Module 2 - chem534
... Heat of Dissolution (ΔHd): The amount of energy absorbed/released when a solute dissolves. Heat of Neutralization (ΔHn): The amount of energy absorbed/released when a solute dissolves. Heat of Combustion (ΔHcombustion): amount of energy released when a material burns. Heat of Fusion (melting) or Sol ...
... Heat of Dissolution (ΔHd): The amount of energy absorbed/released when a solute dissolves. Heat of Neutralization (ΔHn): The amount of energy absorbed/released when a solute dissolves. Heat of Combustion (ΔHcombustion): amount of energy released when a material burns. Heat of Fusion (melting) or Sol ...
Heat Effects - Association of Chemical Engineering Students
... Heat transfer is one of the most common operations in the chemical industry. Consider, for example, the manufacture of ethylene glycol (an antifreeze agent) by the oxidation of ethylene to ethylene oxide and its subsequent hydration to glycol. The catalytic oxidation reaction is most effective when ...
... Heat transfer is one of the most common operations in the chemical industry. Consider, for example, the manufacture of ethylene glycol (an antifreeze agent) by the oxidation of ethylene to ethylene oxide and its subsequent hydration to glycol. The catalytic oxidation reaction is most effective when ...
Chemistry Entrance Material for Grade 11 to 12
... Filtration: to separate heterogeneous mixture of solid in liquid 45. To obtain dry sand and salt from a mixture of sand and salt we need to follow which of the following steps and in what order? 1. Add excess water to the mixture and stir. 2. Heat the solution to crystallize. 3. Filter, and allow th ...
... Filtration: to separate heterogeneous mixture of solid in liquid 45. To obtain dry sand and salt from a mixture of sand and salt we need to follow which of the following steps and in what order? 1. Add excess water to the mixture and stir. 2. Heat the solution to crystallize. 3. Filter, and allow th ...
ION SELECTIVE ELECTRODES
... The buffer controls the overall ionic strength as well as the pH. This buffer is also known as Total Ionic Strength Adjusting Buffer (TISAB) solution. ...
... The buffer controls the overall ionic strength as well as the pH. This buffer is also known as Total Ionic Strength Adjusting Buffer (TISAB) solution. ...
Chemistry Entrance Material for Grade 11 to 12 Answer Key
... Know how many moles of ions one mole of AgNO3 provides in water 99. One mole of silver nitrate, AgNO3, in water provides how many moles of ions? [-A-] One mole of Ag+(aq) and one mole of N–. [-B-] One mole of Ag+(aq) and three moles of NO 3 (aq). [-C-] One mole of Ag+(aq) and four moles of negative ...
... Know how many moles of ions one mole of AgNO3 provides in water 99. One mole of silver nitrate, AgNO3, in water provides how many moles of ions? [-A-] One mole of Ag+(aq) and one mole of N–. [-B-] One mole of Ag+(aq) and three moles of NO 3 (aq). [-C-] One mole of Ag+(aq) and four moles of negative ...
Folie 1
... • Isotherms below Tc behave as described above. • If the compression takes place at Tc itself, a surface separating two phases does not appear, and the volumes at each end of the horizontal part of the isotherm have merged to a single point, the critical point of the gas. The corresponding parameter ...
... • Isotherms below Tc behave as described above. • If the compression takes place at Tc itself, a surface separating two phases does not appear, and the volumes at each end of the horizontal part of the isotherm have merged to a single point, the critical point of the gas. The corresponding parameter ...
b - PianetaChimica
... Please note the following: • It is recommended that you first record your answer on this question paper by circling ONE of the letters A, B, C, D or E. • Then transfer these answers on to the computer sheet which will be computer marked for assessment. ...
... Please note the following: • It is recommended that you first record your answer on this question paper by circling ONE of the letters A, B, C, D or E. • Then transfer these answers on to the computer sheet which will be computer marked for assessment. ...
Lab Manual
... law, if the constant specifying the quantity of gas is expressed in terms of the number of molecules of gas. This is done by using as the mass unit the gram-mole; i.e., the molecular weight expressed in grams. The equation of state of n gram-moles of a perfect gas can then be written as PV/T = nR, i ...
... law, if the constant specifying the quantity of gas is expressed in terms of the number of molecules of gas. This is done by using as the mass unit the gram-mole; i.e., the molecular weight expressed in grams. The equation of state of n gram-moles of a perfect gas can then be written as PV/T = nR, i ...
Focus 4A-F
... U, P, and V are the internal energy, pressure, and volume of the system. Enthalpy is a state function because U (from the first law), P, and V are also state functions. Constant pressure means the system is open, and the work is pushing against the atmosphere; that is the constant pressure is the co ...
... U, P, and V are the internal energy, pressure, and volume of the system. Enthalpy is a state function because U (from the first law), P, and V are also state functions. Constant pressure means the system is open, and the work is pushing against the atmosphere; that is the constant pressure is the co ...
Physical Vapor Deposition
... High Throughput Evaporation Techniques • Box coaters are used for evaporating large substrate materials, often up to several meters in size. • Large amounts of source material are required, but cannot be all heated at once because of realistic power limitations. • Two popular techniques: – Powder t ...
... High Throughput Evaporation Techniques • Box coaters are used for evaporating large substrate materials, often up to several meters in size. • Large amounts of source material are required, but cannot be all heated at once because of realistic power limitations. • Two popular techniques: – Powder t ...
0922085
... At its fourteenth session, the ADN Safety Committee, recalling that, under 8.2.2.7.2.3 of the Regulations annexed to ADN, the ADN Administrative Committee was required to prepare a catalogue of questions for the ADN examinations, decided that the item should be put on the agenda for future sessions, ...
... At its fourteenth session, the ADN Safety Committee, recalling that, under 8.2.2.7.2.3 of the Regulations annexed to ADN, the ADN Administrative Committee was required to prepare a catalogue of questions for the ADN examinations, decided that the item should be put on the agenda for future sessions, ...
H - sintak
... Since both graphite and oxygen are stable allotrophic forms, ∆H°ƒ (C, graphite) and ∆H°ƒ (O2, g) are zero. ∆H°rxn = (1mol) ∆H°ƒ (CO2, g) = -393.5 kJ ∆H°ƒ (CO2, g) = -393.5 kJ/mol ...
... Since both graphite and oxygen are stable allotrophic forms, ∆H°ƒ (C, graphite) and ∆H°ƒ (O2, g) are zero. ∆H°rxn = (1mol) ∆H°ƒ (CO2, g) = -393.5 kJ ∆H°ƒ (CO2, g) = -393.5 kJ/mol ...
AP Chemistry 2015-2016 Name: Chapter 5: Thermodynamics Date
... state the units of heat capacity, specific heat, and molar heat capacity as well as the significance of each. use calorimetry (q=mCT) to calculate heat changes during temperature changes. calculate the heat transferred when two objects, at different temperatures, come into contact. Energy = H ...
... state the units of heat capacity, specific heat, and molar heat capacity as well as the significance of each. use calorimetry (q=mCT) to calculate heat changes during temperature changes. calculate the heat transferred when two objects, at different temperatures, come into contact. Energy = H ...
Thermochemistry - Xavier High School
... The molar heat of fusion is the heat absorbed by one mole of a substance in melting from a solid to a liquid at a constant temperature. The heat lost when one mole of a liquid solidifies at a constant temperature is the molar heat of solidification. Because energy is conserved in all chemical and ...
... The molar heat of fusion is the heat absorbed by one mole of a substance in melting from a solid to a liquid at a constant temperature. The heat lost when one mole of a liquid solidifies at a constant temperature is the molar heat of solidification. Because energy is conserved in all chemical and ...
Sec 6.2 Enthalpy - Okemos Public Schools
... Enthalpy can be defined as the heat content of a given substance in a specific condition. The letter H is used to represent enthalpy. The symbol H stands for Hproducts – Hreactants . It represents the amount of heat released or absorbed in a chemical reaction that takes place at constant pressure. ...
... Enthalpy can be defined as the heat content of a given substance in a specific condition. The letter H is used to represent enthalpy. The symbol H stands for Hproducts – Hreactants . It represents the amount of heat released or absorbed in a chemical reaction that takes place at constant pressure. ...
The Physical Properties And Physical Changes of Substances
... contacts the cold inner surface of the CONDENSER. The gas cools and condenses back into a liquid form, dropping out the end of the condenser as a purified liquid called a DISTILLATE. e.g. a water/ethanol mixture can be separated by distillation Demo CuSO4(aq) with CH3OH ...
... contacts the cold inner surface of the CONDENSER. The gas cools and condenses back into a liquid form, dropping out the end of the condenser as a purified liquid called a DISTILLATE. e.g. a water/ethanol mixture can be separated by distillation Demo CuSO4(aq) with CH3OH ...
B. The Physical Properties of Matter
... contacts the cold inner surface of the CONDENSER. The gas cools and condenses back into a liquid form, dropping out the end of the condenser as a purified liquid called a DISTILLATE. e.g. a water/ethanol mixture can be separated by distillation Demo CuSO4(aq) with CH3OH ...
... contacts the cold inner surface of the CONDENSER. The gas cools and condenses back into a liquid form, dropping out the end of the condenser as a purified liquid called a DISTILLATE. e.g. a water/ethanol mixture can be separated by distillation Demo CuSO4(aq) with CH3OH ...
First Law of Thermodynamics
... in Kelvin. However, since the Celsius and Kelvin scales differ only by an additive constant, temperature changes are the same in the two systems of units. Note that the heat capacity of the potassium nitrate is not required in this problem. A foxy instructor might provide the number on an exam as a ...
... in Kelvin. However, since the Celsius and Kelvin scales differ only by an additive constant, temperature changes are the same in the two systems of units. Note that the heat capacity of the potassium nitrate is not required in this problem. A foxy instructor might provide the number on an exam as a ...
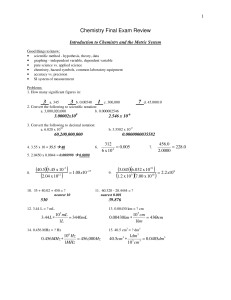
Chemistry Final Exam Review
... 157,700J The Gas Laws Good things to know: • Kinetic Theory of Gases • directly proportional, inversely proportional • 5 assumptions for Ideal Gases - conditions in which ideal behavior is not exhibited • Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP) Problems: 1. If you have 35.0 mL of a gas in a closed c ...
... 157,700J The Gas Laws Good things to know: • Kinetic Theory of Gases • directly proportional, inversely proportional • 5 assumptions for Ideal Gases - conditions in which ideal behavior is not exhibited • Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP) Problems: 1. If you have 35.0 mL of a gas in a closed c ...
Thermochemistry ppt
... The specific heat of an object is the amount of energy necessary to raise one gram of the substance 1oC (J/goC). At 4.184 J/goC, water has a very high specific heat. Most metals have a relatively low specific heat. The vast amount of water that covers Earth (about 3/4ths it surface) results in slow ...
... The specific heat of an object is the amount of energy necessary to raise one gram of the substance 1oC (J/goC). At 4.184 J/goC, water has a very high specific heat. Most metals have a relatively low specific heat. The vast amount of water that covers Earth (about 3/4ths it surface) results in slow ...
Spring Exam 2 - Chemistry
... the amount of work done on a system is independent of pathway. the total energy in or out of a system is equal to the sum of the heat absorbed and the work done on the system. the heat flow in or out of a system is independent of pathway. the total work done on a system must equal the heat absorbed ...
... the amount of work done on a system is independent of pathway. the total energy in or out of a system is equal to the sum of the heat absorbed and the work done on the system. the heat flow in or out of a system is independent of pathway. the total work done on a system must equal the heat absorbed ...
33 C? (1)
... ___ 109. When the vapor pressure of a liquid in an open container equals the atmospheric pressure then the liquid will (1) freeze; (2) crystallize; (3) melt; (4) boil. ___ 110. In a closed system, as the temperature of a liquid increases, the kinetic energy of its molecules (1) decreases; (2) increa ...
... ___ 109. When the vapor pressure of a liquid in an open container equals the atmospheric pressure then the liquid will (1) freeze; (2) crystallize; (3) melt; (4) boil. ___ 110. In a closed system, as the temperature of a liquid increases, the kinetic energy of its molecules (1) decreases; (2) increa ...
Unit 5 Student Packet
... 2. A 0.150 g sample of octane (liquid) was burned in a bomb calorimeter causing the temperature to change from 25.246C to 26.386C. If the heat capacity of the calorimeter was 7.15 kJ/C, calculate H comb for octane. 3. Calcium oxide (lime) reacts with water to give calcium hydroxide. A 5.40 g sam ...
... 2. A 0.150 g sample of octane (liquid) was burned in a bomb calorimeter causing the temperature to change from 25.246C to 26.386C. If the heat capacity of the calorimeter was 7.15 kJ/C, calculate H comb for octane. 3. Calcium oxide (lime) reacts with water to give calcium hydroxide. A 5.40 g sam ...
Chem 221 Quiz
... Methyl ether has polar bonds (2 C-O), but does not have a partial plus on hydrogen, only carbon. As a result, its strongest intermolecular force is dipole-dipole attractions. It has a lot of hydrogens, but cannot hydrogen bond because there aren’t any partial pluses on those H’s. Dipole dipole inter ...
... Methyl ether has polar bonds (2 C-O), but does not have a partial plus on hydrogen, only carbon. As a result, its strongest intermolecular force is dipole-dipole attractions. It has a lot of hydrogens, but cannot hydrogen bond because there aren’t any partial pluses on those H’s. Dipole dipole inter ...
HEAT CAPACITY OF MINERALS: A HANDS
... from one form to another but it cannot be created or destroyed; energy is always conserved. Heat is thermal energy that passes from a substance at high temperature to a substance at a lower temperature. The enthalpy, or total thermal energy content, of a system (or phase) is largely a function of te ...
... from one form to another but it cannot be created or destroyed; energy is always conserved. Heat is thermal energy that passes from a substance at high temperature to a substance at a lower temperature. The enthalpy, or total thermal energy content, of a system (or phase) is largely a function of te ...
Membrane distillation

Membrane distillation is a thermally driven separational programm in which separation is enabled due to phase change. A hydrophobic membrane displays a barrier for the liquid phase, allowing the vapour phase (e.g. water vapour) pass through the membrane's pores. The driving force of the process is given by a partial vapour pressure difference commonly triggered by a temperature difference.