
Historic Development by Mihai
... wavelength is short enough. The photoelectric effect is observed below some threshold wavelength which is specific to the material. Especially the fact that light of large wavelengths has no effect at all even if it is extremely intensive, appeared mysterious for the scientists. Albert Einstein fina ...
... wavelength is short enough. The photoelectric effect is observed below some threshold wavelength which is specific to the material. Especially the fact that light of large wavelengths has no effect at all even if it is extremely intensive, appeared mysterious for the scientists. Albert Einstein fina ...
CHEMISTRY 30A CHAPTER 2 NOTES FALL 2014
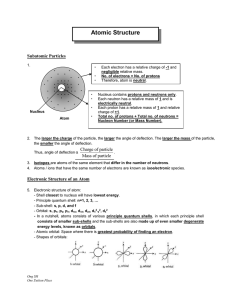
... same number of electrons and protons. An atom with unequal numbers of protons and neutrons is called an ION. Example: The Na+ ion has 11 protons in the nucleus (obviously!) and 10 electrons in the orbitals surrounding the nucleus. Electrons and electronic configuration Electrons occupy orbitals. An ...
... same number of electrons and protons. An atom with unequal numbers of protons and neutrons is called an ION. Example: The Na+ ion has 11 protons in the nucleus (obviously!) and 10 electrons in the orbitals surrounding the nucleus. Electrons and electronic configuration Electrons occupy orbitals. An ...
Homework for the electron microscopy class
... energy of a particle is given by E = ½ mv2 where m is its mass and v is its velocity. 1. The wavelength of visible light typically falls within the range of 400 - 800 nm. What energy range does this correspond to? 2. Electrons in electron microscopes are typically accelerated by potentials of 100 V ...
... energy of a particle is given by E = ½ mv2 where m is its mass and v is its velocity. 1. The wavelength of visible light typically falls within the range of 400 - 800 nm. What energy range does this correspond to? 2. Electrons in electron microscopes are typically accelerated by potentials of 100 V ...
Document
... At ν < νo (hν < Φ) the photon energy is insufficient to extract an electron from metal Einstein suggested that light consists of a stream of packets of energy called photons Therefore, light behaves like a particle (a stream of photons) and as a wave! ...
... At ν < νo (hν < Φ) the photon energy is insufficient to extract an electron from metal Einstein suggested that light consists of a stream of packets of energy called photons Therefore, light behaves like a particle (a stream of photons) and as a wave! ...
Characteristics of Waves
... Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle: states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle. Quantum Theory: describes mathematically the wave properties of electrons and other very small particles. ...
... Heisenberg’s Uncertainty Principle: states that it is impossible to determine simultaneously both the position and velocity of an electron or any other particle. Quantum Theory: describes mathematically the wave properties of electrons and other very small particles. ...
The Electron - Student Moodle
... energy level. Sometimes called the “planetary model” because it looks like a solar system, with the nucleus in place of the sun and electrons in place of the planets. What actually happens is not that simple. If an electron is in the first energy level (n = 1), the Bohr model may predict its average ...
... energy level. Sometimes called the “planetary model” because it looks like a solar system, with the nucleus in place of the sun and electrons in place of the planets. What actually happens is not that simple. If an electron is in the first energy level (n = 1), the Bohr model may predict its average ...
Quantum mechanic and Particle physics
... • Quantum mechanics is a set of mathematical principles and rules that apply to quantum objects. • It is a highly abstract theory that attempts to formulate the quantum behavior of sub-atomic processes through mathematical models that can be used to predict the probabilities of various outcomes. • ...
... • Quantum mechanics is a set of mathematical principles and rules that apply to quantum objects. • It is a highly abstract theory that attempts to formulate the quantum behavior of sub-atomic processes through mathematical models that can be used to predict the probabilities of various outcomes. • ...
polarization of the allotropic hollow foms of carbon and its use in
... quantum charged particles with total energy E > 0 is offered. The problem is shown to classical quantum-mechanical effect: «a particle in a box» (a Q-particle) in which power conditions are defined by the sizes of a box with the polarizing forces locally operating as a potential barrier or "mirror", ...
... quantum charged particles with total energy E > 0 is offered. The problem is shown to classical quantum-mechanical effect: «a particle in a box» (a Q-particle) in which power conditions are defined by the sizes of a box with the polarizing forces locally operating as a potential barrier or "mirror", ...
Ch. 6 Electric Structure HW
... 5C) Describe a particle like characteristic of an electron. (Hint: Think back to Ch. 2) 5D) According to De Broglie’s Theory, why would an electron show more wave-like properties than a golf ball? 5E) Describe how the wave properties of the electron were demonstrated experimentally after De Broglie’ ...
... 5C) Describe a particle like characteristic of an electron. (Hint: Think back to Ch. 2) 5D) According to De Broglie’s Theory, why would an electron show more wave-like properties than a golf ball? 5E) Describe how the wave properties of the electron were demonstrated experimentally after De Broglie’ ...
Chapter 1 Quiz
... a) Write the time-independent Schrodinger Equation for each region of this potential, and give the general form of the wavefunctions for an electron traveling through such a potential. Remember, the electron is not bound, so your solutions will take the form of traveling waves (e±ikx), which cannot ...
... a) Write the time-independent Schrodinger Equation for each region of this potential, and give the general form of the wavefunctions for an electron traveling through such a potential. Remember, the electron is not bound, so your solutions will take the form of traveling waves (e±ikx), which cannot ...




















![introduction [Kompatibilitätsmodus]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017596641_1-03cad833ad630350a78c42d7d7aa10e3-300x300.png)
