Parallel Programming in C with the Message Passing Interface
... Block decomposition allows same marking as sequential algorithm: j, j + k, j + 2k, j + 3k, … ...
... Block decomposition allows same marking as sequential algorithm: j, j + k, j + 2k, j + 3k, … ...
Chapter 1.3 - Hey Ms Dee!
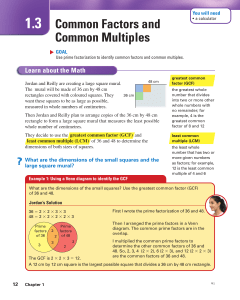
... decide on the dimensions of the small squares and the large square mural? 2. Why do you think Jordan multiplied the factors in the overlap of the Venn diagram to determine other common factors of 36 and 48? 3. Why do you think Reilly multiplied the numbers in the three sections of the Venn diagram t ...
... decide on the dimensions of the small squares and the large square mural? 2. Why do you think Jordan multiplied the factors in the overlap of the Venn diagram to determine other common factors of 36 and 48? 3. Why do you think Reilly multiplied the numbers in the three sections of the Venn diagram t ...
Wilson Theorems for Double-, Hyper-, Sub-and Super
... Wilson’s theorem states that (p−1)! ≡ −1 if p is prime, and (p−1)! ≡ 0 otherwise, except for the one special case, p = 4. The result is attributed to John Wilson, a student of Waring, but it has apparently been known for over a thousand years; see [21], [8, Ch. II], [19, Ch. 11], [10, Chap. 3] and [ ...
... Wilson’s theorem states that (p−1)! ≡ −1 if p is prime, and (p−1)! ≡ 0 otherwise, except for the one special case, p = 4. The result is attributed to John Wilson, a student of Waring, but it has apparently been known for over a thousand years; see [21], [8, Ch. II], [19, Ch. 11], [10, Chap. 3] and [ ...
Pretty Primes Class Notes
... That’s because products are the key to the very structure of natural numbers. Example: Find all possible values of a square number with the property that, if you add 15 to it, the result is still a square number. 7. The Return of the Unique Prime Factorisation, or Panicky Primes We return to the rul ...
... That’s because products are the key to the very structure of natural numbers. Example: Find all possible values of a square number with the property that, if you add 15 to it, the result is still a square number. 7. The Return of the Unique Prime Factorisation, or Panicky Primes We return to the rul ...