An Ultra-Simple Receiver For 6 Meters
... with a twisted pair of wire leads. Connect C13 directly to U1, pin 8. I recommend a 10-turn potentiometer for the REGENERATION CONTROL and a reduction drive for the TUNING capacitor. These make the receiver much easier to operate. Always build receiver circuits backwards. Start with the audio stage ...
... with a twisted pair of wire leads. Connect C13 directly to U1, pin 8. I recommend a 10-turn potentiometer for the REGENERATION CONTROL and a reduction drive for the TUNING capacitor. These make the receiver much easier to operate. Always build receiver circuits backwards. Start with the audio stage ...
Chapter 5
... – the amplitude of a carrier wave is varied (or modulated) to represent the magnitude of the input signal – many forms of modulation – shown here is full amplitude modulation (as used in medium wave transmission) – here the envelope of the waveform represents the input signal Storey: Electrical & El ...
... – the amplitude of a carrier wave is varied (or modulated) to represent the magnitude of the input signal – many forms of modulation – shown here is full amplitude modulation (as used in medium wave transmission) – here the envelope of the waveform represents the input signal Storey: Electrical & El ...
edssc_2015_full_paper - DR-NTU
... part is enabled (en cal = 1 in Fig. 2), the ring oscillator and some digital logics begin to work. A counter records the number of ring oscillator cycles when the RC oscillator is at high voltage level. It is used to compare with the number of cycles in the room temperature which is recorded in the ...
... part is enabled (en cal = 1 in Fig. 2), the ring oscillator and some digital logics begin to work. A counter records the number of ring oscillator cycles when the RC oscillator is at high voltage level. It is used to compare with the number of cycles in the room temperature which is recorded in the ...
A Single-Chip Dual-Mode CW/Pulse Electron Paramagnetic
... the center of an RF resonator inside a DC magnetic field, B0. In CW-EPR, a continuous RF signal is sent to the resonator and the change in reflected power is monitored to calculate the RF power absorbed by the sample. The absorbed power varies with the B0 field and this absorption line shape reveals ...
... the center of an RF resonator inside a DC magnetic field, B0. In CW-EPR, a continuous RF signal is sent to the resonator and the change in reflected power is monitored to calculate the RF power absorbed by the sample. The absorbed power varies with the B0 field and this absorption line shape reveals ...
Lab 2: Heart Rate Monitor
... the leg. 5-lead and 12-lead systems are also common and provide more information. An ECG signal has several peaks, such as is shown in Fig. 1, which is an example of a normal signal for “lead II”, which is between the right arm and the left leg. The shape of ECG signals are used to diagnose heart he ...
... the leg. 5-lead and 12-lead systems are also common and provide more information. An ECG signal has several peaks, such as is shown in Fig. 1, which is an example of a normal signal for “lead II”, which is between the right arm and the left leg. The shape of ECG signals are used to diagnose heart he ...
150Vdc Servo System
... PWM signal. To reduce noise, twisted shielded cable must be used and cables should not be bundled in the same conduit. Since energy is coupled in accordance to the square root law, separation of cables by a few inches can produce a substantial reduction in cross coupling. Additionally, using an edge ...
... PWM signal. To reduce noise, twisted shielded cable must be used and cables should not be bundled in the same conduit. Since energy is coupled in accordance to the square root law, separation of cables by a few inches can produce a substantial reduction in cross coupling. Additionally, using an edge ...
Lecture 2 - Auburn University
... Spur Measurement “Spur” is a spurious or unintended frequency in the output of an RF device. Example: leakage of reference frequency used in the phase detector of PLL. ...
... Spur Measurement “Spur” is a spurious or unintended frequency in the output of an RF device. Example: leakage of reference frequency used in the phase detector of PLL. ...
DOC
... 7. The cursors are not used simply to measure time constant. There are two of them and they can be used to measure voltage and time differences. If you got these points confused or did not know that there were multiple cursors points were taken off. Part B: This part was 35 points total. Most of the ...
... 7. The cursors are not used simply to measure time constant. There are two of them and they can be used to measure voltage and time differences. If you got these points confused or did not know that there were multiple cursors points were taken off. Part B: This part was 35 points total. Most of the ...
DATAFLEX® Torque measuring shaft NEW
... twisting of the torsion shaft by measuring the quantity of light. For that purpose the light is directed through two disks the transparency of which is amended proportionally to the torque. The overall electronics are situated in a stationary housing to make sure that no signals have to be transmitt ...
... twisting of the torsion shaft by measuring the quantity of light. For that purpose the light is directed through two disks the transparency of which is amended proportionally to the torque. The overall electronics are situated in a stationary housing to make sure that no signals have to be transmitt ...
M3001A MMS (Multiple Monitoring System)
... Use of a high pass filter at 20Hz, and a low pass filter at 150Hz We identified the main source of noise as that coming from various power lines across the room A notch filter is used (bandstop) for the frequency range 57Hz-62Hz Sensor is sensitive, picks up the slightest movement, another s ...
... Use of a high pass filter at 20Hz, and a low pass filter at 150Hz We identified the main source of noise as that coming from various power lines across the room A notch filter is used (bandstop) for the frequency range 57Hz-62Hz Sensor is sensitive, picks up the slightest movement, another s ...
Module 1
... A step voltage is applied to the circuit in figure 2 at time t = 0. (a) Obtain the expression for vo(t), (b) Obtain expression for rise time in terms of time constant RC and cut-off frequency f2. ...
... A step voltage is applied to the circuit in figure 2 at time t = 0. (a) Obtain the expression for vo(t), (b) Obtain expression for rise time in terms of time constant RC and cut-off frequency f2. ...
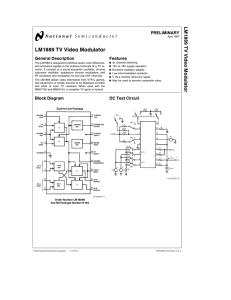
LM1889 TV Video Modulator
... 7, 8 and 9. The signal inputs (pins 12, 13) to both modulators are common, but removing the power supply from an RF oscillator tank circuit will also disable that modulator. As with the chrominance modulators, it is the offset between the two signal input pins that determines the level of RF carrier ...
... 7, 8 and 9. The signal inputs (pins 12, 13) to both modulators are common, but removing the power supply from an RF oscillator tank circuit will also disable that modulator. As with the chrominance modulators, it is the offset between the two signal input pins that determines the level of RF carrier ...
SA602A RF mixer
... The SA602A is a low-power VHF monolithic double-balanced mixer with input amplifier, on-board oscillator, and voltage regulator. It is intended for high performance, low power communication systems. The guaranteed parameters of the SA602A make this device particularly well suited for cellular radio ...
... The SA602A is a low-power VHF monolithic double-balanced mixer with input amplifier, on-board oscillator, and voltage regulator. It is intended for high performance, low power communication systems. The guaranteed parameters of the SA602A make this device particularly well suited for cellular radio ...
SA602A Double-balanced mixer and oscillator Philips Semiconductors Product specification
... The SA602A is a low-power VHF monolithic double-balanced mixer with input amplifier, on-board oscillator, and voltage regulator. It is intended for high performance, low power communication systems. The guaranteed parameters of the SA602A make this device particularly well suited for cellular radio ...
... The SA602A is a low-power VHF monolithic double-balanced mixer with input amplifier, on-board oscillator, and voltage regulator. It is intended for high performance, low power communication systems. The guaranteed parameters of the SA602A make this device particularly well suited for cellular radio ...
Optimal pattern-to-signal synchronization for time-frequency
... All the theoretical and experimental statements above explaining the necessity of some kind of synchronization between the time-domain ECG signal and the decomposition start point or the beginning of decomposed segment of signal. The synchronization point is not necessarily the beginning, but falls ...
... All the theoretical and experimental statements above explaining the necessity of some kind of synchronization between the time-domain ECG signal and the decomposition start point or the beginning of decomposed segment of signal. The synchronization point is not necessarily the beginning, but falls ...
MGA-85-A Evaluation Circuit Board Application Note
... real-time control of the amplifier's dynamic range. For applications in which the device current is to be controlled remotely, a small resistor can be added in series with the Rbias pin. The addition of this resistor will de-Q the connection to the external circuit and eliminate resonances. If left ...
... real-time control of the amplifier's dynamic range. For applications in which the device current is to be controlled remotely, a small resistor can be added in series with the Rbias pin. The addition of this resistor will de-Q the connection to the external circuit and eliminate resonances. If left ...
2.1. Short Time Fourier Transform and Spectrogram
... known as a nonlinear phenomenon that cause to overvoltage in power systems. Here, magnitudes of the over voltage variations are several times of the steady case amplitudes in time domain as well as some harmonics and other frequency components which are defined in the frequency domain. As a result, ...
... known as a nonlinear phenomenon that cause to overvoltage in power systems. Here, magnitudes of the over voltage variations are several times of the steady case amplitudes in time domain as well as some harmonics and other frequency components which are defined in the frequency domain. As a result, ...
DOC
... The LM111, LM211 and LM311 are voltage comparators that have input currents nearly a thousand times lower than devices like the LM106 or LM710. They are also designed to operate over a wider range of supply voltages: from standard±15V op amp supplies down to the single 5V supply used for IC logic. T ...
... The LM111, LM211 and LM311 are voltage comparators that have input currents nearly a thousand times lower than devices like the LM106 or LM710. They are also designed to operate over a wider range of supply voltages: from standard±15V op amp supplies down to the single 5V supply used for IC logic. T ...
LabS2004_2 - University of Kentucky College of Engineering
... characterized by transfer functions, differential equations, and/or impulse responses. For linear circuits these characterizations, along with the initial conditions, completely describe the inputoutput relationship. Circuits containing no energy storage elements are referred to as instantaneous or ...
... characterized by transfer functions, differential equations, and/or impulse responses. For linear circuits these characterizations, along with the initial conditions, completely describe the inputoutput relationship. Circuits containing no energy storage elements are referred to as instantaneous or ...
Induced Polarisation (IP)
... Fig. (A) Application of a pulsed current with alternate polarity, and the consequent measured voltage showing the effect of the overvoltage (Vp) and the rise-time on the leading edge of the voltage pulse. (B) To forms of measurement of the overvoltage at discrete time intervals V(t1), etc., and by t ...
... Fig. (A) Application of a pulsed current with alternate polarity, and the consequent measured voltage showing the effect of the overvoltage (Vp) and the rise-time on the leading edge of the voltage pulse. (B) To forms of measurement of the overvoltage at discrete time intervals V(t1), etc., and by t ...
SSM2142 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... The following data, taken from the THD test circuit on an Audio Precision System One using the internal 80 kHz noise filter, demonstrates the typical performance of a balanced pair system based on the SSM2142/SSM2141 chip set. Both differential and single-ended modes of operation are shown, under a ...
... The following data, taken from the THD test circuit on an Audio Precision System One using the internal 80 kHz noise filter, demonstrates the typical performance of a balanced pair system based on the SSM2142/SSM2141 chip set. Both differential and single-ended modes of operation are shown, under a ...
Heterodyne
Heterodyning is a radio signal processing technique invented in 1901 by Canadian inventor-engineer Reginald Fessenden, in which new frequencies are created by combining or mixing two frequencies. Heterodyning is used to shift one frequency range into another, new one, and is also involved in the processes of modulation and demodulation. The two frequencies are combined in a nonlinear signal-processing device such as a vacuum tube, transistor, or diode, usually called a mixer. In the most common application, two signals at frequencies f1 and f2 are mixed, creating two new signals, one at the sum f1 + f2 of the two frequencies, and the other at the difference f1 − f2. These new frequencies are called heterodynes. Typically only one of the new frequencies is desired, and the other signal is filtered out of the output of the mixer. Heterodynes are related to the phenomenon of ""beats"" in acoustics.A major application of the heterodyne process is in the superheterodyne radio receiver circuit, which is used in virtually all modern radio receivers.