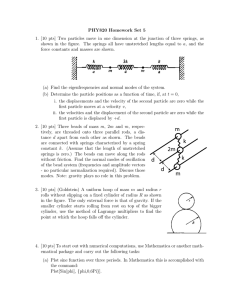
Main postulates
... swapped. Particles with wavefunctions symmetric under exchange are called bosons; The wave function of a system of identical half-integer spin particles changes sign when two particles are swapped. Particles with wavefunctions anti-symmetric under exchange are called fermions. (3) The Pauli exclusio ...
... swapped. Particles with wavefunctions symmetric under exchange are called bosons; The wave function of a system of identical half-integer spin particles changes sign when two particles are swapped. Particles with wavefunctions anti-symmetric under exchange are called fermions. (3) The Pauli exclusio ...
The Origin of Inertia
... Center in Palo Alto and the California State University in Long Beach. That study found the more general result that the relativistic equation of motion could be derived from consideration of the Poynting vector of the Zero-Point Field in accelerated reference frames. Again, within the context (and ...
... Center in Palo Alto and the California State University in Long Beach. That study found the more general result that the relativistic equation of motion could be derived from consideration of the Poynting vector of the Zero-Point Field in accelerated reference frames. Again, within the context (and ...
May 2006
... M06Q.3 - Two Interacting Particles Problem Consider two particles of mass m moving in one dimension. Particle 1 moves freely, while particle 2 experiences a harmonic potential V (x2 ) = 21 mω 2 x22 . The two particles interact via a delta function potential Vint (x12 ) = λδ(x12 ), with x12 ≡ x1 − x2 ...
... M06Q.3 - Two Interacting Particles Problem Consider two particles of mass m moving in one dimension. Particle 1 moves freely, while particle 2 experiences a harmonic potential V (x2 ) = 21 mω 2 x22 . The two particles interact via a delta function potential Vint (x12 ) = λδ(x12 ), with x12 ≡ x1 − x2 ...
powerpoint
... Separating to Basis States Basis State: a quantum state with a well-defined particle property (position, momentum, angle, angular momentum, polarization, energy, etc.) A set of basis states is measured for each dimension. A basis state for one measurement is not necessarily a basis for another. A b ...
... Separating to Basis States Basis State: a quantum state with a well-defined particle property (position, momentum, angle, angular momentum, polarization, energy, etc.) A set of basis states is measured for each dimension. A basis state for one measurement is not necessarily a basis for another. A b ...
Physics 564 – Particle Physics
... • Which particles are truly elementary? • Do we understand why particles have their observed properties? • What can we calculate? • Are the calculations reliable? • Can we compare them with experiment? • Is there an underlying theory that explains everything? ...
... • Which particles are truly elementary? • Do we understand why particles have their observed properties? • What can we calculate? • Are the calculations reliable? • Can we compare them with experiment? • Is there an underlying theory that explains everything? ...
SET 2 Option J — Particle physics J1. This question is about
... in the early universe/when the temperature was very high particles collided with antiparticles to create photons and the photons materialized into particleantiparticle pairs; As the temperature dropped, the second process became impossible and so the universe was left with (the small number of exces ...
... in the early universe/when the temperature was very high particles collided with antiparticles to create photons and the photons materialized into particleantiparticle pairs; As the temperature dropped, the second process became impossible and so the universe was left with (the small number of exces ...
The Step Function – Getting Started
... In this problem we have four (complex) free parameters (A and B in each region) and two boundary conditions. This means that after solving the boundary condition equations we will still be left with two free parameters (such as A and B in one region). As was true with the free particle case, one of ...
... In this problem we have four (complex) free parameters (A and B in each region) and two boundary conditions. This means that after solving the boundary condition equations we will still be left with two free parameters (such as A and B in one region). As was true with the free particle case, one of ...