Слайд 1 - QUARKS
... • Lorentzian Wormhole is a region in spacetime in which 3-dim space-like sections have non-trivial topology. • By non-trivial topology we mean that these sections are not simply connected • In the simplest case a WH has two mouths which join different regions of the space-time. • We can also imagine ...
... • Lorentzian Wormhole is a region in spacetime in which 3-dim space-like sections have non-trivial topology. • By non-trivial topology we mean that these sections are not simply connected • In the simplest case a WH has two mouths which join different regions of the space-time. • We can also imagine ...
magical magnets
... MAGICAL MAGNETS Just what are they? And where do these magnetic fields come from? ...
... MAGICAL MAGNETS Just what are they? And where do these magnetic fields come from? ...
REU Research Project: Simulating neutron interaction with the Super
... and that the number and positions of the various PMTs were centrally managed by a modified version of Geant4’s Parameterized Volume class. To enable differentiation between data read from physically identical PMTs in the simulation, however, each PMT was each given a unique ID number upon creation. ...
... and that the number and positions of the various PMTs were centrally managed by a modified version of Geant4’s Parameterized Volume class. To enable differentiation between data read from physically identical PMTs in the simulation, however, each PMT was each given a unique ID number upon creation. ...
The Origin of Mass - Massachusetts Institute of Technology
... The theoryof quarks and gluons is called quantum chromodynamics, or QCD. QCD is a generalization of quantum electrodynamics (QED). For a nice description of quantum electrodynamics, written by an MIT grad who made good, I highly recommend QED: The Strange Theory of Electrons and Light, byRichard Fey ...
... The theoryof quarks and gluons is called quantum chromodynamics, or QCD. QCD is a generalization of quantum electrodynamics (QED). For a nice description of quantum electrodynamics, written by an MIT grad who made good, I highly recommend QED: The Strange Theory of Electrons and Light, byRichard Fey ...
Chapter 3, Lecture 2
... called the CPT theorem, which states if a local theory of interacting fields is invariant under the proper Lorentz group, it will also be invariant under the combination of C (particle-anti particle conjugation), space inversion (P) and time reversal (T). Consequences: if CP is violated then T is vi ...
... called the CPT theorem, which states if a local theory of interacting fields is invariant under the proper Lorentz group, it will also be invariant under the combination of C (particle-anti particle conjugation), space inversion (P) and time reversal (T). Consequences: if CP is violated then T is vi ...
Chp 19- reaction rates and equilibrium
... Atom—the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element; Daltons atomic theory—all elements composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms, atoms of same element identical and different from other elements, atoms of different elements can physically mix or chemicall ...
... Atom—the smallest particle of an element that retains the properties of that element; Daltons atomic theory—all elements composed of tiny indivisible particles called atoms, atoms of same element identical and different from other elements, atoms of different elements can physically mix or chemicall ...
gaseous tracking chambers
... cannot be made by directly depositing metal on the semiconductor (else a rectifing junction extending into the semiconductor is formed). So heavily doped layers of n+ or p+ are used between the semiconductor and the ...
... cannot be made by directly depositing metal on the semiconductor (else a rectifing junction extending into the semiconductor is formed). So heavily doped layers of n+ or p+ are used between the semiconductor and the ...
Fulltext PDF - Indian Academy of Sciences
... While the electron, muon, T -lepton, and their corresponding neutrinos and their antiparticles are considered to be one set of fundamental particles that can be 0 bserved experimentally, called leptons, all other matter, hadrons, are assumed to be made up of another set of fundamental particles call ...
... While the electron, muon, T -lepton, and their corresponding neutrinos and their antiparticles are considered to be one set of fundamental particles that can be 0 bserved experimentally, called leptons, all other matter, hadrons, are assumed to be made up of another set of fundamental particles call ...
PHY313 - CEI544 The Mystery of Matter From Quarks to the
... there. The description of a result the master of symmetries should not depend on the measuring “gauge”. • Gauge transformations transform a description of a solution at one point in space to another description in another point in space. ...
... there. The description of a result the master of symmetries should not depend on the measuring “gauge”. • Gauge transformations transform a description of a solution at one point in space to another description in another point in space. ...
Time-Independent Perturbation Theory Atomic Physics Applications 1 Introduction
... hydrogen is a system with many degeneracies, in which physically important results can be obtained from low-order degenerate perturbation theory, so it is an excellent area to practice applying what we have learned. We only have time to touch on atomic physics in this course, and we will focus only ...
... hydrogen is a system with many degeneracies, in which physically important results can be obtained from low-order degenerate perturbation theory, so it is an excellent area to practice applying what we have learned. We only have time to touch on atomic physics in this course, and we will focus only ...
Elastic electron-proton scattering
... Energies and momenta of the scattered electrons are measured in spectrometers: ...
... Energies and momenta of the scattered electrons are measured in spectrometers: ...
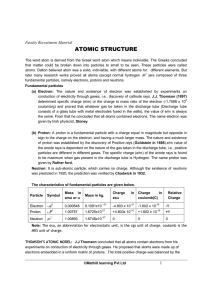
Electronic Structure
... In a potassium atom, the two electrons in the lowest energy level are closest to the nucleus. They are most strongly attracted by the positive nucleus electrostatically. These two electrons are said to occupy the first quantum shell ( n = 1 ) The following 8 electrons occupy the second quantum shell ...
... In a potassium atom, the two electrons in the lowest energy level are closest to the nucleus. They are most strongly attracted by the positive nucleus electrostatically. These two electrons are said to occupy the first quantum shell ( n = 1 ) The following 8 electrons occupy the second quantum shell ...
Chapter 4 Section 1 The Development of a New Atomic Model
... c = λν • In the equation, c is the speed of light (in m/s), λ is the wavelength of the electromagnetic wave (in m), and ν is the frequency of the electromagnetic wave (in s−1). ...
... c = λν • In the equation, c is the speed of light (in m/s), λ is the wavelength of the electromagnetic wave (in m), and ν is the frequency of the electromagnetic wave (in s−1). ...
Correlation Effects in Quantum Dot Wave Function Imaging
... wave functions was addressed.11 The authors observe an anomalous filling sequence up to 6 holes (s, s, p, p, d, d) and interpret it in terms of a generalized Hund’s rule for the two p and the two d orbitals together, namely the total spin should be maximized as N increases as an effect of strong Cou ...
... wave functions was addressed.11 The authors observe an anomalous filling sequence up to 6 holes (s, s, p, p, d, d) and interpret it in terms of a generalized Hund’s rule for the two p and the two d orbitals together, namely the total spin should be maximized as N increases as an effect of strong Cou ...
Ripplon-induced tunneling transverse to the magnetic field P. M. Platzman
... The first two terms in the operator V̂ q describe a kinematic interaction with ripplons which is due to the curvature of the surface on which the electron wave function is set equal to 0. The polarization interaction K q(z) is given in Ref. 7. The kinematic interaction turns out to be more important ...
... The first two terms in the operator V̂ q describe a kinematic interaction with ripplons which is due to the curvature of the surface on which the electron wave function is set equal to 0. The polarization interaction K q(z) is given in Ref. 7. The kinematic interaction turns out to be more important ...
Science Theatre Nuclear Physics and FRIB Show INTRO – 4 people
... We’re familiar with them because they’re long range—that is, we can see their effects in our everyday lives. The other two forces – which are the strong force, and the (also descriptively named) weak force -- can only reach very short distances, only about the size of a nucleus! Because of that, tho ...
... We’re familiar with them because they’re long range—that is, we can see their effects in our everyday lives. The other two forces – which are the strong force, and the (also descriptively named) weak force -- can only reach very short distances, only about the size of a nucleus! Because of that, tho ...
Facilitator`s Guide PDF
... participants the visualization of atomic orbitals for hydrogen at http://www.falstad.com/qmatom/. Use the “real orbitals” and start at n=1, moving to n=2 and n=3. Then change the value of l. (Optional: The changing color represents the phase of the wave—this is what’s “waving.” The probability densi ...
... participants the visualization of atomic orbitals for hydrogen at http://www.falstad.com/qmatom/. Use the “real orbitals” and start at n=1, moving to n=2 and n=3. Then change the value of l. (Optional: The changing color represents the phase of the wave—this is what’s “waving.” The probability densi ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.