Spectroscopy studies of few particle effects in pyramidal quantum dots Daniel Dufåker
... a wave or a wave packet. The wave or more precisely the wave function associated with a particle has no physical meaning but the square of the wave function tells us the probability of finding the particle at a certain position. In this view the probability of finding the particle is thus spread out ...
... a wave or a wave packet. The wave or more precisely the wave function associated with a particle has no physical meaning but the square of the wave function tells us the probability of finding the particle at a certain position. In this view the probability of finding the particle is thus spread out ...
1 DEPARTMENT OF PHYSICS JAHANGIRNAGAR UNIVERSITY
... 3. Work, Energy and Power: Work done by constant and variable forces; Kinetic and potential energies; Work-energy theorem; Conservative and non-conservative forces; One dimensional forces depending on position only; two and three dimensional conservative systems; Principle of conservation of energy. ...
... 3. Work, Energy and Power: Work done by constant and variable forces; Kinetic and potential energies; Work-energy theorem; Conservative and non-conservative forces; One dimensional forces depending on position only; two and three dimensional conservative systems; Principle of conservation of energy. ...
Lorentz violating field theories and nonperturbative physics
... At the fundamental (usually Planck scale) level, models with LIV have been put forward in roughly two categories. 1. Models with a Lorentz-invariant Lagrangian (dynamical Lorentz invariance) that exhibit spontaneous symmetry breaking of Lorentz invariance. 2. Models without Lorentz symmetry at the f ...
... At the fundamental (usually Planck scale) level, models with LIV have been put forward in roughly two categories. 1. Models with a Lorentz-invariant Lagrangian (dynamical Lorentz invariance) that exhibit spontaneous symmetry breaking of Lorentz invariance. 2. Models without Lorentz symmetry at the f ...
Encyclopedia - KSU Faculty Member websites
... end of the 17th cent. In 1690, Christian Huygens proposed a theory that explained light as a wave phenomenon. However, a rival theory was offered by Sir Isaac Newton in 1704. Newton, who had discovered the visible spectrum in 1666, held that light is composed of tiny particles, or corpuscles, emitte ...
... end of the 17th cent. In 1690, Christian Huygens proposed a theory that explained light as a wave phenomenon. However, a rival theory was offered by Sir Isaac Newton in 1704. Newton, who had discovered the visible spectrum in 1666, held that light is composed of tiny particles, or corpuscles, emitte ...
Measuring Fractional Quantum Hall Effect
... hereby forcing electrons to occupy states in the next higher Landau level. According to this picture RH would take on quantized values only at very precise values3 of the magnetic field, as given in equation (1.10). This would result in measurements showing the same linear dependence of RH on B as f ...
... hereby forcing electrons to occupy states in the next higher Landau level. According to this picture RH would take on quantized values only at very precise values3 of the magnetic field, as given in equation (1.10). This would result in measurements showing the same linear dependence of RH on B as f ...
Matter Waves and Obital Quantum Numbers
... - The electron orbits are located in shells, a shell conceptually being a spherical surface with the atomic nucleus located at the center of the sphere. The locations available for electron orbits are in a series of concentric shells corresponding to the orbit number, n, referred to as the principal ...
... - The electron orbits are located in shells, a shell conceptually being a spherical surface with the atomic nucleus located at the center of the sphere. The locations available for electron orbits are in a series of concentric shells corresponding to the orbit number, n, referred to as the principal ...
Document
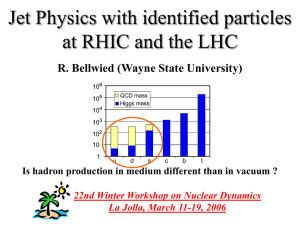
... Why is canonical suppression (CS) a baryon effect ? CS > energy loss effect @ high pt Is c more suppressed than s ? Is there still CS at LHC energies ? ...
... Why is canonical suppression (CS) a baryon effect ? CS > energy loss effect @ high pt Is c more suppressed than s ? Is there still CS at LHC energies ? ...
Indistinguishable particles in quantum mechanics
... where a; b 2 C are chosen such that jaj2 þ jbj2 ¼ 1. So, we actually have an infinity of different mathematical descriptions for the same physical state. This is a consequence of the indistinguishability of particles and is known as exchange degeneracy. How can we then decide which of the above vector ...
... where a; b 2 C are chosen such that jaj2 þ jbj2 ¼ 1. So, we actually have an infinity of different mathematical descriptions for the same physical state. This is a consequence of the indistinguishability of particles and is known as exchange degeneracy. How can we then decide which of the above vector ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.