CHAPTER 9- CONSERVATION of MOMENTUM DEFINITION of
... In physics we define force as the time rate of change of momentum. Momentum as force is a vector quantity. F = dP /dt where P = M V COLLISONS In a collision between objects the internal forces are equal and opposite thus balance. The net work performed is zero! Since F = M dV/dt = d/dt (MV) = 0 we s ...
... In physics we define force as the time rate of change of momentum. Momentum as force is a vector quantity. F = dP /dt where P = M V COLLISONS In a collision between objects the internal forces are equal and opposite thus balance. The net work performed is zero! Since F = M dV/dt = d/dt (MV) = 0 we s ...
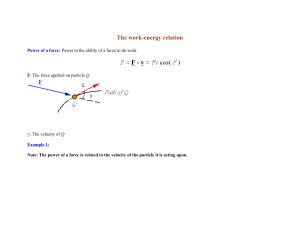
The work-energy relation
... Note: The work done on a particle by the resultant force applied on it over a given interval of time will be equal to the change in kinetic energy of the particle. In other words, the kinetic energy of a particle is changed by an amount equal to the work which is done on the particle by the resultan ...
... Note: The work done on a particle by the resultant force applied on it over a given interval of time will be equal to the change in kinetic energy of the particle. In other words, the kinetic energy of a particle is changed by an amount equal to the work which is done on the particle by the resultan ...
3.6 The Feynman-rules for QED For any given action (Lagrangian
... and denotes the center-of-mass energy squared. In the limit of massless particles and energies are equal to . The total cross section all momenta is obtained by integrating over the solid angle ...
... and denotes the center-of-mass energy squared. In the limit of massless particles and energies are equal to . The total cross section all momenta is obtained by integrating over the solid angle ...
photoelectric effect Work function
... liberating the highest occupied energy level.) Clearly for frequencies less than a critical frequency no electrons are liberated, however strong the intensity of the incident light. The quantum explanation depends on the assumption that each photon has an energy hν and this is absorbed by an individ ...
... liberating the highest occupied energy level.) Clearly for frequencies less than a critical frequency no electrons are liberated, however strong the intensity of the incident light. The quantum explanation depends on the assumption that each photon has an energy hν and this is absorbed by an individ ...
section on Compton effect
... fractional change (l2 l1)>l1 is appreciable. For this reason Compton effect is generally only observed for x rays and gamma radiation. Compton verified his result experimentally using the characteristic x-ray line of wavelength 0.0711 nm from molybdenum for the incident monochromatic photons and s ...
... fractional change (l2 l1)>l1 is appreciable. For this reason Compton effect is generally only observed for x rays and gamma radiation. Compton verified his result experimentally using the characteristic x-ray line of wavelength 0.0711 nm from molybdenum for the incident monochromatic photons and s ...
Chapter 17 - Probing Deep into Matter
... (reference to baryon and conservation of numbers have gone, as have hadrons) From the spec: Learning outcomes Candidates should demonstrate evidence of: (a) knowledge and understanding of phenomena, concepts and relationships by describing and explaining: ...
... (reference to baryon and conservation of numbers have gone, as have hadrons) From the spec: Learning outcomes Candidates should demonstrate evidence of: (a) knowledge and understanding of phenomena, concepts and relationships by describing and explaining: ...
Newton`s Cradle - Mercer Physics
... Let us now further our development by examining the special case where m 1 equals m 2 . First we must re-write equations (1) and (2) so as to solve for v 1 f and v 2 f in terms of the mass and the initial velocity: ...
... Let us now further our development by examining the special case where m 1 equals m 2 . First we must re-write equations (1) and (2) so as to solve for v 1 f and v 2 f in terms of the mass and the initial velocity: ...
A Quantum-Corrected Monte Carlo Study on Quasi
... The MC method is a powerful tool in investigating carrier transport with various scattering processes in ultrasmall SiMOSFETs. Lately, the quantum mechanical effects can be incorporated in the MC method by considering a quantum correction of potential in the equations of motion [12], [13], ...
... The MC method is a powerful tool in investigating carrier transport with various scattering processes in ultrasmall SiMOSFETs. Lately, the quantum mechanical effects can be incorporated in the MC method by considering a quantum correction of potential in the equations of motion [12], [13], ...
The Step Function – Getting Started
... In the previous in-gagement, you studied the eigenfunctions and wave functions of a free particle. Now we are interested in looking at how those functions change when the particle undergoes an interaction. The general idea of a particle coming to an area where the potential is changing, interacting ...
... In the previous in-gagement, you studied the eigenfunctions and wave functions of a free particle. Now we are interested in looking at how those functions change when the particle undergoes an interaction. The general idea of a particle coming to an area where the potential is changing, interacting ...
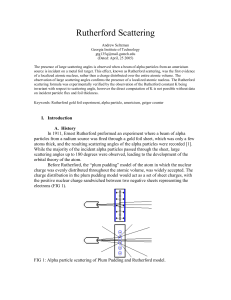
rutherford - RTF Technologies
... An americium source is positioned such that the emitted beam of alpha particles is incident perpendicularly on a thin metal foil, either gold or aluminum. The metal foil is partially blocked with a plastic slit, which limits the initial divergence of the alpha particle beam by collimating the partic ...
... An americium source is positioned such that the emitted beam of alpha particles is incident perpendicularly on a thin metal foil, either gold or aluminum. The metal foil is partially blocked with a plastic slit, which limits the initial divergence of the alpha particle beam by collimating the partic ...
kinematics, units, etc
... and the units for Γ are energy units, GeV. The Uncertainty Principle tells us that ∆E∆t & ~. As a consequence, if we know to some accuracy how long a particle lives, there is a limit to how well we know its energy. It follows that if we reconstruct the energy of a decaying particle from its products ...
... and the units for Γ are energy units, GeV. The Uncertainty Principle tells us that ∆E∆t & ~. As a consequence, if we know to some accuracy how long a particle lives, there is a limit to how well we know its energy. It follows that if we reconstruct the energy of a decaying particle from its products ...