Chapter 3: Ionic and Covalent Compounds Chapter 3: Ionic and
... shared equally. D) A bond dipole is the separation of charge that results when atoms sharing electrons have different electronegativities. Ans: C Difficulty: Medium 43. How many covalent bonds are generally formed by atoms with five valence electrons? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 Ans: C Difficulty: Medi ...
... shared equally. D) A bond dipole is the separation of charge that results when atoms sharing electrons have different electronegativities. Ans: C Difficulty: Medium 43. How many covalent bonds are generally formed by atoms with five valence electrons? A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 4 E) 5 Ans: C Difficulty: Medi ...
Paper
... repulsive interactions between the atoms36 — or it collapsed owing to attractive interactions between the atoms37. Without these interactions, the BEC would be an ideal gas with properties similar to the photons in the optical laser. The interactions make the BEC a rich, many-body system that displa ...
... repulsive interactions between the atoms36 — or it collapsed owing to attractive interactions between the atoms37. Without these interactions, the BEC would be an ideal gas with properties similar to the photons in the optical laser. The interactions make the BEC a rich, many-body system that displa ...
Photoemission studies of quantum well states in thin films
... textbooks of quantum mechanics. Although this is effectively a one-dimensional problem, the electronic wave functions are extended within the ®lm along the x and y directions. The con®nement does not generally lead to enhanced electron correlation effects compared to the bulk case (except possibly w ...
... textbooks of quantum mechanics. Although this is effectively a one-dimensional problem, the electronic wave functions are extended within the ®lm along the x and y directions. The con®nement does not generally lead to enhanced electron correlation effects compared to the bulk case (except possibly w ...
Atom
... b. Explain why the atoms of inert elements do not react with one another or combine with atoms of other elements. c. Explain how cations and anions form. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... b. Explain why the atoms of inert elements do not react with one another or combine with atoms of other elements. c. Explain how cations and anions form. © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Unit 12: Electrochemistry
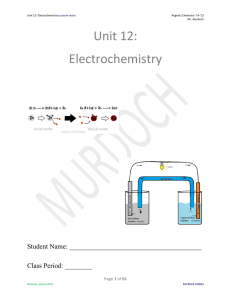
... Redox Reactions Objective: What steps do we take to balance Redox Reactions? Balancing Redox Reactions: Previous examples have shown how the spectator ions in a redox reaction may be ignored during redox reactions. We can therefore eliminate any spectator ions from the balancing of half-reactions. ...
... Redox Reactions Objective: What steps do we take to balance Redox Reactions? Balancing Redox Reactions: Previous examples have shown how the spectator ions in a redox reaction may be ignored during redox reactions. We can therefore eliminate any spectator ions from the balancing of half-reactions. ...
New Concepts in Inverse Quantum Chemistry - ETH E
... where the individual variables have a similar meaning as above, but referring to the electronic structure (in a fixed nuclear framework) only. The molecular structure, defined as an assembly of atomic nuclei fixed in space, is a direct consequence of this approximation. For a given assembly of atomi ...
... where the individual variables have a similar meaning as above, but referring to the electronic structure (in a fixed nuclear framework) only. The molecular structure, defined as an assembly of atomic nuclei fixed in space, is a direct consequence of this approximation. For a given assembly of atomi ...
Introduction to Inorganic Chemistry
... order to achieve its ends. This means that a good chemist is one who not only has a mastery of chemical theory, but also a good knowledge of chemical facts. With such a knowledge, he can direct a trial and error approach to practical problems in the most promising directions. Inorganic Chemistry Org ...
... order to achieve its ends. This means that a good chemist is one who not only has a mastery of chemical theory, but also a good knowledge of chemical facts. With such a knowledge, he can direct a trial and error approach to practical problems in the most promising directions. Inorganic Chemistry Org ...
Imaging electrostatically confined Dirac fermions in graphene
... distribution (Fig. 4b) closely resembles the experimental eigenstate distribution (Fig. 4a). Both have a characteristic parabolic envelope due to the confinement potential, as well as a complex set of interior nodal patterns. The characteristic energy spacing seen experimentally is in good agreement ...
... distribution (Fig. 4b) closely resembles the experimental eigenstate distribution (Fig. 4a). Both have a characteristic parabolic envelope due to the confinement potential, as well as a complex set of interior nodal patterns. The characteristic energy spacing seen experimentally is in good agreement ...
Chemistry Challenge Problems
... he chemical properties of an element depend primarily on its number of valence electrons in its atoms. The noble gas elements, for example, all have similar chemical properties because the outermost energy levels of their atoms are completely filled. The chemical properties of ions also depend on th ...
... he chemical properties of an element depend primarily on its number of valence electrons in its atoms. The noble gas elements, for example, all have similar chemical properties because the outermost energy levels of their atoms are completely filled. The chemical properties of ions also depend on th ...
Interband optical investigation of Bloch oscillations in semiconductor superlattices TOPICAL REVIEW
... It is interesting to note that it was recently possible to perform an experiment in an artificial ‘lattice’ (consisting of an optical standing wave) in which atoms were performing Bloch oscillations. This experiment comes very close to the Gedanken experiment just described [21]. More realistic appr ...
... It is interesting to note that it was recently possible to perform an experiment in an artificial ‘lattice’ (consisting of an optical standing wave) in which atoms were performing Bloch oscillations. This experiment comes very close to the Gedanken experiment just described [21]. More realistic appr ...
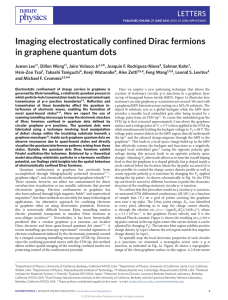
Chapter 20 Electrochemistry
... Cr2O72(aq) + 14 H+(aq) + 6 I(aq) 2 Cr3+(aq) + 3 I2(s) + 7 H2O(l) is spontaneous. A solution containing K2Cr2O7 and H2SO4 is poured into one beaker, and a solution of KI is poured into another. A salt bridge is used to join the beakers. A metallic conductor that will not react with either solutio ...
... Cr2O72(aq) + 14 H+(aq) + 6 I(aq) 2 Cr3+(aq) + 3 I2(s) + 7 H2O(l) is spontaneous. A solution containing K2Cr2O7 and H2SO4 is poured into one beaker, and a solution of KI is poured into another. A salt bridge is used to join the beakers. A metallic conductor that will not react with either solutio ...
Spectroscopic Selection Rules: The Role of Photon States
... Selection rules are vital in the interpretation of atomic and molecular spectra. The usual starting point for a derivation of selection rules is the transition moment which, in introductory spectroscopy courses, is normally taken on trust. However, many students find the transition moment to be a so ...
... Selection rules are vital in the interpretation of atomic and molecular spectra. The usual starting point for a derivation of selection rules is the transition moment which, in introductory spectroscopy courses, is normally taken on trust. However, many students find the transition moment to be a so ...
Minerals - UNLV Geoscience
... Atomic Numbers and Mass Isotopes and radioactive decay • Mass number is the sum of neutrons plus protons in an atom • An isotope is an atom that exhibits ...
... Atomic Numbers and Mass Isotopes and radioactive decay • Mass number is the sum of neutrons plus protons in an atom • An isotope is an atom that exhibits ...
Electron configuration
In atomic physics and quantum chemistry, the electron configuration is the distribution of electrons of an atom or molecule (or other physical structure) in atomic or molecular orbitals. For example, the electron configuration of the neon atom is 1s2 2s2 2p6.Electronic configurations describe electrons as each moving independently in an orbital, in an average field created by all other orbitals. Mathematically, configurations are described by Slater determinants or configuration state functions.According to the laws of quantum mechanics, for systems with only one electron, an energy is associated with each electron configuration and, upon certain conditions, electrons are able to move from one configuration to another by the emission or absorption of a quantum of energy, in the form of a photon.Knowledge of the electron configuration of different atoms is useful in understanding the structure of the periodic table of elements. The concept is also useful for describing the chemical bonds that hold atoms together. In bulk materials, this same idea helps explain the peculiar properties of lasers and semiconductors.