circuit, which is used in virtually all modern radio receivers.