Chapter 7 Lecture Presentation
... Establishing an explicit connection for each stream across network requires all network elements (NEs) to be aware of connection; All NEs have to be involved in reestablishment of connections in case of network fault In connectionless network operation, NEs do not deal with each explicit connection ...
... Establishing an explicit connection for each stream across network requires all network elements (NEs) to be aware of connection; All NEs have to be involved in reestablishment of connections in case of network fault In connectionless network operation, NEs do not deal with each explicit connection ...
3 Router Configuration - Cisco Networking Academy
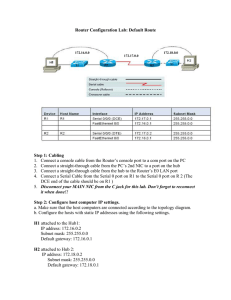
... Step 15 Configure a default route on each router. In order for the routers to talk to each other, they must know how to reach all of the networks connected to each router. A default route will tell each router to send all packets that are not destined for its own LAN to the S0 interface of the other ...
... Step 15 Configure a default route on each router. In order for the routers to talk to each other, they must know how to reach all of the networks connected to each router. A default route will tell each router to send all packets that are not destined for its own LAN to the S0 interface of the other ...
3rd Edition: Chapter 4 - Sun Yat
... run routing algorithms/protocol (RIP, OSPF, BGP) forwarding datagrams from incoming to outgoing link ...
... run routing algorithms/protocol (RIP, OSPF, BGP) forwarding datagrams from incoming to outgoing link ...
ch05 - The University of Texas at Dallas
... – Uses a variety of information types to decide how to route a packet (more sophisticated) • e.g., number of hops, congestion, speed of circuit – Links state info exchanged periodically by each node to keep every node in the network up to date – Provides more reliable, up to date paths to destinatio ...
... – Uses a variety of information types to decide how to route a packet (more sophisticated) • e.g., number of hops, congestion, speed of circuit – Links state info exchanged periodically by each node to keep every node in the network up to date – Provides more reliable, up to date paths to destinatio ...
ppt - FSU Computer Science
... “smart” end systems need for guaranteed (computers) service can adapt, perform “dumb” end systems control, error recovery telephones simple inside network, complexity inside complexity at “edge” network many link types different characteristics uniform service difficult Network L ...
... “smart” end systems need for guaranteed (computers) service can adapt, perform “dumb” end systems control, error recovery telephones simple inside network, complexity inside complexity at “edge” network many link types different characteristics uniform service difficult Network L ...
3rd Edition, Chapter 5
... passes data in frame to network layer protocol otherwise, adapter discards frame Type: indicates higher layer protocol (mostly IP ...
... passes data in frame to network layer protocol otherwise, adapter discards frame Type: indicates higher layer protocol (mostly IP ...
JA2315061508
... aspects. OBS burst immediately follow their request headers without waiting for a reservation acknowledgement. Burst may use bandwidth along several links and still be blocked and lost without completing their routers. In circuit switching, transmission starts after end to end reservation is acknowl ...
... aspects. OBS burst immediately follow their request headers without waiting for a reservation acknowledgement. Burst may use bandwidth along several links and still be blocked and lost without completing their routers. In circuit switching, transmission starts after end to end reservation is acknowl ...
Network Layer Data Plane - CSE Labs User Home Pages
... – Routing: determine next hop to each destination a priori – Forwarding: destination address in packet header, used at each hop to look up for next hop • routes may change during “session” – analogy: driving, asking directions at every gas station, or based on the road signs at every turn ...
... – Routing: determine next hop to each destination a priori – Forwarding: destination address in packet header, used at each hop to look up for next hop • routes may change during “session” – analogy: driving, asking directions at every gas station, or based on the road signs at every turn ...
EE 122: Computer Networks - EECS Instructional Support Group
... • Different devices switch different things – Physical layer: electrical signals (repeaters and hubs) – Link layer: frames (bridges and switches) ...
... • Different devices switch different things – Physical layer: electrical signals (repeaters and hubs) – Link layer: frames (bridges and switches) ...
Node 1 `s Topology Table
... • When router joins network, it builds routing table, using information from neighbors. • If more than one possible path exists to a network, router chooses path with best feasible distances • If serial link goes down, router must find a new route to destination network ...
... • When router joins network, it builds routing table, using information from neighbors. • If more than one possible path exists to a network, router chooses path with best feasible distances • If serial link goes down, router must find a new route to destination network ...
Agile Networks 2.0
... wavelength blockers and PLC based ROADM’s were deployed with WSS catching up … ...
... wavelength blockers and PLC based ROADM’s were deployed with WSS catching up … ...
3rd Edition: Chapter 4
... routers establish virtual connection routers get involved network vs transport layer connection service: network: between two hosts (may also involve inervening routers in case of VCs) transport: between two processes ...
... routers establish virtual connection routers get involved network vs transport layer connection service: network: between two hosts (may also involve inervening routers in case of VCs) transport: between two processes ...
Juniper Networks Presentation Template-EMEA
... MPLS supports the requirements of Intelligent Network Resource Plane MPLS was designed to ease the provisioning and maintenance of efficient packet data networks IGP and BGP routing protocols building forwarding tables based on shortest path only MPLS separates the route control and packet f ...
... MPLS supports the requirements of Intelligent Network Resource Plane MPLS was designed to ease the provisioning and maintenance of efficient packet data networks IGP and BGP routing protocols building forwarding tables based on shortest path only MPLS separates the route control and packet f ...
cs6551 computer networks - MET Engineering College
... Error detection means using redundant information (parity bits) along with data to enable the receiver detect whether the received data is corrupted or not. Examples are Two dimensional parity, Internet checksum, CRC, etc. When an error is detected, the data is discarded and a retransmission is done ...
... Error detection means using redundant information (parity bits) along with data to enable the receiver detect whether the received data is corrupted or not. Examples are Two dimensional parity, Internet checksum, CRC, etc. When an error is detected, the data is discarded and a retransmission is done ...
Chapter 4 - ECE Users Pages
... “smart” end systems need for guaranteed (computers) service can adapt, perform “dumb” end systems control, error recovery telephones simple inside network, complexity inside complexity at “edge” network many link types different characteristics uniform service difficult Network L ...
... “smart” end systems need for guaranteed (computers) service can adapt, perform “dumb” end systems control, error recovery telephones simple inside network, complexity inside complexity at “edge” network many link types different characteristics uniform service difficult Network L ...
NEBULA - A Future Internet That Supports Trustworthy Cloud
... security, another long-held goal of Internet research. For example, several schemes seek the flexibility of forwarding packets along multiple paths to improve performance and reliability, while schemes such as network capabilities seek to constrain packets to a single “approved” network path. We wi ...
... security, another long-held goal of Internet research. For example, several schemes seek the flexibility of forwarding packets along multiple paths to improve performance and reliability, while schemes such as network capabilities seek to constrain packets to a single “approved” network path. We wi ...
Network-INT201-05 - Department of Computer Engineering
... need for guaranteed (computers) service can adapt, perform “dumb” end systems control, error recovery telephones simple inside network, complexity inside complexity at “edge” network many link types different characteristics uniform service difficult Network Layer (part1) 5-19 ...
... need for guaranteed (computers) service can adapt, perform “dumb” end systems control, error recovery telephones simple inside network, complexity inside complexity at “edge” network many link types different characteristics uniform service difficult Network Layer (part1) 5-19 ...
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE)
... Fast and reliable communications is a basic requirement in almost all modern applications, but the real time systems take it to extreme and require real time responses from the network. In some cases, the requirements are so tough that may require special hardware to achieve desired performance .In ...
... Fast and reliable communications is a basic requirement in almost all modern applications, but the real time systems take it to extreme and require real time responses from the network. In some cases, the requirements are so tough that may require special hardware to achieve desired performance .In ...
ppt - Temple University
... run routing algorithms/protocol (RIP, OSPF, BGP) forwarding datagrams from incoming to outgoing link ...
... run routing algorithms/protocol (RIP, OSPF, BGP) forwarding datagrams from incoming to outgoing link ...
Chapter 10
... As a frame is received at a router interface, the destination MAC address is extracted. The address is checked to see if the frame is directly addressed to the router interface, or if it is a broadcast. In either of these two cases, the frame is accepted. Otherwise, the frame is discarded since it i ...
... As a frame is received at a router interface, the destination MAC address is extracted. The address is checked to see if the frame is directly addressed to the router interface, or if it is a broadcast. In either of these two cases, the frame is accepted. Otherwise, the frame is discarded since it i ...
Ch4_3ed
... (max.transfer size) - largest possible link-level frame. The links on a route can use different link types, different link-layer protocols, and different MTUs large IP datagram are divided (“fragmented”) within network one datagram becomes several datagrams “reassembled” only at final destin ...
... (max.transfer size) - largest possible link-level frame. The links on a route can use different link types, different link-layer protocols, and different MTUs large IP datagram are divided (“fragmented”) within network one datagram becomes several datagrams “reassembled” only at final destin ...