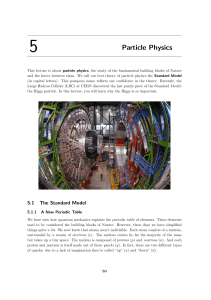
Webquest: Dividing the Indivisible Use the following web sites and
... electron, the nucleus, the proton, and the neutron. These discoveries happened over a 35year period and each discovery had a huge impact on our understanding of atoms. Suggested Web Resources: • A Look Inside the Atom • Rutherford and the Atomic Nucleus • Chadwick Discovers the Neutron As you comple ...
... electron, the nucleus, the proton, and the neutron. These discoveries happened over a 35year period and each discovery had a huge impact on our understanding of atoms. Suggested Web Resources: • A Look Inside the Atom • Rutherford and the Atomic Nucleus • Chadwick Discovers the Neutron As you comple ...
Lecture 4 — January 14, 2016 1 Outline 2 Weyl
... Last Time: Motivated by the boxcar function, whose Fourier transform is not summable, we introduced the space of square-integrable functions L2 (R). We proved the Parseval-Plancherel theorem, which shows the Fourier transform preserves the L2 -inner product and is therefore an isometry (modulo a fac ...
... Last Time: Motivated by the boxcar function, whose Fourier transform is not summable, we introduced the space of square-integrable functions L2 (R). We proved the Parseval-Plancherel theorem, which shows the Fourier transform preserves the L2 -inner product and is therefore an isometry (modulo a fac ...
Green function in solid
... both in computational time and in memory e.g. Nc=16, memory requirement for wave function vector:16GB; Hamiltonian matrix: 7x1010GB ! ...
... both in computational time and in memory e.g. Nc=16, memory requirement for wave function vector:16GB; Hamiltonian matrix: 7x1010GB ! ...
The Ideal Gas on the Canonical Ensemble
... molecules being in different states. We can now see the problem. When the particles are in different state, we have counted each state twice. The state with one molecule in state 1, the other in state 2, could be written as s = 1, t = 2 or as s = 2, t = 1. Now except for the fact that we’ve labelled ...
... molecules being in different states. We can now see the problem. When the particles are in different state, we have counted each state twice. The state with one molecule in state 1, the other in state 2, could be written as s = 1, t = 2 or as s = 2, t = 1. Now except for the fact that we’ve labelled ...
CR2
... where i is the imaginary unit, ħ is the Planck constant divided by 2π, the symbol ∂/∂t indicates a partial derivative with respect to time t, Ψ (the Greek letter Psi) is the wave function of the quantum system, and Ĥ is the Hamiltonian operator (which characterizes the total energy of any given wave ...
... where i is the imaginary unit, ħ is the Planck constant divided by 2π, the symbol ∂/∂t indicates a partial derivative with respect to time t, Ψ (the Greek letter Psi) is the wave function of the quantum system, and Ĥ is the Hamiltonian operator (which characterizes the total energy of any given wave ...
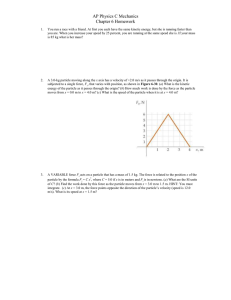
1. Consider an electron moving between two atoms making up a
... (b) Write down completeness and orthonormality relations for the ONB {| i}. Note that these states have both a continuous index and a discrete one, so that one has to do the correct kind of summation, and use the correct delta function for each index. (c) Express an arbitrary state vector |i ...
... (b) Write down completeness and orthonormality relations for the ONB {| i}. Note that these states have both a continuous index and a discrete one, so that one has to do the correct kind of summation, and use the correct delta function for each index. (c) Express an arbitrary state vector |i ...
Quantum mechanics is the theory that we use to describe the
... uncertainty at the most fundamental level when we try to measure any value, or observable, of a system. This is unlike classical and relativistic theories, where everything exists with precise and definite values, and the time evolution of a system can theoretically be determined as far into the fut ...
... uncertainty at the most fundamental level when we try to measure any value, or observable, of a system. This is unlike classical and relativistic theories, where everything exists with precise and definite values, and the time evolution of a system can theoretically be determined as far into the fut ...
Possible new effects in superconductive tunnelling
... to IN + 2) In ~ e theory of Gor'kov 4): ff Cf. N.N. Bogoltubov ~t el. ~').The phase of a n 3 oper~tor Is related to t ~ orientation of the plume e o r ~ n i r ~ the pseudospin ~rators ~.. Physical ob~ervable~ ~.aanot depe~A on the phase of s single S operatol~, but they can depend on the r~atlve pha ...
... to IN + 2) In ~ e theory of Gor'kov 4): ff Cf. N.N. Bogoltubov ~t el. ~').The phase of a n 3 oper~tor Is related to t ~ orientation of the plume e o r ~ n i r ~ the pseudospin ~rators ~.. Physical ob~ervable~ ~.aanot depe~A on the phase of s single S operatol~, but they can depend on the r~atlve pha ...