Petrography of the Biotite-Hornblende Bearing Quartzo
... Quartz grains are granoblastic, few with undulatory extinction It shows lobed and concavo convex contact and contains inclusions of biotite and sphene It occurs as inclusion within garnet Biotite is in elongated flakes it is pleochroic from greenish brown (X), to greenish black (almost dark-Y = Z), ...
... Quartz grains are granoblastic, few with undulatory extinction It shows lobed and concavo convex contact and contains inclusions of biotite and sphene It occurs as inclusion within garnet Biotite is in elongated flakes it is pleochroic from greenish brown (X), to greenish black (almost dark-Y = Z), ...
EarthComm_c3s1
... Figure 9 Garnets often grow in dodecahedral is sometimes tinted red by shapes. small amounts of chromium. These crystals are known as rubies. A sapphire is the same mineral tinted blue by small amounts of titanium. Quartz is usually transparent. However, it can be many other colors, depending on wha ...
... Figure 9 Garnets often grow in dodecahedral is sometimes tinted red by shapes. small amounts of chromium. These crystals are known as rubies. A sapphire is the same mineral tinted blue by small amounts of titanium. Quartz is usually transparent. However, it can be many other colors, depending on wha ...
Identification Tables for Common Minerals in Thin Section
... (ii) IMS: this gives a simple assessment of whether the mineral is common in igneous (I), metamorphic (M) or sedimentary (S) rocks. These are not infallible guides - in particular many igneous and metamorphic minerals can occur occasionally in sediments. Bear this in mind, even if minerals are not m ...
... (ii) IMS: this gives a simple assessment of whether the mineral is common in igneous (I), metamorphic (M) or sedimentary (S) rocks. These are not infallible guides - in particular many igneous and metamorphic minerals can occur occasionally in sediments. Bear this in mind, even if minerals are not m ...
Metamorphic Textures
... between the mineral and its overgrowth. Both the mineral and the overgrowth must belong to the same structural group, and may possibly be the same mineral. This type of overgrowth is controlled fully by the the matrix mineral. 18- Topotactic replacement: One mineral overgrows another of a similar st ...
... between the mineral and its overgrowth. Both the mineral and the overgrowth must belong to the same structural group, and may possibly be the same mineral. This type of overgrowth is controlled fully by the the matrix mineral. 18- Topotactic replacement: One mineral overgrows another of a similar st ...
Minerals - Mrs. DiLorenzo Earth Science
... How are Minerals Related to Rocks? • A rock is any naturally formed solid that is part of Earth or any other celestial object. – Organic or glassy rocks are NOT minerals. ...
... How are Minerals Related to Rocks? • A rock is any naturally formed solid that is part of Earth or any other celestial object. – Organic or glassy rocks are NOT minerals. ...
Minerals - Mrs. Plante Science
... How are Minerals Related to Rocks? • A rock is any naturally formed solid that is part of Earth or any other celestial object. – Organic or glassy rocks are NOT minerals. ...
... How are Minerals Related to Rocks? • A rock is any naturally formed solid that is part of Earth or any other celestial object. – Organic or glassy rocks are NOT minerals. ...
UNIT 7: Metamorphic Rocks
... metamorphism. • The three agents of metamorphism are heat, pressure (stress), and chemically active fluids. The mineral makeup of the parent rock determines, to a large extent, the degree to which each metamorphic agent will cause change. Heat is the most important agent because it provides the ener ...
... metamorphism. • The three agents of metamorphism are heat, pressure (stress), and chemically active fluids. The mineral makeup of the parent rock determines, to a large extent, the degree to which each metamorphic agent will cause change. Heat is the most important agent because it provides the ener ...
Matter and Minerals Earth 9th edition Chapter 3
... –Hard and resistant to weathering –Conchoidal fracture –Often forms hexagonal crystals ...
... –Hard and resistant to weathering –Conchoidal fracture –Often forms hexagonal crystals ...
17. THE MOBILITY OF IRON, CALCIUM, MAGNESIUM, AND
... more sodic (An40), and quartz, K-feldspar, microcline, garnet, and sillimanite appear and increase in abundance. Locally, in zones of strongest deformation but which are most open for fluid migration, concentrations of magnetite (10 to 15 m wide) occur in magnesium-rich biotite skarns. The adjacent ...
... more sodic (An40), and quartz, K-feldspar, microcline, garnet, and sillimanite appear and increase in abundance. Locally, in zones of strongest deformation but which are most open for fluid migration, concentrations of magnetite (10 to 15 m wide) occur in magnesium-rich biotite skarns. The adjacent ...
the shininess of minerals
... entirely different object is brought into existence. The same goes for crystals. To get other varieties of minerals certain elements are needed to make their transformation happen, once all the parts are present a process starts and in the end, another type of crystal is created from the original m ...
... entirely different object is brought into existence. The same goes for crystals. To get other varieties of minerals certain elements are needed to make their transformation happen, once all the parts are present a process starts and in the end, another type of crystal is created from the original m ...
EBS 425 -industrial minerals
... groups, bulk rocks, and ore minerals. Bulk rocks are those that are used as aggregate, or for the production of lime, ceramics, Portland cement, or as a product used in coal-fired electricity-generating plants for the removal of sulphur. These bulk rocks or sediments include limestone, dolostone, cl ...
... groups, bulk rocks, and ore minerals. Bulk rocks are those that are used as aggregate, or for the production of lime, ceramics, Portland cement, or as a product used in coal-fired electricity-generating plants for the removal of sulphur. These bulk rocks or sediments include limestone, dolostone, cl ...
unit-ii mineralogy
... potassium and calcium with the following general formula : WZ4 O8 where W=Na ,K, Ca and Ba and Z= Si and Al . ...
... potassium and calcium with the following general formula : WZ4 O8 where W=Na ,K, Ca and Ba and Z= Si and Al . ...
minerals of igneous rocks
... grain of plagioclase. The chalky appearance is a result of weathering of plagioclase to clay and this can often be used to aid in identification. Most plagioclase appears frosty white to gray-white in igneous rocks, but in gabbro it can be dark gray to blue-gray. If you examine plagioclase with a ha ...
... grain of plagioclase. The chalky appearance is a result of weathering of plagioclase to clay and this can often be used to aid in identification. Most plagioclase appears frosty white to gray-white in igneous rocks, but in gabbro it can be dark gray to blue-gray. If you examine plagioclase with a ha ...
Minerals
... Silicates The silica tetrahedron consists of four oxygen atoms packed closely around a single silicon atom. Named for its shape (like a 3D pyramid). ...
... Silicates The silica tetrahedron consists of four oxygen atoms packed closely around a single silicon atom. Named for its shape (like a 3D pyramid). ...
Inside the Restless Earth
... Differentiate between minerals and rocks. Describe the distinguishing properties that can be used to classify minerals. (texture, smell, luster, hardness, crystal shape, streak, reaction to magnets, and acids. Describe the methods used to identify the distinguishing properties of minerals. ...
... Differentiate between minerals and rocks. Describe the distinguishing properties that can be used to classify minerals. (texture, smell, luster, hardness, crystal shape, streak, reaction to magnets, and acids. Describe the methods used to identify the distinguishing properties of minerals. ...
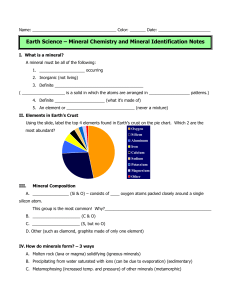
Name
... This group is the most common! Why?_______________________________________________ B. _____________________ (C & O) C. _____________________ (S, but no O) D. Other (such as diamond, graphite made of only one element) IV. How do minerals form? – 3 ways A. Molten rock (lava or magma) solidifying (igne ...
... This group is the most common! Why?_______________________________________________ B. _____________________ (C & O) C. _____________________ (S, but no O) D. Other (such as diamond, graphite made of only one element) IV. How do minerals form? – 3 ways A. Molten rock (lava or magma) solidifying (igne ...
Minerals 101
... Cleavage is the ability of a mineral to break along preferred planes. Planes of weakness exist in some minerals because of their atomic structure. Atomic bonds may be weaker in some directions than in others, so the mineral will tend to break, or cleave, in that direction. Minerals may have clea ...
... Cleavage is the ability of a mineral to break along preferred planes. Planes of weakness exist in some minerals because of their atomic structure. Atomic bonds may be weaker in some directions than in others, so the mineral will tend to break, or cleave, in that direction. Minerals may have clea ...
Mineral Characteristics
... called “silicates”. These two minerals combine to form most of the minerals in the earth’s crust. • They are the most abundant single minerals in the earth’s crust (oxygen-46.6%; silicon-27.7%) • More than half of the minerals in the earth’s crust are feldspars which is a silicate • Some other examp ...
... called “silicates”. These two minerals combine to form most of the minerals in the earth’s crust. • They are the most abundant single minerals in the earth’s crust (oxygen-46.6%; silicon-27.7%) • More than half of the minerals in the earth’s crust are feldspars which is a silicate • Some other examp ...
Garnet

Garnets /ˈɡɑrnət/ are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives.All species of garnets possess similar physical properties and crystal forms, but differ in chemical composition. The different species are pyrope, almandine, spessartine, grossular (varieties of which are hessonite or cinnamon-stone and tsavorite), uvarovite and andradite. The garnets make up two solid solution series: pyrope-almandine-spessartine and uvarovite-grossular-andradite.