msc_pre_chemistry_pap1_bl2
... In an octahedral ligand field, only the t2g orbitals remain degenerate and rotationally related. The eg orbitals get separated by 10Dq. Hence, orbital momentum due to the dx2-y2 orbital electron gets quenched, and the spin-only formula should apply. It can be seen that the orbital angular momentum f ...
... In an octahedral ligand field, only the t2g orbitals remain degenerate and rotationally related. The eg orbitals get separated by 10Dq. Hence, orbital momentum due to the dx2-y2 orbital electron gets quenched, and the spin-only formula should apply. It can be seen that the orbital angular momentum f ...
Quantum numbers and Angular Momentum Algebra Quantum
... two-body state, and obviously our final holy grail, a many-boyd state. For the single-particle states, due to the fact that we have the spin-orbit force, the quantum numbers for the projection of orbital momentum l, that is ml , and for spin s, that is ms , are no longer so-called good quantum numbe ...
... two-body state, and obviously our final holy grail, a many-boyd state. For the single-particle states, due to the fact that we have the spin-orbit force, the quantum numbers for the projection of orbital momentum l, that is ml , and for spin s, that is ms , are no longer so-called good quantum numbe ...
Electronic structure, plane waves and pseudopotentials
... In the special case that the electrons are evenly spread throughout space, we can actually compute Exc [ρ]. We can use this as an approximation to the true Exc in our calculations. ...
... In the special case that the electrons are evenly spread throughout space, we can actually compute Exc [ρ]. We can use this as an approximation to the true Exc in our calculations. ...
Qualification Exam: Quantum Mechanics
... 2. Show that the total angular momentum J is conserved. 3. The energy of the electron is 52 ~ω. A measurement of J is performed. What are the possible results? 4. List, in the basis of part first part, all the wavefunctions corresponding to each possible eigenvalue of J in the third part. ...
... 2. Show that the total angular momentum J is conserved. 3. The energy of the electron is 52 ~ω. A measurement of J is performed. What are the possible results? 4. List, in the basis of part first part, all the wavefunctions corresponding to each possible eigenvalue of J in the third part. ...
Critical analysis and extension of the Hirshfeld atoms in molecules
... shortcomings pertain to the deeper context of previous theoretical work on the Hirshfeld idea, but all are relevant to the way these charges are currently obtained computationally and used, for example, in reactivity studies. As will be shown, meaningful charges can be obtained from the present, new ...
... shortcomings pertain to the deeper context of previous theoretical work on the Hirshfeld idea, but all are relevant to the way these charges are currently obtained computationally and used, for example, in reactivity studies. As will be shown, meaningful charges can be obtained from the present, new ...
Organic Chemistry Curriculum Map - Belle Vernon Area School District
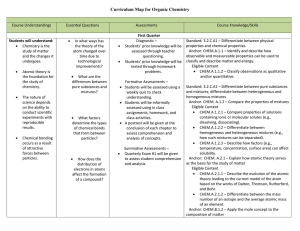
... Standard: 3.2.C.A4 – Predict how combinations of substances can result in physical and/or chemical changes. Anchor: CHEM.B.1.1 – Explain how the mole is a fundamental unit of chemistry. Eligible Content CHEM.B.1.1.1 – Apply the mole concept to representative particles (e.g., counting, determining ...
... Standard: 3.2.C.A4 – Predict how combinations of substances can result in physical and/or chemical changes. Anchor: CHEM.B.1.1 – Explain how the mole is a fundamental unit of chemistry. Eligible Content CHEM.B.1.1.1 – Apply the mole concept to representative particles (e.g., counting, determining ...
Interacting Cold Rydberg Atoms: a Toy Many-Body
... from the simple underlying physical laws that govern the interactions between constituents of matter, like atoms or molecules. Interactions between particles are for the most part well-understood, and the equations of quantum mechanics governing an ensemble of interacting particles are known. Howeve ...
... from the simple underlying physical laws that govern the interactions between constituents of matter, like atoms or molecules. Interactions between particles are for the most part well-understood, and the equations of quantum mechanics governing an ensemble of interacting particles are known. Howeve ...
Relativistic effects in atomic and molecular properties
... of quantum chemistry. Theory of relativity, however, was awaiting for recognition of its fundamental importance in molecular physics and chemistry much longer. It took several decades after Dirac’s formulation of his fundamental relativistic quantum mechanics in 1928 [4] until his theory was develop ...
... of quantum chemistry. Theory of relativity, however, was awaiting for recognition of its fundamental importance in molecular physics and chemistry much longer. It took several decades after Dirac’s formulation of his fundamental relativistic quantum mechanics in 1928 [4] until his theory was develop ...
Scattering with longitudinally coherent matter beams F. Robicheaux
... large target recoil; again, the inclusion of large target recoil is straightforward but does not appear to add anything of interest. Atomic units are used throughout this paper unless explicitly stated otherwise. ...
... large target recoil; again, the inclusion of large target recoil is straightforward but does not appear to add anything of interest. Atomic units are used throughout this paper unless explicitly stated otherwise. ...
Atomic orbital
An atomic orbital is a mathematical function that describes the wave-like behavior of either one electron or a pair of electrons in an atom. This function can be used to calculate the probability of finding any electron of an atom in any specific region around the atom's nucleus. The term may also refer to the physical region or space where the electron can be calculated to be present, as defined by the particular mathematical form of the orbital.Each orbital in an atom is characterized by a unique set of values of the three quantum numbers n, ℓ, and m, which respectively correspond to the electron's energy, angular momentum, and an angular momentum vector component (the magnetic quantum number). Any orbital can be occupied by a maximum of two electrons, each with its own spin quantum number. The simple names s orbital, p orbital, d orbital and f orbital refer to orbitals with angular momentum quantum number ℓ = 0, 1, 2 and 3 respectively. These names, together with the value of n, are used to describe the electron configurations of atoms. They are derived from the description by early spectroscopists of certain series of alkali metal spectroscopic lines as sharp, principal, diffuse, and fundamental. Orbitals for ℓ > 3 continue alphabetically, omitting j (g, h, i, k, …).Atomic orbitals are the basic building blocks of the atomic orbital model (alternatively known as the electron cloud or wave mechanics model), a modern framework for visualizing the submicroscopic behavior of electrons in matter. In this model the electron cloud of a multi-electron atom may be seen as being built up (in approximation) in an electron configuration that is a product of simpler hydrogen-like atomic orbitals. The repeating periodicity of the blocks of 2, 6, 10, and 14 elements within sections of the periodic table arises naturally from the total number of electrons that occupy a complete set of s, p, d and f atomic orbitals, respectively.