The de Broglie wavelength is inversely proportional to
... localized particles. This division was challenged when, in his 1905 paper on the photoelectric ...
... localized particles. This division was challenged when, in his 1905 paper on the photoelectric ...
Relativistic theory of one– and two electron systems: valley of
... by Sommerfeld (in the framework of the elliptical orbits model) and after in the year 1926 by use of the relativistic wave equation established by Dirac after the discovery of the spin electron (1925) by Uhlenberg and Goudsmith. However, it would be very interesting to make relativistic correction o ...
... by Sommerfeld (in the framework of the elliptical orbits model) and after in the year 1926 by use of the relativistic wave equation established by Dirac after the discovery of the spin electron (1925) by Uhlenberg and Goudsmith. However, it would be very interesting to make relativistic correction o ...
Berry phase correction to electron density of states in solids
... state. For simpler notation, we will drop the band index n and assume that the integral over k includes the sum ...
... state. For simpler notation, we will drop the band index n and assume that the integral over k includes the sum ...
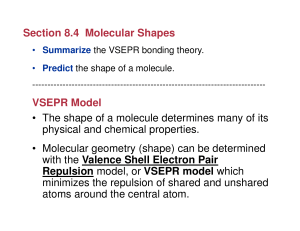
Section 8.4 Molecular Shapes VSEPR Model • The shape of a
... Shapes of Molecules (cont.) • Remember to focus on the central atom. Here is a review of the shapes: Linear- 1 bond, no central atom - 2 bonds, no unshared pairs of eBent- 2 bonds, 2 unshared pairs of ePyramidal- 3 bonds, 1 unshared pair of eTriangular planar or Trigonal3 bonds, no unshared pair of ...
... Shapes of Molecules (cont.) • Remember to focus on the central atom. Here is a review of the shapes: Linear- 1 bond, no central atom - 2 bonds, no unshared pairs of eBent- 2 bonds, 2 unshared pairs of ePyramidal- 3 bonds, 1 unshared pair of eTriangular planar or Trigonal3 bonds, no unshared pair of ...
Describe properties of particles and thermochemical - Mr
... Lewis structures and shapes (up to six electron pairs about the central atom for molecules and polyatomic ions, including those with multiple bonds) polarity of molecules attractive forces between atoms, ions, and molecules. These will include ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and intermolecular at ...
... Lewis structures and shapes (up to six electron pairs about the central atom for molecules and polyatomic ions, including those with multiple bonds) polarity of molecules attractive forces between atoms, ions, and molecules. These will include ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and intermolecular at ...
effective nuclear charge
... for transition metals electrons, may be removed from the sublevel closest to the valence shell Al atom = 1s22s22p63s23p1 Al+3 ion = 1s22s22p6 Fe atom = 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d6 Fe+2 ion = 1s22s22p63s23p63d6 Fe+3 ion = 1s22s22p63s23p63d5 Cu atom = 1s22s22p63s23p64s13d10 Cu+1 ion = 1s22s22p63s23p63d10 ...
... for transition metals electrons, may be removed from the sublevel closest to the valence shell Al atom = 1s22s22p63s23p1 Al+3 ion = 1s22s22p6 Fe atom = 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d6 Fe+2 ion = 1s22s22p63s23p63d6 Fe+3 ion = 1s22s22p63s23p63d5 Cu atom = 1s22s22p63s23p64s13d10 Cu+1 ion = 1s22s22p63s23p63d10 ...
The Hydrogen Atom Revisited
... inception in the beginning of the last century or based on recent experimental evidence. It is taught in textbooks that atomic hydrogen cannot go below the ground state. Atomic hydrogen having an experimental ground state of 13.6 eV can only exist in a vacuum or in isolation, and atomic hydrogen can ...
... inception in the beginning of the last century or based on recent experimental evidence. It is taught in textbooks that atomic hydrogen cannot go below the ground state. Atomic hydrogen having an experimental ground state of 13.6 eV can only exist in a vacuum or in isolation, and atomic hydrogen can ...
2 - FacultyWeb
... • Sharing of electrons may be equal or unequal • Atoms with six or seven valence shell electrons are electronegative, e.g., oxygen • Atoms with one or two valence shell electrons are electropositive, e.g., sodium Equal sharing of electrons produces electrically balanced nonpolar ...
... • Sharing of electrons may be equal or unequal • Atoms with six or seven valence shell electrons are electronegative, e.g., oxygen • Atoms with one or two valence shell electrons are electropositive, e.g., sodium Equal sharing of electrons produces electrically balanced nonpolar ...
with x
... breaks down and the relativistic treatment designed by Einstein must be used. Now, we will see that the description of light in terms of waves breaks down when looking at very small scales. In addition, we will see that objects that we usually refer to as particles (like electrons) exhibit wave-ph ...
... breaks down and the relativistic treatment designed by Einstein must be used. Now, we will see that the description of light in terms of waves breaks down when looking at very small scales. In addition, we will see that objects that we usually refer to as particles (like electrons) exhibit wave-ph ...
Nucleus-mediated spin-flip transitions in GaAs quantum dots
... The electron spin states in bulk semiconductor and heterostructures have attracted much attention in recent years. Experiments indicate very long spin decoherence times and small transition rates between states of different spin.1–3 These promising results have motivated proposals for information pr ...
... The electron spin states in bulk semiconductor and heterostructures have attracted much attention in recent years. Experiments indicate very long spin decoherence times and small transition rates between states of different spin.1–3 These promising results have motivated proposals for information pr ...
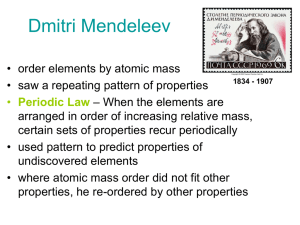
Dmitri Mendeleev
... The mass of an atom is measured relative to the mass of a chosen standard (carbon-12 atom), and is expressed in atomic mass units (amu). The average atomic mass of an element is the mass of that element’s natural occurring ...
... The mass of an atom is measured relative to the mass of a chosen standard (carbon-12 atom), and is expressed in atomic mass units (amu). The average atomic mass of an element is the mass of that element’s natural occurring ...
Final Exam Review
... 7. If 100 moles of Mg and 100 moles of O2 are allowed to react to form MgO, the maximum mass of MgO that can be formed is (Ch. 9) 2 Mg + O2 → 2 MgO 8. Which of the following statements about ionic and covalent bonding is false? (Ch. 12) a. Covalent bonds are always formed between atoms having high i ...
... 7. If 100 moles of Mg and 100 moles of O2 are allowed to react to form MgO, the maximum mass of MgO that can be formed is (Ch. 9) 2 Mg + O2 → 2 MgO 8. Which of the following statements about ionic and covalent bonding is false? (Ch. 12) a. Covalent bonds are always formed between atoms having high i ...
lecture CH8 A chem161pikul
... • 1 photon = 1 quantum of energy • Energy gained or lost in whole number mulKples of hν E = nhν • If n = NA, then one mole of photons gained or lost E = 6.02 × ...
... • 1 photon = 1 quantum of energy • Energy gained or lost in whole number mulKples of hν E = nhν • If n = NA, then one mole of photons gained or lost E = 6.02 × ...
pages 851-900 - Light and Matter
... numbers of photons: four photons in figure i/3, for example. A wrong interpretation: photons interfering with each other One possible interpretation of wave-particle duality that occurred to physicists early in the game was that perhaps the interference effects came from photons interacting with eac ...
... numbers of photons: four photons in figure i/3, for example. A wrong interpretation: photons interfering with each other One possible interpretation of wave-particle duality that occurred to physicists early in the game was that perhaps the interference effects came from photons interacting with eac ...
chem3322_metaphysics.. - The University of Texas at Dallas
... between measurement, but we can never know what those values are since the values can only be determined by measurement, which indeterministically disturbs the system. This implies that the system was in a definite state before measurement, and that the quantum mechanical formalism gives an incomple ...
... between measurement, but we can never know what those values are since the values can only be determined by measurement, which indeterministically disturbs the system. This implies that the system was in a definite state before measurement, and that the quantum mechanical formalism gives an incomple ...
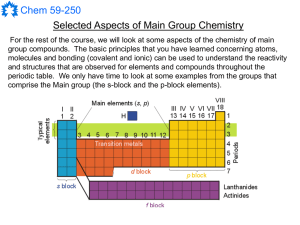
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as defined by the particular mathematical form of the orbital.Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a unique set of values of the three quantum numbers n, ℓ, and m, which respectively correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component (the magnetic quantum number). Any orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own spin quantum number. The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2 and 3 respectively. These names, together with the value of n, are used to describe the electron configurations of atoms. They are derived from the description by early spectroscopists of certain series of alkali metal spectroscopic lines as sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. Orbitals for ℓ > 3 continue alphabetically, omitting j (g, h, i, k, …).Atomic orbitals are the basic building blocks of the atomic orbital model (alternatively known as the electron cloud or wave mechanics model), a modern framework for visualizing the submicroscopic behavior of electrons in matter. In this model the electron cloud of a multi-electron atom may be seen as being built up (in approximation) in an electron configuration that is a product of simpler hydrogen-like atomic orbitals. The repeating periodicity of the blocks of 2, 6, 10, and 14 elements within sections of the periodic table arises naturally from the total number of electrons that occupy a complete set of s, p, d and f atomic orbitals, respectively.