Data Structures through C++ Lab Manual
... in response to the call. Dynamic Binding (also known as late binding) means that the code associated with a given function which is to be used is not known until the time of the call at run-time. A function call associated with a polymorphic reference depends on the dynamic type of that reference. 7 ...
... in response to the call. Dynamic Binding (also known as late binding) means that the code associated with a given function which is to be used is not known until the time of the call at run-time. A function call associated with a polymorphic reference depends on the dynamic type of that reference. 7 ...
Pattern matching in concatenative programming languages
... In this design, a quotation is inverted by recursively inverting each word in the quotation, and each word that that calls, etc, until a word with a pre-defined inverse is reached. There are four types of pre-defined inverses. • Literals are handled very simply. The inverse of 1 is 1 =/fail where =/ ...
... In this design, a quotation is inverted by recursively inverting each word in the quotation, and each word that that calls, etc, until a word with a pre-defined inverse is reached. There are four types of pre-defined inverses. • Literals are handled very simply. The inverse of 1 is 1 =/fail where =/ ...
Finishing code generation
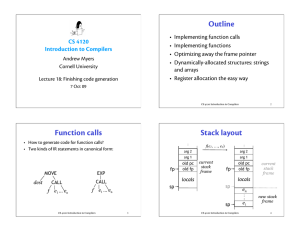
... • Really no need for frame pointer register! • Idea: maintain constant offset k between frame pointer and stack pointer – Use RISC-style argument passing rather than pushing arguments on stack – All references to MEM(FP+n) translated to operand [esp+(n+k)] instead of to [ebp+n] ...
... • Really no need for frame pointer register! • Idea: maintain constant offset k between frame pointer and stack pointer – Use RISC-style argument passing rather than pushing arguments on stack – All references to MEM(FP+n) translated to operand [esp+(n+k)] instead of to [ebp+n] ...
Document
... • Given instruction, replace every temporary in instruction with one of three registers • Add mov instructions before instruction to load registers properly • Add mov instructions after instruction to put data back onto stack (if necessary) push t1 mov eax, [fp - t1off]; push eax mov [fp+4], t3 ...
... • Given instruction, replace every temporary in instruction with one of three registers • Add mov instructions before instruction to load registers properly • Add mov instructions after instruction to put data back onto stack (if necessary) push t1 mov eax, [fp - t1off]; push eax mov [fp+4], t3 ...
Programming Languages and Paradigms
... push and pop are defined and implemented as functions the solution consists of code that invoke these functions Copyright 2008, by the authors of these slides, and Ateneo de Manila University. All rights reserved. ...
... push and pop are defined and implemented as functions the solution consists of code that invoke these functions Copyright 2008, by the authors of these slides, and Ateneo de Manila University. All rights reserved. ...
Programming Languages and Paradigms
... push and pop are defined and implemented as functions the solution consists of code that invoke these functions Copyright 2005, by the authors of these slides, and Ateneo de Manila University. All rights reserved. ...
... push and pop are defined and implemented as functions the solution consists of code that invoke these functions Copyright 2005, by the authors of these slides, and Ateneo de Manila University. All rights reserved. ...
Applied Programming and Computer Science, DD2325
... The examination in this course consists of two parts: 1 written exam in January (TEN1; 3 cr) Grade A,B,C,D,E,FX,F. 2 computer assignments (LAB1; 4.5 cr). Mandatory. Grade P/F. Computer assignments include: ...
... The examination in this course consists of two parts: 1 written exam in January (TEN1; 3 cr) Grade A,B,C,D,E,FX,F. 2 computer assignments (LAB1; 4.5 cr). Mandatory. Grade P/F. Computer assignments include: ...
ppt
... Stack is generic to allow any type of value to be stored
Stack wordStack = new Stack();
Stack numStack = new Stack();
...
... Stack
Stacks - Courses
... • The names of the methods supported by an ADT • How those methods are to be declared and used – e.g., what order the parameters are listed in ...
... • The names of the methods supported by an ADT • How those methods are to be declared and used – e.g., what order the parameters are listed in ...
EE4390 Microprocessors
... – Declare as last location in largest RAM space plus 1 – For the “A4”, this is $8000 (user RAM: $4000 - $7FFF) • First-in-last-out data structure • Temporary storage during program execution – PUSH: place register contents on stack – PULL: place stack location contents in register EX] PSHA, PSHX, PU ...
... – Declare as last location in largest RAM space plus 1 – For the “A4”, this is $8000 (user RAM: $4000 - $7FFF) • First-in-last-out data structure • Temporary storage during program execution – PUSH: place register contents on stack – PULL: place stack location contents in register EX] PSHA, PSHX, PU ...
Chapter 8 Subroutines and Control Abstraction June 25, 2015
... The maintenance of stacks (or, indeed, anything else, particularly registers) prior to and at the end of a subroutine invocation is called the “calling sequence”. While in assembly language programming this is often ad hoc, in higher languages, it is generally quite rigid. In most languages today, a ...
... The maintenance of stacks (or, indeed, anything else, particularly registers) prior to and at the end of a subroutine invocation is called the “calling sequence”. While in assembly language programming this is often ad hoc, in higher languages, it is generally quite rigid. In most languages today, a ...