Sine Pulse Width Modulation (SPWM)
... The main advantage of PWM is that power loss in the switching devices is very low. When a switch is off there is practically no current, and when it is on, there is almost no voltage drop across the switch. Power loss, being the product of voltage and current, is thus in both cases close to ze ...
... The main advantage of PWM is that power loss in the switching devices is very low. When a switch is off there is practically no current, and when it is on, there is almost no voltage drop across the switch. Power loss, being the product of voltage and current, is thus in both cases close to ze ...
EMI Control in Electronic Governing Systems
... the middle of the circuit. For controls with isolated power supplies, the shields may be connected at both ends to circuit common—providing there are no other connections between the controls to create a ground loop. Shielding for high frequencies is different than for low frequencies. When the shie ...
... the middle of the circuit. For controls with isolated power supplies, the shields may be connected at both ends to circuit common—providing there are no other connections between the controls to create a ground loop. Shielding for high frequencies is different than for low frequencies. When the shie ...
AVTRON ACCel500 FREQUENCY CONVERTERS Frames 4-12
... DO NOT OPERATE RADIO TRANSMITTERS or CELL PHONES IN THE VICINITY OF THE ACCel500 DRIVE. The ACCel500 Drive is an electronic device. Although it is designed to operate reliably in typical industrial environments, the ACCel500 Drive can be affected by radio and/or cell phone transmitters. It is possib ...
... DO NOT OPERATE RADIO TRANSMITTERS or CELL PHONES IN THE VICINITY OF THE ACCel500 DRIVE. The ACCel500 Drive is an electronic device. Although it is designed to operate reliably in typical industrial environments, the ACCel500 Drive can be affected by radio and/or cell phone transmitters. It is possib ...
Wayguard Simis LC – Intelligent Protection of Level Crossings
... complexity. Simis LC vB is now available as this scalable system. This system is used for simplified conditions in railway operations and, in contrast to Simis LC, features restricted functions such as the following: • two open lines with a standard speed of max. 120 km/h • Hp (main signal) and ÜS ( ...
... complexity. Simis LC vB is now available as this scalable system. This system is used for simplified conditions in railway operations and, in contrast to Simis LC, features restricted functions such as the following: • two open lines with a standard speed of max. 120 km/h • Hp (main signal) and ÜS ( ...
Lab03 - Weber State University
... Fig. 1 shows the differential amplifier which uses the resistor REE as the bias resistor. Here VCC=VEE=10 V, Ic=1mA (IE≈1mA). Q1 and Q2 should be a matched pair of NPN transistors (you will have to find the two that are closely matched by trial and error). As explained the class, the differential am ...
... Fig. 1 shows the differential amplifier which uses the resistor REE as the bias resistor. Here VCC=VEE=10 V, Ic=1mA (IE≈1mA). Q1 and Q2 should be a matched pair of NPN transistors (you will have to find the two that are closely matched by trial and error). As explained the class, the differential am ...
... For every monitored variable the characteristic frequency of its waveform variation can be determined according to the operation conditions. This characteristic frequency determines the optimal sample rate selection (POŠTA, PAVLÍČEK 1999). For oscilloscopic measurements the sample rate selection is ...
Vanya Ignatova*, Pierre Granjon**, Seddik Bacha
... can not give an analytical harmonic solution for the considered system and the relations between harmonics can not be expressed. In the frequency domain, several methods for power network harmonic analysis exist [1]. The simplest consists to model the network presenting power electronic devices by k ...
... can not give an analytical harmonic solution for the considered system and the relations between harmonics can not be expressed. In the frequency domain, several methods for power network harmonic analysis exist [1]. The simplest consists to model the network presenting power electronic devices by k ...
Accelerating Voltage Amplitude and Phase Stabilization for the
... input signals of the phase detector, in order to give a constant contribution to the loop gain, must have a phase difference = 90’ at any frequency and their amplitude must be kept constant, in spite of the ...
... input signals of the phase detector, in order to give a constant contribution to the loop gain, must have a phase difference = 90’ at any frequency and their amplitude must be kept constant, in spite of the ...
Third-Order ΣΑ Modulator with 61-dB SNR and 6-MHz
... power request and, possibly, their number. Since the power of an op-amp increases in a quadratic way with its bandwidth, it is mandatory to keep at the minimum the clock frequency and, accordingly, the OSR. However, with low OSR, it is necessary to use high-order modulators, that means more op-amps, ...
... power request and, possibly, their number. Since the power of an op-amp increases in a quadratic way with its bandwidth, it is mandatory to keep at the minimum the clock frequency and, accordingly, the OSR. However, with low OSR, it is necessary to use high-order modulators, that means more op-amps, ...
EC0323 COMMUNICATION LAB II LABORATORY MANUAL SEMESTER V
... a given message signal, transmission of the associated PAM wave engages the communication channel for only a fraction of the sampling interval on a periodic basis. Hence, some of the time interval between adjacent pulses of the PAM wave is cleared for use by the other independent message signals on ...
... a given message signal, transmission of the associated PAM wave engages the communication channel for only a fraction of the sampling interval on a periodic basis. Hence, some of the time interval between adjacent pulses of the PAM wave is cleared for use by the other independent message signals on ...
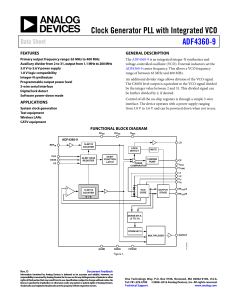
ADF4360-9 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... Charge Pump Ground. This is the ground return path for the charge pump. Analog Power Supply. This ranges from 3.0 V to 3.6 V. Decoupling capacitors to the analog ground plane should be placed as close as possible to this pin. AVDD must have the same value as DVDD. Analog Ground. This is the ground r ...
... Charge Pump Ground. This is the ground return path for the charge pump. Analog Power Supply. This ranges from 3.0 V to 3.6 V. Decoupling capacitors to the analog ground plane should be placed as close as possible to this pin. AVDD must have the same value as DVDD. Analog Ground. This is the ground r ...
Pulse Density Modulation Adopted Dc
... tank is formed by a heating coil and a capacitor, in a series resonant inverter (SRI) or in a parallel resonant inverter. They are used to heat metals to be welded, melted, or hardened. The use of SRIs that are fed with a voltage source represents a cost-effective solution; however, it does not have ...
... tank is formed by a heating coil and a capacitor, in a series resonant inverter (SRI) or in a parallel resonant inverter. They are used to heat metals to be welded, melted, or hardened. The use of SRIs that are fed with a voltage source represents a cost-effective solution; however, it does not have ...
ADF4360-9 - Analog Devices
... Charge Pump Ground. This is the ground return path for the charge pump. Analog Power Supply. This ranges from 3.0 V to 3.6 V. Decoupling capacitors to the analog ground plane should be placed as close as possible to this pin. AVDD must have the same value as DVDD. Analog Ground. This is the ground r ...
... Charge Pump Ground. This is the ground return path for the charge pump. Analog Power Supply. This ranges from 3.0 V to 3.6 V. Decoupling capacitors to the analog ground plane should be placed as close as possible to this pin. AVDD must have the same value as DVDD. Analog Ground. This is the ground r ...
AP5101 1.5A Step-Down Converter with 1.4MHz Switching Frequency
... sum of the Current Sense Amplifier output and the Slope Compensation signal exceeds the EA output voltage, the RS FlipFlop is reset and HS MOSFET is turned off. The external Schottky rectifier diode (D1) conducts the inductor current. For one whole switching cycle, if the sum of the Current Sense Am ...
... sum of the Current Sense Amplifier output and the Slope Compensation signal exceeds the EA output voltage, the RS FlipFlop is reset and HS MOSFET is turned off. The external Schottky rectifier diode (D1) conducts the inductor current. For one whole switching cycle, if the sum of the Current Sense Am ...
Negative feedback and Applications using Operational Amplifier
... multiple purposes. Often, however, filters with flatter pass-bands and steeper roll-off are needed. One solution may consists of cascading many RC filters, using buffer amplifiers (as indicated in Fig. 12) to avoid loading effects. It turns out, such an approach produces indeed steeper rolloff, but ...
... multiple purposes. Often, however, filters with flatter pass-bands and steeper roll-off are needed. One solution may consists of cascading many RC filters, using buffer amplifiers (as indicated in Fig. 12) to avoid loading effects. It turns out, such an approach produces indeed steeper rolloff, but ...
Evaluation of ITS Equipment Generation and analysis of RF signals
... Evaluation of Vehicle Components 쎲 Simulate voltage change and noise, and measure the results The GS610 is a highly accurate, programmable voltage/current source with a measurement function. For example, it can be programmed to output a signal representing a power supply voltage drop at the startup ...
... Evaluation of Vehicle Components 쎲 Simulate voltage change and noise, and measure the results The GS610 is a highly accurate, programmable voltage/current source with a measurement function. For example, it can be programmed to output a signal representing a power supply voltage drop at the startup ...
Heterodyne
Heterodyning is a radio signal processing technique invented in 1901 by Canadian inventor-engineer Reginald Fessenden, in which new frequencies are created by combining or mixing two frequencies. Heterodyning is used to shift one frequency range into another, new one, and is also involved in the processes of modulation and demodulation. The two frequencies are combined in a nonlinear signal-processing device such as a vacuum tube, transistor, or diode, usually called a mixer. In the most common application, two signals at frequencies f1 and f2 are mixed, creating two new signals, one at the sum f1 + f2 of the two frequencies, and the other at the difference f1 − f2. These new frequencies are called heterodynes. Typically only one of the new frequencies is desired, and the other signal is filtered out of the output of the mixer. Heterodynes are related to the phenomenon of ""beats"" in acoustics.A major application of the heterodyne process is in the superheterodyne radio receiver circuit, which is used in virtually all modern radio receivers.