Optical Receiver 80Mbit/s front-end
... CMOS technologies are in this range, they are becoming increasingly radiation tolerant. This has been confirmed on commercial-grade CMOS processes in several works [3, 4]. Ionising radiation can nevertheless induce positive charge trapping in the still thick field and lateral oxides of modern CMOS t ...
... CMOS technologies are in this range, they are becoming increasingly radiation tolerant. This has been confirmed on commercial-grade CMOS processes in several works [3, 4]. Ionising radiation can nevertheless induce positive charge trapping in the still thick field and lateral oxides of modern CMOS t ...
GSR - switching regulator modules High-efficiency step-down switching regulator modules
... GS-R12F and 500 kHz for GS-R12FP. The GSR modules include all the components required to drive the ST embedded regulator, providing a plug and play-like point of regulation. The main features common to the GSR family are: pulse-by-pulse and frequency foldback current protection, overvoltage protecti ...
... GS-R12F and 500 kHz for GS-R12FP. The GSR modules include all the components required to drive the ST embedded regulator, providing a plug and play-like point of regulation. The main features common to the GSR family are: pulse-by-pulse and frequency foldback current protection, overvoltage protecti ...
this document - Mutable Instruments
... cheap with a passive RC filter (22kΩ, 68nF , yielding a cutoff frequency of 106Hz), but there’s a big caveat here! From the SSM2164 datasheet, the CV inputs of the SSM2164 are connected to a 4.5kΩ / 500Ω resistor divider. With the RC filter in place adding some impedance at the input, the ...
... cheap with a passive RC filter (22kΩ, 68nF , yielding a cutoff frequency of 106Hz), but there’s a big caveat here! From the SSM2164 datasheet, the CV inputs of the SSM2164 are connected to a 4.5kΩ / 500Ω resistor divider. With the RC filter in place adding some impedance at the input, the ...
Oscillator
... Describe the operation of Phase-Shift Oscillator, Wien Bridge Oscillator, Crystal Oscillator and Relaxation Oscillator ...
... Describe the operation of Phase-Shift Oscillator, Wien Bridge Oscillator, Crystal Oscillator and Relaxation Oscillator ...
A 350 mu W CMOS MSK Transmitter and 400 mu... Super-Regenerative Receiver for Medical Implant Communications
... The poor efficiency of small loop antennas is manifested in their low radiation resistance and results in their impedance exhibiting a high quality factor (Q). To achieve high power transfer, the inductive element of the antenna must be resonated out by a capacitor. The high Q, however, poses challe ...
... The poor efficiency of small loop antennas is manifested in their low radiation resistance and results in their impedance exhibiting a high quality factor (Q). To achieve high power transfer, the inductive element of the antenna must be resonated out by a capacitor. The high Q, however, poses challe ...
- CAREERFUNDA.IN
... 3. Hysteresis is desirable in Schmitt-trigger, because (A) energy is to be stored/discharged in parasitic capacitances. (B) effects of temperature would be compensated. (C) devices in the circuit should be allowed time for saturation and desaturation. (D) it would prevent noise from causing false tr ...
... 3. Hysteresis is desirable in Schmitt-trigger, because (A) energy is to be stored/discharged in parasitic capacitances. (B) effects of temperature would be compensated. (C) devices in the circuit should be allowed time for saturation and desaturation. (D) it would prevent noise from causing false tr ...
this PDF file. - barton musical circuits
... circuit for division control. On the far left of the diagram are the two pots, the top is attenuating the external CV, and the bottom is providing a variable voltage from +5V to ground. The outputs of these pots are mixed together by two unity gain inverting op-amp stages. The output of the second s ...
... circuit for division control. On the far left of the diagram are the two pots, the top is attenuating the external CV, and the bottom is providing a variable voltage from +5V to ground. The outputs of these pots are mixed together by two unity gain inverting op-amp stages. The output of the second s ...
III. Low Frequency Response and Quasi
... Figure 3b is a Bode plot or graph of the low frequency response of an LIVM sensor. A very significant point on the graph is the corner frequency fc . At this frequency the output from the sensor has decreased by 3db or approximately 30% from its reference sensitivity (the sensitivity that would be o ...
... Figure 3b is a Bode plot or graph of the low frequency response of an LIVM sensor. A very significant point on the graph is the corner frequency fc . At this frequency the output from the sensor has decreased by 3db or approximately 30% from its reference sensitivity (the sensitivity that would be o ...
Multiband UWB Transceivers
... are accommodated. In order to cover as many as 14 bands, both a broadband, low-noise signal path and a large set of PLLs and SSB mixers become necessary. We introduce in this paper a frequency plan that employs only three phase-locked loops to cover the first 12 bands in Fig. 1. Illustrated in Fig. ...
... are accommodated. In order to cover as many as 14 bands, both a broadband, low-noise signal path and a large set of PLLs and SSB mixers become necessary. We introduce in this paper a frequency plan that employs only three phase-locked loops to cover the first 12 bands in Fig. 1. Illustrated in Fig. ...
CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... Figure 4 shows the response of the AGC RF output to a pulse on VSET. As VSET decreases to 1 V, the AGC loop responds with an RF burst. Response time and the amount of signal integration are controlled by the capacitance at the AD8318 CLPF pin—a function analogous to the feedback capacitor around an ...
... Figure 4 shows the response of the AGC RF output to a pulse on VSET. As VSET decreases to 1 V, the AGC loop responds with an RF burst. Response time and the amount of signal integration are controlled by the capacitance at the AD8318 CLPF pin—a function analogous to the feedback capacitor around an ...
here - Stepper Motor Controllers
... transition on the step pulse. When the EPROM input address A0 is low the EPROM outputs data associated to driver channel 1. When A0 is high data associated to driver channel 2 is output from the EPROM. This means that 128 consecutive 2 byte entities in the EPROM make up one microstep cycle, which is ...
... transition on the step pulse. When the EPROM input address A0 is low the EPROM outputs data associated to driver channel 1. When A0 is high data associated to driver channel 2 is output from the EPROM. This means that 128 consecutive 2 byte entities in the EPROM make up one microstep cycle, which is ...
Hartley oscillator
... The actual oscillation frequency will be slightly lower than given above, because of parasitic capacitance in the coil and loading by the transistor. Advantages of the Hartley oscillator include: ■ The frequency may be adjusted using a single variable capacitor, one side of which can be earthed ■ Th ...
... The actual oscillation frequency will be slightly lower than given above, because of parasitic capacitance in the coil and loading by the transistor. Advantages of the Hartley oscillator include: ■ The frequency may be adjusted using a single variable capacitor, one side of which can be earthed ■ Th ...
Differential PECL Series
... Pin 1 and Pin 2 together on the models with Q & QN OUT on pins 4 & 5. This allows having E/D on either pin 1 or pin 2. ...
... Pin 1 and Pin 2 together on the models with Q & QN OUT on pins 4 & 5. This allows having E/D on either pin 1 or pin 2. ...
Audio Interconnect Cables
... audio interconnects. In other words, you can still hear the difference between cables. ...
... audio interconnects. In other words, you can still hear the difference between cables. ...
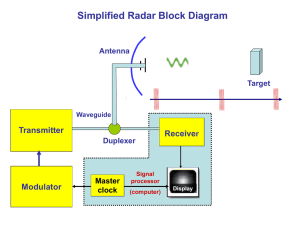
Heterodyne
Heterodyning is a radio signal processing technique invented in 1901 by Canadian inventor-engineer Reginald Fessenden, in which new frequencies are created by combining or mixing two frequencies. Heterodyning is used to shift one frequency range into another, new one, and is also involved in the processes of modulation and demodulation. The two frequencies are combined in a nonlinear signal-processing device such as a vacuum tube, transistor, or diode, usually called a mixer. In the most common application, two signals at frequencies f1 and f2 are mixed, creating two new signals, one at the sum f1 + f2 of the two frequencies, and the other at the difference f1 − f2. These new frequencies are called heterodynes. Typically only one of the new frequencies is desired, and the other signal is filtered out of the output of the mixer. Heterodynes are related to the phenomenon of ""beats"" in acoustics.A major application of the heterodyne process is in the superheterodyne radio receiver circuit, which is used in virtually all modern radio receivers.