1 Rutherford`s Nuclear Model of the atom A is the currently accepted
... The lowest orbital energy is reached when the number of electrons with the same spin is maximized. This statement describes __________. A ...
... The lowest orbital energy is reached when the number of electrons with the same spin is maximized. This statement describes __________. A ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... 16. Show that when masses P and Q are connected by a string over the edge of a table, the tension is the same whether P hangs and Q is on the table or Q hangs and P is on the table. 17. A particle is projected so as to graze the tops of 2 walls, each of height 20 feet, at distances of 30 ft and 170 ...
... 16. Show that when masses P and Q are connected by a string over the edge of a table, the tension is the same whether P hangs and Q is on the table or Q hangs and P is on the table. 17. A particle is projected so as to graze the tops of 2 walls, each of height 20 feet, at distances of 30 ft and 170 ...
The Sub-Atomic Particle * J
... that the cause of electrical energy is a particle smaller than what was previously thought to be the smallest particle in existence, the atom. This smaller particle is called subatomic (smaller than an atom) or an ...
... that the cause of electrical energy is a particle smaller than what was previously thought to be the smallest particle in existence, the atom. This smaller particle is called subatomic (smaller than an atom) or an ...
Document
... Section 5.2 Quantum Theory and the Atom • Compare the Bohr and quantum mechanical models of the atom. • Explain the impact of de Broglie's wave article duality and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle on the current view of electrons in atoms. • Identify the relationships among a hydrogen atom's e ...
... Section 5.2 Quantum Theory and the Atom • Compare the Bohr and quantum mechanical models of the atom. • Explain the impact of de Broglie's wave article duality and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle on the current view of electrons in atoms. • Identify the relationships among a hydrogen atom's e ...
C. - Taylor County Schools
... Section 5.2 Quantum Theory and the Atom • Compare the Bohr and quantum mechanical models of the atom. • Explain the impact of de Broglie's wave article duality and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle on the current view of electrons in atoms. • Identify the relationships among a hydrogen atom's e ...
... Section 5.2 Quantum Theory and the Atom • Compare the Bohr and quantum mechanical models of the atom. • Explain the impact of de Broglie's wave article duality and the Heisenberg uncertainty principle on the current view of electrons in atoms. • Identify the relationships among a hydrogen atom's e ...
CHAPTER 9: Statistical Physics
... Physical properties (states) defined in average sense. It is what we measure or see. Need to introduce concepts of statistics and probability Eventually, we want to learn quantum statistics (developed in ...
... Physical properties (states) defined in average sense. It is what we measure or see. Need to introduce concepts of statistics and probability Eventually, we want to learn quantum statistics (developed in ...
3. atomic structure and periodic table
... Q. Why is there a general increase in first ionisation energy across a period? A. As one goes across a period , the number of protons increases making the effective attraction of the nucleus greater. The electrons are being added to the same shell which has the same shielding effect and the electron ...
... Q. Why is there a general increase in first ionisation energy across a period? A. As one goes across a period , the number of protons increases making the effective attraction of the nucleus greater. The electrons are being added to the same shell which has the same shielding effect and the electron ...
Density functional theory
... potential which I will later introduce as exchange and correlation. It proposed an expected value of the kinetic term in the H operator that depends solely on the density. This approach is acceptable only in high electron density metals where the quantum corrections to the Couloumb potential can be ...
... potential which I will later introduce as exchange and correlation. It proposed an expected value of the kinetic term in the H operator that depends solely on the density. This approach is acceptable only in high electron density metals where the quantum corrections to the Couloumb potential can be ...
REVISION CLASS SHEET - SEM - 2 CHEM
... (i) n = 3, l = 2 and m = +1 (ii) n = 3, l = 2 and m = -1 52. How can you say that electron is a universal constituent of all atoms ? 53. Give experiments to show that (i) Cathode rays carry negative charge (ii) Cathode rays consist of material particles. 54. How was proton discovered ? 55. How can y ...
... (i) n = 3, l = 2 and m = +1 (ii) n = 3, l = 2 and m = -1 52. How can you say that electron is a universal constituent of all atoms ? 53. Give experiments to show that (i) Cathode rays carry negative charge (ii) Cathode rays consist of material particles. 54. How was proton discovered ? 55. How can y ...
Chapter 8 Multielectron Atoms – Spin and Term Symbols
... Note: This is a 4N-dimensional integral! (Remember (f unction) dτ means integration over the entire space of all the varibles.) The Pauli Principle states that all electronic wavefunctions must be antisymmetric under the interchange of any two electrons. e.g. Ψ(1, 2) = −Ψ(2, 1) This is an implicatio ...
... Note: This is a 4N-dimensional integral! (Remember (f unction) dτ means integration over the entire space of all the varibles.) The Pauli Principle states that all electronic wavefunctions must be antisymmetric under the interchange of any two electrons. e.g. Ψ(1, 2) = −Ψ(2, 1) This is an implicatio ...
Document
... There is a particle in nature called a muon, which has the same charge as the electron but is 207 times heavier. A muon can form a hydrogen-like atom by binding to a proton. ...
... There is a particle in nature called a muon, which has the same charge as the electron but is 207 times heavier. A muon can form a hydrogen-like atom by binding to a proton. ...
RIKEN radioactive isotope beam factory project – Present status and
... with stable Cs ions at KSR-ring in Kyoto University has successfully demonstrated the feasibility of the SCRIT scheme [20]. The luminosity achieved at KSR was 1026 /cm2 /s with a number of trapped ions of 4×107 . The SCRIT system under construction consists of an e-storage ring and a 150 MeV microtr ...
... with stable Cs ions at KSR-ring in Kyoto University has successfully demonstrated the feasibility of the SCRIT scheme [20]. The luminosity achieved at KSR was 1026 /cm2 /s with a number of trapped ions of 4×107 . The SCRIT system under construction consists of an e-storage ring and a 150 MeV microtr ...
Bonding in Solids, Structural and Chemical Properties
... nuclei of solids. Here we approach this problem by solving the Schrödinger equation, approximately, for simple systems, thereby developing the framework that allows us to understand much more complex systems. Initially, we consider solutions for atoms, which provide us with the hydrogen-like orbital ...
... nuclei of solids. Here we approach this problem by solving the Schrödinger equation, approximately, for simple systems, thereby developing the framework that allows us to understand much more complex systems. Initially, we consider solutions for atoms, which provide us with the hydrogen-like orbital ...
Functional RG for few
... Ideas of effective field theory and the renormalisation group are now well-developed for few-body systems ...
... Ideas of effective field theory and the renormalisation group are now well-developed for few-body systems ...
Lecture 5
... Because of Pauli’s Exclusion principle (no two electrons with same set of quantum numbers), there is a tendency to avoid overlapping orbitals in neighboring electronic shells. ...
... Because of Pauli’s Exclusion principle (no two electrons with same set of quantum numbers), there is a tendency to avoid overlapping orbitals in neighboring electronic shells. ...
quantum - UCI Physics and Astronomy
... Can material particles exhibit wave nature ? Prince Louis de Broglie while doing his Ph.D. research said particles should have wave like properties. Yodh ...
... Can material particles exhibit wave nature ? Prince Louis de Broglie while doing his Ph.D. research said particles should have wave like properties. Yodh ...
Plasma Process 5 col..
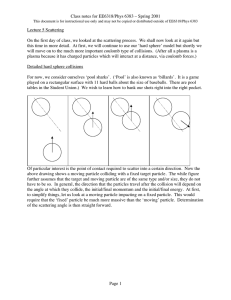
... Of particular interest is the point of contact required to scatter into a certain direction. Now the above drawing shows a moving particle colliding with a fixed target particle. The while figure further assumes that the target and moving particle are of the same type and/or size, they do not have t ...
... Of particular interest is the point of contact required to scatter into a certain direction. Now the above drawing shows a moving particle colliding with a fixed target particle. The while figure further assumes that the target and moving particle are of the same type and/or size, they do not have t ...
Quantum linear Boltzmann equation with finite intercollision time
... where the subscripts 储 refer to the components parallel to Q. It is obvious that after our single collision the particle’s density matrix ˆ , whatever it was before the collision, becomes perfect diagonal in P储. Gradually, after many collisions, the state ˆ becomes a mixture of plane waves, no off ...
... where the subscripts 储 refer to the components parallel to Q. It is obvious that after our single collision the particle’s density matrix ˆ , whatever it was before the collision, becomes perfect diagonal in P储. Gradually, after many collisions, the state ˆ becomes a mixture of plane waves, no off ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.