Unit 1 Foundations - Marketing and DECA
... VIII. Channels of Distribution A. A _________ ___ ___________ is the path that a product takes from the producer to the consumer. The iTunes Store allows consumers to purchase music and download it directly to their device. B. Sports and entertainment events are distributed to viewers using mass med ...
... VIII. Channels of Distribution A. A _________ ___ ___________ is the path that a product takes from the producer to the consumer. The iTunes Store allows consumers to purchase music and download it directly to their device. B. Sports and entertainment events are distributed to viewers using mass med ...
The Seven Deadly Sins Of Car Buying That Could Cost You Dearly
... Lee Iacocca once said that car buyers would rather have a root canal than have to go through the process of buying a new car. Here are some of the reasons why: a. The car buying process is unnecessarily complicated and you almost have to be an accountant to figure it out, especially when it comes ...
... Lee Iacocca once said that car buyers would rather have a root canal than have to go through the process of buying a new car. Here are some of the reasons why: a. The car buying process is unnecessarily complicated and you almost have to be an accountant to figure it out, especially when it comes ...
Lecture 10 - Md.ahsan
... company and offer the same product at a relatively lower price. So today we can see huge price war in every product category. Toyota is shrinking its market share in home as well as in Asian market due to competitors like Nissan, Mitsubishi, Honda. To meet ever increasing customer expectations compa ...
... company and offer the same product at a relatively lower price. So today we can see huge price war in every product category. Toyota is shrinking its market share in home as well as in Asian market due to competitors like Nissan, Mitsubishi, Honda. To meet ever increasing customer expectations compa ...
PDF
... for the following reasons. We know that for any processor price, W, in this model the retailer demands the quantity that comes from the intersection of that price line and the marginal revenue curve. In other words, you can read from the marginal revenue curve in the top graph the quantity the retai ...
... for the following reasons. We know that for any processor price, W, in this model the retailer demands the quantity that comes from the intersection of that price line and the marginal revenue curve. In other words, you can read from the marginal revenue curve in the top graph the quantity the retai ...
The Source - Prianka Jhingan
... be well informed and will be able to see that The Source provides the lowest price with the same selection as Big Box stores because they have been extensively engaged in the online community. Moment of truth: Realization of what The Source offers and how it benefits the consumer. ...
... be well informed and will be able to see that The Source provides the lowest price with the same selection as Big Box stores because they have been extensively engaged in the online community. Moment of truth: Realization of what The Source offers and how it benefits the consumer. ...
عرض تقديمي من PowerPoint
... international arena: 1. Global firms offering better products or lower prices can attack the company's domestic market. The company might want to counterattack these competitors in their home markets. 2. The company discovers that some foreign markets present higher profit opportunities than the dom ...
... international arena: 1. Global firms offering better products or lower prices can attack the company's domestic market. The company might want to counterattack these competitors in their home markets. 2. The company discovers that some foreign markets present higher profit opportunities than the dom ...
Figure 13.3 13-14 Marketing: Real People, Real Decisions
... Ethical and Legal Pricing Issues (continued) • Price discrimination: the illegal practice of offering the same product of like quality and quantity to different business customers at different prices, thus lessening competition. • The charging of different prices to different customers is allowed if ...
... Ethical and Legal Pricing Issues (continued) • Price discrimination: the illegal practice of offering the same product of like quality and quantity to different business customers at different prices, thus lessening competition. • The charging of different prices to different customers is allowed if ...
create value
... To create value for your product To become the preferred supplier To establish, maintain, and improve relationships at all levels of the client and agency (keep agency informed) To provide the best research, information, and advice ...
... To create value for your product To become the preferred supplier To establish, maintain, and improve relationships at all levels of the client and agency (keep agency informed) To provide the best research, information, and advice ...
Services
... Product mix width refers to the number of different product lines the company carries. Product mix length refers to the total number of items the company carries within its product lines. Product mix depth refers to the number of versions offered of each product in the line. Product mix consistency ...
... Product mix width refers to the number of different product lines the company carries. Product mix length refers to the total number of items the company carries within its product lines. Product mix depth refers to the number of versions offered of each product in the line. Product mix consistency ...
Chapter 2
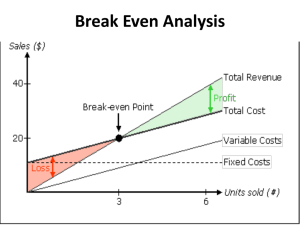
... Sometimes the target return or profit goal is expressed as a percentage of sales. For example, a firm may say that it wants to make a profit of at least 10 percent on sales. In such cases, this profit is added to the variable cost in calculating the break-even point. Break-even analysis does not pro ...
... Sometimes the target return or profit goal is expressed as a percentage of sales. For example, a firm may say that it wants to make a profit of at least 10 percent on sales. In such cases, this profit is added to the variable cost in calculating the break-even point. Break-even analysis does not pro ...
Marketing - Revision
... Most businesses sell a range of products this range represents a product mix or product portfolio. Businesses manage their product portfolios so to keep up overall sales new products are launched as others decline. A product portfolio analysis is therefore an analysis of the range of products within ...
... Most businesses sell a range of products this range represents a product mix or product portfolio. Businesses manage their product portfolios so to keep up overall sales new products are launched as others decline. A product portfolio analysis is therefore an analysis of the range of products within ...
Economics 308 Handout 1 Professor Tom K
... and satisfaction. Relationship varies from basic relationship to full partnership. Customer lifetime value is the present value of the entire stream of purchases that the customer would make less the perceived cost of obtaining the product or service over a lifetime of patronage. Customer satisfacti ...
... and satisfaction. Relationship varies from basic relationship to full partnership. Customer lifetime value is the present value of the entire stream of purchases that the customer would make less the perceived cost of obtaining the product or service over a lifetime of patronage. Customer satisfacti ...
Core concepts - WordPress.com
... Basic Concepts of Marketing Market Segmentation & Target Selection Needs, Wants & Demand ...
... Basic Concepts of Marketing Market Segmentation & Target Selection Needs, Wants & Demand ...
Micropropagation Enterprice
... opportunities are favorable conditions in the environment that could produce rewards for the organization if acted upon properly threats are conditions or barriers that may prevent the firm from reaching its objectives O&T stem from many sources in the ...
... opportunities are favorable conditions in the environment that could produce rewards for the organization if acted upon properly threats are conditions or barriers that may prevent the firm from reaching its objectives O&T stem from many sources in the ...
MARKETING
... 2. How many leads you got from each activity. 3. How many leads led to new customers. 4. What it cost for each activity and compare costs 5. Measure which marketing activities produced better results than others, enabling you to continue those that work and reassign the resource (money or time) to n ...
... 2. How many leads you got from each activity. 3. How many leads led to new customers. 4. What it cost for each activity and compare costs 5. Measure which marketing activities produced better results than others, enabling you to continue those that work and reassign the resource (money or time) to n ...