15245Chapter_5_V6.01
... We’re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They’re in PowerPoint form so you see the animations; and can add, modify, and delete slides (including this one) and slide content to suit your needs. They obviously represent a lot of work on our part. In return for us ...
... We’re making these slides freely available to all (faculty, students, readers). They’re in PowerPoint form so you see the animations; and can add, modify, and delete slides (including this one) and slide content to suit your needs. They obviously represent a lot of work on our part. In return for us ...
Slides for Chapter 5
... R forwards datagram with IP source A, destination B R creates link-layer frame with B's MAC address as dest, frame contains A-to-B IP datagram MAC src: 1A-23-F9-CD-06-9B MAC dest: 49-BD-D2-C7-56-2A IP src: 111.111.111.111 IP dest: 222.222.222.222 ...
... R forwards datagram with IP source A, destination B R creates link-layer frame with B's MAC address as dest, frame contains A-to-B IP datagram MAC src: 1A-23-F9-CD-06-9B MAC dest: 49-BD-D2-C7-56-2A IP src: 111.111.111.111 IP dest: 222.222.222.222 ...
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE)
... search and rescue, and disaster relief operations. Later, it found civilian applications such as community networks. A great deal of research results have been published since its early days in the 1980s. The most salient research challenges in this area include end-to-end data transfer, link access ...
... search and rescue, and disaster relief operations. Later, it found civilian applications such as community networks. A great deal of research results have been published since its early days in the 1980s. The most salient research challenges in this area include end-to-end data transfer, link access ...
pptx - Cambridge Computer Laboratory
... • understand principles behind network layer services: – network layer service models – forwarding versus routing (versus switching) – how a router works – routing (path selection) – IPv6 ...
... • understand principles behind network layer services: – network layer service models – forwarding versus routing (versus switching) – how a router works – routing (path selection) – IPv6 ...
Cooperation in Wireless Communication Networks
... However, the improvement is achieved at added complexity to the communication operation such as at the physical layer. One challenge that faces these strategies is that, for optimal decoding at the destination node, the channel coefficients between the source node and the cooperating entities should ...
... However, the improvement is achieved at added complexity to the communication operation such as at the physical layer. One challenge that faces these strategies is that, for optimal decoding at the destination node, the channel coefficients between the source node and the cooperating entities should ...
download
... promiscuously on sizes and types of packets • Three groups associated with the stations • Routing group gathers on routing ...
... promiscuously on sizes and types of packets • Three groups associated with the stations • Routing group gathers on routing ...
Open Network Programming
... Northbound Interfaces But on the northbound side… the situation is bleak Current controllers provide a variety of abstractions: • Device abstraction layers • Isolated slices • Virtual networks • QoS provisioning • NFV service chaining • Custom services (discovery, firewall, etc.) But the developme ...
... Northbound Interfaces But on the northbound side… the situation is bleak Current controllers provide a variety of abstractions: • Device abstraction layers • Isolated slices • Virtual networks • QoS provisioning • NFV service chaining • Custom services (discovery, firewall, etc.) But the developme ...
Interdomain and Policy Routing, BGP, MPLS
... The maximum rate at which you can transmit data is limited by how fast (in Hertz) the sender’s hardware can change voltage level and how sensitive the receiver’s hardware is to voltage level changes ...
... The maximum rate at which you can transmit data is limited by how fast (in Hertz) the sender’s hardware can change voltage level and how sensitive the receiver’s hardware is to voltage level changes ...
Encounter based Routing in Opportunistic Networks Nidhi , R. K. Chauhan
... In [9] studied opportunistic network architecture and investigated the social measurements from encounter, social elements and social properties, individually. They demonstrated that experience data is essential embodiment of social measurements in opportunistic networks. Social measurements, for ex ...
... In [9] studied opportunistic network architecture and investigated the social measurements from encounter, social elements and social properties, individually. They demonstrated that experience data is essential embodiment of social measurements in opportunistic networks. Social measurements, for ex ...
TamVu_TCP_lec_DR13 - Winlab
... Applications requirements vs. IP layer limitations Guarantee message delivery Network may drop messages. Deliver messages in the same order they are sent Messages may be reordered in networks and incurs a long delay. Delivers at most one copy of each message Messages may duplicate in ne ...
... Applications requirements vs. IP layer limitations Guarantee message delivery Network may drop messages. Deliver messages in the same order they are sent Messages may be reordered in networks and incurs a long delay. Delivers at most one copy of each message Messages may duplicate in ne ...
Ch. 9 – Basic Router Troubleshooting
... RTC to Host Y 1. RTC looks up the IP destination address in its routing table. • 192.168.4.0/24 is a directly connected network with an exit-interface of e0. • RTC realizes that this destination ip address is on the same network as one of its interfaces and it can sent the packet directly to the des ...
... RTC to Host Y 1. RTC looks up the IP destination address in its routing table. • 192.168.4.0/24 is a directly connected network with an exit-interface of e0. • RTC realizes that this destination ip address is on the same network as one of its interfaces and it can sent the packet directly to the des ...
Module 3 - IT, Sligo
... DUAL guarantees loop-free operation at every instant throughout a route computation allowing all routers involved in a topology change to synchronize at the same time ...
... DUAL guarantees loop-free operation at every instant throughout a route computation allowing all routers involved in a topology change to synchronize at the same time ...
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE)
... directly, if they are in other’s wireless links radio range. In order to enable data transfer they either communicate through single hop or through multiple hops with the help of intermediate nodes. Since MANETs allow ubiquitous service access, anywhere, anytime without any fixed infrastructure they ...
... directly, if they are in other’s wireless links radio range. In order to enable data transfer they either communicate through single hop or through multiple hops with the help of intermediate nodes. Since MANETs allow ubiquitous service access, anywhere, anytime without any fixed infrastructure they ...
Document
... will have the same structure when it is received as it did when it was sent. For example, two different protocols might each break data into packets and add on various sequencing, timing, and error-checking information, but each will do it differently. Therefore, a computer using one of these protoc ...
... will have the same structure when it is received as it did when it was sent. For example, two different protocols might each break data into packets and add on various sequencing, timing, and error-checking information, but each will do it differently. Therefore, a computer using one of these protoc ...
A Performance Comparison of Multi-Hop Wireless Ad Hoc
... Each mobile node has a position and a velocity and moves around on a topography that is specified using either a digital elevation map or a flat grid. The position of a mobile node can be calculated as a function of time, and is used by the radio propagation model to calculate the propagation delay ...
... Each mobile node has a position and a velocity and moves around on a topography that is specified using either a digital elevation map or a flat grid. The position of a mobile node can be calculated as a function of time, and is used by the radio propagation model to calculate the propagation delay ...
Restricting Access in the network
... forwarded out on S0/0/0. Traffic from networks other than 192.168.10.0 is blocked. The first line identifies the ACL as access list 1. It permits traffic that matches the selected parameters. access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.0 ...
... forwarded out on S0/0/0. Traffic from networks other than 192.168.10.0 is blocked. The first line identifies the ACL as access list 1. It permits traffic that matches the selected parameters. access-list 1 permit 192.168.10.0 ...
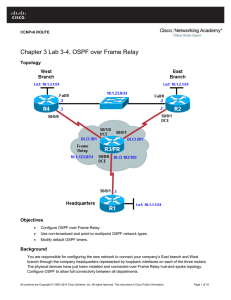
Chapter 3 Lab 3-4, OSPF over Frame Relay
... Note: This lab uses Cisco 1841 routers with Cisco IOS Release 12.4(24)T1 and the Advanced IP Services image c1841-advipservicesk9-mz.124-24.T1.bin. The switch is a Cisco WS-C2960-24TT-L with the Cisco IOS image c2960-lanbasek9-mz.122-46.SE.bin. You can use other routers (such as a 2801 or 2811) and ...
... Note: This lab uses Cisco 1841 routers with Cisco IOS Release 12.4(24)T1 and the Advanced IP Services image c1841-advipservicesk9-mz.124-24.T1.bin. The switch is a Cisco WS-C2960-24TT-L with the Cisco IOS image c2960-lanbasek9-mz.122-46.SE.bin. You can use other routers (such as a 2801 or 2811) and ...
High Speed Communication Protocols
... Current protocols use accumulative acknowledgement; when you ack N this implies that all packets up to N have been received ...
... Current protocols use accumulative acknowledgement; when you ack N this implies that all packets up to N have been received ...
Routing in Sensor Networks: Directed Diffusion and other
... What if Data and ACK travel on different routes ? BS will not see the ACK at all – splitting not feasible ...
... What if Data and ACK travel on different routes ? BS will not see the ACK at all – splitting not feasible ...
On Monitoring of End-to-End Packet Reordering over the Internet Bin Ye
... layer, thus forcing the application to deal with reordering unless the application itself is not sensitive to the order of packets. For delay sensitive applications based on UDP, such as videoconferencing, an out-oforder packet that arrives after the elapse of playback time is as good as lost. Even ...
... layer, thus forcing the application to deal with reordering unless the application itself is not sensitive to the order of packets. For delay sensitive applications based on UDP, such as videoconferencing, an out-oforder packet that arrives after the elapse of playback time is as good as lost. Even ...