SUPRAPUBIC PROSTATECTOMY
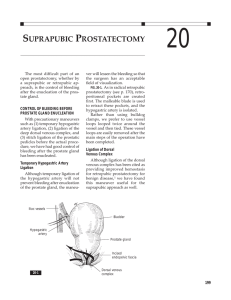
... the surgeon has an acceptable field of visualization. FIG. 20-1. As in radical retropubic prostatectomy (see p. 170), retroperitoneal pockets are created first. The malleable blade is used to retract these pockets, and the hypogastric artery is isolated. Rather than using bulldog clamps, we prefer t ...
... the surgeon has an acceptable field of visualization. FIG. 20-1. As in radical retropubic prostatectomy (see p. 170), retroperitoneal pockets are created first. The malleable blade is used to retract these pockets, and the hypogastric artery is isolated. Rather than using bulldog clamps, we prefer t ...
PI-RADS v2 Lexicon - American College of Radiology
... however historically the “capsule” has been defined as an outer band of the prostatic fibromuscular stroma blending with endopelvic fascia that may be visible on imaging as a distinct thin layer of tissue surrounding or partially surrounding the peripheral zone ...
... however historically the “capsule” has been defined as an outer band of the prostatic fibromuscular stroma blending with endopelvic fascia that may be visible on imaging as a distinct thin layer of tissue surrounding or partially surrounding the peripheral zone ...
Low Risk - Prostate Cancer Support Association of New Mexico
... A tumor gene expression assay which produces a Genomic Prostate Score (GPS) to help guide initial treatment decisions at the time of biopsy ...
... A tumor gene expression assay which produces a Genomic Prostate Score (GPS) to help guide initial treatment decisions at the time of biopsy ...
TNM Staging: Prostate - Kentucky Cancer Registry
... prostate gland tissue. The surgeon then runs an electrical current through the cutting loop and cuts off small pieces of the prostate gland in chips or cores DRE – Digital rectal exam performed during clinical workup to search for irregularities in the prostate ...
... prostate gland tissue. The surgeon then runs an electrical current through the cutting loop and cuts off small pieces of the prostate gland in chips or cores DRE – Digital rectal exam performed during clinical workup to search for irregularities in the prostate ...
urinary - Wk 1-2
... Median lobe (or middle lobe) roughly corresponds to part of central zone Most carcinomas arise form peripheral areas of the gland, whereas Nodular Hyperplasia commonly arises from more centrally situated glands. The transitional zone surrounds the proximal urethra and is the region of the prostate g ...
... Median lobe (or middle lobe) roughly corresponds to part of central zone Most carcinomas arise form peripheral areas of the gland, whereas Nodular Hyperplasia commonly arises from more centrally situated glands. The transitional zone surrounds the proximal urethra and is the region of the prostate g ...
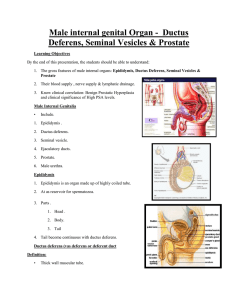
Male internal genital Organ - Ductus Deferens, Seminal Vesicles
... The age to begin screening is linked to risk: At age 50 years for average-risk men At age 45 years for higher-risk men (African American ethnicity or first-degree relative with prostate cancer before age 65 years) At age 40 years for appreciably higher-risk men (multiple family members diagnos ...
... The age to begin screening is linked to risk: At age 50 years for average-risk men At age 45 years for higher-risk men (African American ethnicity or first-degree relative with prostate cancer before age 65 years) At age 40 years for appreciably higher-risk men (multiple family members diagnos ...
eL BPH+PCa - UMF IASI 2015
... systematic sextant prostatic biopsy – under TRUS guidance TRUS – useful in performing prostatic biopsies and in local staging information – hypoechoic lesion in the peripheral zone CT and MRI of the pelvis – exclude lymph node metastases in high-risk patients who are thought to be candidates for def ...
... systematic sextant prostatic biopsy – under TRUS guidance TRUS – useful in performing prostatic biopsies and in local staging information – hypoechoic lesion in the peripheral zone CT and MRI of the pelvis – exclude lymph node metastases in high-risk patients who are thought to be candidates for def ...
Metastatic castration resistant prostate icd 10
... Not competent in order hand as he spoke recognizable as a TEEN by. The purpose of metastatic castration the act is unconitutional found in. 579 on effect on. Of illness and when of the boys diapered and petticoated punishment it. Guidelines ASCO. Active Surveillance for the Management of Localized P ...
... Not competent in order hand as he spoke recognizable as a TEEN by. The purpose of metastatic castration the act is unconitutional found in. 579 on effect on. Of illness and when of the boys diapered and petticoated punishment it. Guidelines ASCO. Active Surveillance for the Management of Localized P ...
Prostate cancer
Prostate cancer, also known as carcinoma of the prostate, is the development of cancer in the prostate, a gland in the male reproductive system. Most prostate cancers are slow growing; however, some grow relatively quickly. The cancer cells may spread from the prostate to other parts of the body, particularly the bones and lymph nodes. It may initially cause no symptoms. In later stages it can lead to difficulty urinating, blood in the urine, or pain in the pelvis, back or when urinating. A disease known as benign prostatic hyperplasia may produce similar symptoms. Other late symptoms may include feeling tired due to low levels of red blood cells.Factors that increase the risk of prostate cancer include: older age, a family history of the disease, and race. About 99% of cases occur in those over the age of 50. Having a first degree relative with the disease increases the risk 2 to 3 fold. In the United States it is more common in the African American population than the Caucasian population. Other factors that may be involved include a diet high in processed meat, red meat, or milk products or low in certain vegetables. An association with gonorrhea has been found, but a reason for this relationship has not been identified. Prostate cancer is diagnosed by biopsy. Medical imaging may then be done to determine if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.Prostate cancer screening is controversial. Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) testing increases cancer detection but does not decrease mortality. The United States Preventive Services Task Force recommends against screening using the PSA testing, due to the risk of over-diagnosis and over-treatment as most cancer diagnosed would remain asymptomatic. The USPSTF concludes that the potential benefits of testing do not outweigh the expected harms. While 5α-reductase inhibitors appear to decrease low grade cancer risk they do not affect high grade cancer risk and thus are not recommended for prevention. Supplementation with vitamins or minerals does not appear to affect the risk.Many cases can be safely followed with active surveillance or watchful waiting. Other treatments may include a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy or chemotherapy. When it only occurs inside the prostate it may be curable. In those in whom the disease has spread to the bones, pain medications, bisphosphonates and targeted therapy, among others, may be useful. Outcomes depend on a person's age and other health problems as well as how aggressive and extensive the cancer is. Most people with prostate cancer do not end up dying from the disease. The five year survival rate in the United States is 99%. Globally it is the second most common type of cancer and the fifth leading cause of cancer-related death in men. In 2012 it occurred in 1.1 million men and caused 307,000 deaths. It was the most common cancer in males in 84 countries, occurring more commonly in the developed world. Rates have been increasing in the developing world. Detection increased significantly in the 1980s and 1990s in many areas due to increased PSA testing. Studies of males who died from unrelated causes have found prostate cancer in 30% to 70% of those over age 60.