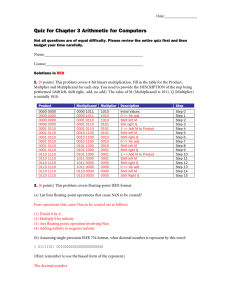
Quiz for Chapter 3 with Solutions
... (4) Unbiased to the nearest even: +0.100101100binary The result is +0.100110 (5) Unbiased to the nearest even: -0.100100110binary The result is -0.100100 (d) What is the result of the square root of a negative number? In the IEEE 754 standard (defined since 1985), the square root of negative number ...
... (4) Unbiased to the nearest even: +0.100101100binary The result is +0.100110 (5) Unbiased to the nearest even: -0.100100110binary The result is -0.100100 (d) What is the result of the square root of a negative number? In the IEEE 754 standard (defined since 1985), the square root of negative number ...
Optimality of Walrand-Varaiya Type Policies and Markov Sources
... Π = {αt }t≥0 such that αt : X → P(A) and at has distribution αt (xt ). The set of all Markov policies is denoted ΠM . Definition 1.15 (Stationary Policy [9]). A stationary policy is a Markov policy Π = {αt }t≥0 such that αt = α ∀t ≥ 0, where α : X → P(A). The set of all stationary policies is denote ...
... Π = {αt }t≥0 such that αt : X → P(A) and at has distribution αt (xt ). The set of all Markov policies is denoted ΠM . Definition 1.15 (Stationary Policy [9]). A stationary policy is a Markov policy Π = {αt }t≥0 such that αt = α ∀t ≥ 0, where α : X → P(A). The set of all stationary policies is denote ...
Introduction To Modular Arithmetic
... table you made problem 10(c), we see that c ⌘ 6 (mod 7). Thus, we write 3 ÷ 4 ⌘ 6 (mod 7) This is true because 6 ⇥ 4 ⌘ 3 (mod 7). Please solve the following division problems in modular arithmetic (remember to use the tables you made). (a) ...
... table you made problem 10(c), we see that c ⌘ 6 (mod 7). Thus, we write 3 ÷ 4 ⌘ 6 (mod 7) This is true because 6 ⇥ 4 ⌘ 3 (mod 7). Please solve the following division problems in modular arithmetic (remember to use the tables you made). (a) ...
DevStat8e_15_03
... A.13 once the desired level of significance is specified. For fixed x1, , xn, the 100(1 – )% signed-rank interval will consist of all 0 for which H0: = 0 is not rejected at level . To identify this interval, it is convenient to express the test statistic S+ in another form. ...
... A.13 once the desired level of significance is specified. For fixed x1, , xn, the 100(1 – )% signed-rank interval will consist of all 0 for which H0: = 0 is not rejected at level . To identify this interval, it is convenient to express the test statistic S+ in another form. ...
doc
... The simplest way of using N bits to represent integers is to use the binary number system directly. Then it is possible to represent the integers from 0 to 2N-1. For example, with 12 bits we can represent the numbers from 0 to 4095. 000000000000 represents 0, 000000000001 represents 1, and 111111111 ...
... The simplest way of using N bits to represent integers is to use the binary number system directly. Then it is possible to represent the integers from 0 to 2N-1. For example, with 12 bits we can represent the numbers from 0 to 4095. 000000000000 represents 0, 000000000001 represents 1, and 111111111 ...
Notes
... the other special exponent is used to encode ±∞ and NaN (Not a Number). For a general real number x, we will write fl(x) = correctly rounded floating point representation of x. By default, “correctly rounded” means that we find the closest floating point number to x, breaking any ties by rounding to ...
... the other special exponent is used to encode ±∞ and NaN (Not a Number). For a general real number x, we will write fl(x) = correctly rounded floating point representation of x. By default, “correctly rounded” means that we find the closest floating point number to x, breaking any ties by rounding to ...
Arabic Mathematical Diverse Symbols
... those characters is not very important, many characters and their mirrored (e.g., < and >) are already both encoded and the presence of some names ambiguity, we propose them for addition to the Unicode Standard. That allow to obtained them directly. The other symbols are not frequently in use. Of c ...
... those characters is not very important, many characters and their mirrored (e.g., < and >) are already both encoded and the presence of some names ambiguity, we propose them for addition to the Unicode Standard. That allow to obtained them directly. The other symbols are not frequently in use. Of c ...
Chapter 2 Numeric Representation.
... 2.3 Two’s Complement Binary representation works well for positive numbers, but what about negative numbers? How can they be represented with digital signals? One approach is to dedicate one bit, called the sign bit, to indicate whether or not a number is negative. Despite the nuisance of having bot ...
... 2.3 Two’s Complement Binary representation works well for positive numbers, but what about negative numbers? How can they be represented with digital signals? One approach is to dedicate one bit, called the sign bit, to indicate whether or not a number is negative. Despite the nuisance of having bot ...
CIS101 Introduction to Computing
... Numeric data can carry out arithmetic All information in a computer is stored using just 0s and 1s ...
... Numeric data can carry out arithmetic All information in a computer is stored using just 0s and 1s ...
CS112 Lecture: Recursion Last revised 3/20/08 1. Von Koch curve images
... composed of constants, the variable X, and the arithmetic operators +, (unary and binary), *, and /. 1. Example: (3 * (- X)) a) Base case: a constant, by itself, is an arithmetic expression. Example: 3 is an arithmetic expression. b) Another base case: a variable, by itself, is an arithmetic express ...
... composed of constants, the variable X, and the arithmetic operators +, (unary and binary), *, and /. 1. Example: (3 * (- X)) a) Base case: a constant, by itself, is an arithmetic expression. Example: 3 is an arithmetic expression. b) Another base case: a variable, by itself, is an arithmetic express ...
CIS101 week 10
... Numeric data can carry out arithmetic All information in a computer is stored using just 0s and 1s ...
... Numeric data can carry out arithmetic All information in a computer is stored using just 0s and 1s ...
Cell Probe Lower Bounds for Succinct Data Structures
... Chen and Chao [ISAAC 2004, Disc. App. Math. 2007] ...
... Chen and Chao [ISAAC 2004, Disc. App. Math. 2007] ...
Grouping Symbols - Algebra 1 -
... What are grouping symbols? A grouping symbol is used to enclose an expression in order to indicate that that part of the problem should be done first. ...
... What are grouping symbols? A grouping symbol is used to enclose an expression in order to indicate that that part of the problem should be done first. ...
A Novel Asynchronous Communication Paradigm: Detection, Isolation, and Coding
... by the codeword above. Thus, if A = eN (D(Q(·|x )||Q(·|%))+ε) , ε > 0, we expect that the noise will generate many blocks of N symbols that look as if they were generated by the codeword. In this case it is impossible to locate the codeword reliably, i.e., determine ν. Intuitively, it is plausible t ...
... by the codeword above. Thus, if A = eN (D(Q(·|x )||Q(·|%))+ε) , ε > 0, we expect that the noise will generate many blocks of N symbols that look as if they were generated by the codeword. In this case it is impossible to locate the codeword reliably, i.e., determine ν. Intuitively, it is plausible t ...
Lab 3 - KFUPM Faculty List
... meaningful combination of mathematical operators and operands (variables and/or constants of mathematical types (int, float, double, etc.)). An arithmetic expression may contain parentheses that specify the order of evaluation. An operand of an arithmetic expression may be: a numeric constant a ...
... meaningful combination of mathematical operators and operands (variables and/or constants of mathematical types (int, float, double, etc.)). An arithmetic expression may contain parentheses that specify the order of evaluation. An operand of an arithmetic expression may be: a numeric constant a ...
Succinct Data Structure
... Davoodi et al. showed how to support select-inorder for binary tree We simply plug our compression into this framework Need to support two additional operations: is_chain_prefix/suffix Decompress fingerprints, use lookup tables: tree + inorder position ...
... Davoodi et al. showed how to support select-inorder for binary tree We simply plug our compression into this framework Need to support two additional operations: is_chain_prefix/suffix Decompress fingerprints, use lookup tables: tree + inorder position ...
Lab03 Arithmetic Expressions
... meaningful combination of mathematical operators and operands (variables and/or contants of mathematical types (int, float, double, etc.)). An arithmetic expression may contain parentheses that specify the order of evaluation. An operand of an arithmetic expression may be: a numeric constant a n ...
... meaningful combination of mathematical operators and operands (variables and/or contants of mathematical types (int, float, double, etc.)). An arithmetic expression may contain parentheses that specify the order of evaluation. An operand of an arithmetic expression may be: a numeric constant a n ...
Other Symbols - Abstractmath.org
... different names for the same mathematical object. However, in some programming languages it is an assignment operator, and the intent of an expression containing an equals sign may vary. See equation. The other signs may indicate various forms of approximately equal, or may denote an equivalence rel ...
... different names for the same mathematical object. However, in some programming languages it is an assignment operator, and the intent of an expression containing an equals sign may vary. See equation. The other signs may indicate various forms of approximately equal, or may denote an equivalence rel ...
View File - University of Engineering and Technology, Taxila
... • The QPSK signal constellation is shifted by 45 degrees each symbol interval T • Phase transitions from one symbol to the next are restricted to ± 45 degrees and ± 135 degrees ...
... • The QPSK signal constellation is shifted by 45 degrees each symbol interval T • Phase transitions from one symbol to the next are restricted to ± 45 degrees and ± 135 degrees ...
Digital Transmission - Computing Science
... ☺ Any good idea to load an analog signal over a digital signal? (How to send analog information using a digital signal?) ...
... ☺ Any good idea to load an analog signal over a digital signal? (How to send analog information using a digital signal?) ...
Mathematical language
... are three equivalent ways of writing ten divided by 5. We might also read this as ‘how many times will 5 go into 10 ?’. The = sign and its variants Another symbol used frequently is the equals sign =. The = sign does not mean anything on its own - we need a context. For example, in the sum 1 + 2 = 3 ...
... are three equivalent ways of writing ten divided by 5. We might also read this as ‘how many times will 5 go into 10 ?’. The = sign and its variants Another symbol used frequently is the equals sign =. The = sign does not mean anything on its own - we need a context. For example, in the sum 1 + 2 = 3 ...
Document
... The question is not applicable The respondent does not know The respondent refuses to answer No response is marked on the questionnaire (i.e., truly missing and there is no clue why) ...
... The question is not applicable The respondent does not know The respondent refuses to answer No response is marked on the questionnaire (i.e., truly missing and there is no clue why) ...
Arithmetic coding
Arithmetic coding is a form of entropy encoding used in lossless data compression. Normally, a string of characters such as the words ""hello there"" is represented using a fixed number of bits per character, as in the ASCII code. When a string is converted to arithmetic encoding, frequently used characters will be stored with fewer bits and not-so-frequently occurring characters will be stored with more bits, resulting in fewer bits used in total. Arithmetic coding differs from other forms of entropy encoding, such as Huffman coding, in that rather than separating the input into component symbols and replacing each with a code, arithmetic coding encodes the entire message into a single number, a fraction n where (0.0 ≤ n < 1.0).