Seriplex
... field bus-type communication systems that are best suited to transmitting large information data packets. SERIPLEX protocol resides primarily at the physical device level, providing the deterministic, process-critical, real-time I/O updates needed by most control systems and leaves slower, higher-le ...
... field bus-type communication systems that are best suited to transmitting large information data packets. SERIPLEX protocol resides primarily at the physical device level, providing the deterministic, process-critical, real-time I/O updates needed by most control systems and leaves slower, higher-le ...
Management Information Systems
... Often used as the host computer in a network of smaller computers Priced in the tens of thousands to a few hundred thousand dollars Manufacturers: DEC (VAX), IBM (AS/400), and Hewlett-Packard ...
... Often used as the host computer in a network of smaller computers Priced in the tens of thousands to a few hundred thousand dollars Manufacturers: DEC (VAX), IBM (AS/400), and Hewlett-Packard ...
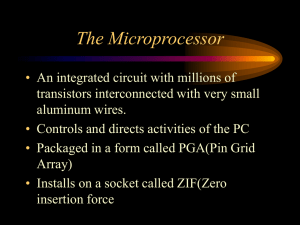
The Microprocessor
... • The 8088 replaced the 8086 and had only an 8 bit external bus • The 8088 CPU was the first chip used in IBM’s microcomputers ...
... • The 8088 replaced the 8086 and had only an 8 bit external bus • The 8088 CPU was the first chip used in IBM’s microcomputers ...
Chapter Overview
... Superscalar technology allows the Pentium to have two instruction Pipelines–called U and V. ...
... Superscalar technology allows the Pentium to have two instruction Pipelines–called U and V. ...
COMPUTER´S MEMORY Paula Michelle
... instruction and a few pieces of data at the time The computer divides each RAM chip into many equal-sized memory locations The central processing unit, is hardware component that executes the step on a software program ...
... instruction and a few pieces of data at the time The computer divides each RAM chip into many equal-sized memory locations The central processing unit, is hardware component that executes the step on a software program ...
Course Arrangements: Higher Computing 6
... fetch-execute cycle registers cache main memory, backing storage Addressability measures of performance: clock speed, MIPS,FLOPS, and application based tests system performance and data bus width, use of cache memory, rate of data transfer to and from peripherals current trends in computer hardware ...
... fetch-execute cycle registers cache main memory, backing storage Addressability measures of performance: clock speed, MIPS,FLOPS, and application based tests system performance and data bus width, use of cache memory, rate of data transfer to and from peripherals current trends in computer hardware ...
Ports
... Ports, used to add keyboard, monitor, printer, etc., are places to attach external devices using connectors. A connector joins a cable to a device. Male connectors have ...
... Ports, used to add keyboard, monitor, printer, etc., are places to attach external devices using connectors. A connector joins a cable to a device. Male connectors have ...
Bus (computing)

In computer architecture, a bus (related to the Latin ""omnibus"", meaning ""for all"") is a communication system that transfers data between components inside a computer, or between computers. This expression covers all related hardware components (wire, optical fiber, etc.) and software, including communication protocols.Early computer buses were parallel electrical wires with multiple connections, but the term is now used for any physical arrangement that provides the same logical functionality as a parallel electrical bus. Modern computer buses can use both parallel and bit serial connections, and can be wired in either a multidrop (electrical parallel) or daisy chain topology, or connected by switched hubs, as in the case of USB.