CHAPTER 8 PERIODIC RELATIONSHIPS AMONG THE ELEMENTS
... of a representative element, one or more electrons are added to the highest partially filled n shell. Representative elements typically gain or lose electrons to achieve a stable noble gas electron configuration. When a cation is formed from an atom of a transition metal, electrons are always remove ...
... of a representative element, one or more electrons are added to the highest partially filled n shell. Representative elements typically gain or lose electrons to achieve a stable noble gas electron configuration. When a cation is formed from an atom of a transition metal, electrons are always remove ...
the problem book
... 3. A ring with mass m1 slides over a uniform rod which has a mass m2 and length ℓ. The rod is pivoted at one end and hangs vertically. The ring is secured to the pivot by a massless spring with the spring constant k and unstretched length r0 , and is constrained to slide along the rod without fricti ...
... 3. A ring with mass m1 slides over a uniform rod which has a mass m2 and length ℓ. The rod is pivoted at one end and hangs vertically. The ring is secured to the pivot by a massless spring with the spring constant k and unstretched length r0 , and is constrained to slide along the rod without fricti ...
The Magnetic Moments of Proton, Neutron and Electron.
... magnetism. Because charge isn't a function of the summed spin. Charge is a function of the summed energy of the photons. This energy is a vector. The neutron is always emitting at a right angle to the proton, so if the charge field is defined in terms of proton emission, the neutron's charge energy ...
... magnetism. Because charge isn't a function of the summed spin. Charge is a function of the summed energy of the photons. This energy is a vector. The neutron is always emitting at a right angle to the proton, so if the charge field is defined in terms of proton emission, the neutron's charge energy ...
arXiv:0912.4058v1 [physics.atom
... smaller interatomic distances. As we will show, this is due to internal quantum reflection at a shape resonance of electron-atom scattering. In addition to reproducing all previously observed lines [6], the calculations predict additional dimer and trimer states that are observed in our new experime ...
... smaller interatomic distances. As we will show, this is due to internal quantum reflection at a shape resonance of electron-atom scattering. In addition to reproducing all previously observed lines [6], the calculations predict additional dimer and trimer states that are observed in our new experime ...
triumph, window, clue, and inspiration
... couples very feebly to H. (That’s a big reason why electrons and protons can be much lighter than W and Z—they don’t feel its drag.) In fact the dominant coupling arises through an indirect process, “gluon fusion,” that I discovered in 1976. It is displayed in Figure 3a. Gluons don’t couple to the H ...
... couples very feebly to H. (That’s a big reason why electrons and protons can be much lighter than W and Z—they don’t feel its drag.) In fact the dominant coupling arises through an indirect process, “gluon fusion,” that I discovered in 1976. It is displayed in Figure 3a. Gluons don’t couple to the H ...
Document
... Suppose a particle with angular momentum of 0 decays into two electrons. By conservation of angular momentum, the sum of the two electrons angular momentum must also be 0. If we measure the z-spin of one electron to be +½ then we know that the other electron must have a z-spin of –½. But before we m ...
... Suppose a particle with angular momentum of 0 decays into two electrons. By conservation of angular momentum, the sum of the two electrons angular momentum must also be 0. If we measure the z-spin of one electron to be +½ then we know that the other electron must have a z-spin of –½. But before we m ...
University-Chemistry-1st-Edition-Brian-Laird-Solution
... Light emitted by fluorescent materials always has lower energy than the light striking the fluorescent substance. Absorption of visible light could not give rise to emitted ultraviolet light because the latter has higher energy. The reverse process, ultraviolet light producing visible light by fluor ...
... Light emitted by fluorescent materials always has lower energy than the light striking the fluorescent substance. Absorption of visible light could not give rise to emitted ultraviolet light because the latter has higher energy. The reverse process, ultraviolet light producing visible light by fluor ...
Lecture 1
... the detector attended by a flash near hole 1 and hole 2, respectively. In column 3 we record those electrons which reached the detector without producing a flash. The data in columns 1 and 2 give rise to the probability distributions P1 and P2 . But the data in column 3 which correspond to unseen ...
... the detector attended by a flash near hole 1 and hole 2, respectively. In column 3 we record those electrons which reached the detector without producing a flash. The data in columns 1 and 2 give rise to the probability distributions P1 and P2 . But the data in column 3 which correspond to unseen ...
TT 8.1–8.10 - DPG
... As a well-established and successful wave-function theory hierarchy in quantum chemistry, the coupled-cluster (CC) ansatz is attracting increasing attention in computational materials science [1]. However, compared to traditional density-functional approximations, CC approaches face much greater cha ...
... As a well-established and successful wave-function theory hierarchy in quantum chemistry, the coupled-cluster (CC) ansatz is attracting increasing attention in computational materials science [1]. However, compared to traditional density-functional approximations, CC approaches face much greater cha ...
Chem 150 Answer Key Problem Introductory Quantum Chemistry 1
... region. The picture changes when we dissolve some copper sulfate. You all know what happens. The resulting solution is blue because the solvated copper ions absorb yellow light (complementary color to blue). b) correct c) FALSE, infrared is less energetic than visible light because it has a smaller ...
... region. The picture changes when we dissolve some copper sulfate. You all know what happens. The resulting solution is blue because the solvated copper ions absorb yellow light (complementary color to blue). b) correct c) FALSE, infrared is less energetic than visible light because it has a smaller ...
Document
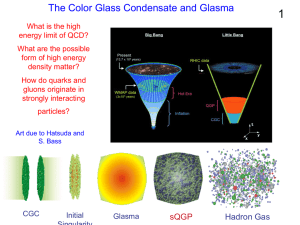
... Time dilation -> Classical field is glassy High phase space density -> Condensate Phase space density: Attractive potential ...
... Time dilation -> Classical field is glassy High phase space density -> Condensate Phase space density: Attractive potential ...
Plasma Physics Definitions
... Plasma Physics Current and Potential Distributions in a DC Glow Discharge 100V ...
... Plasma Physics Current and Potential Distributions in a DC Glow Discharge 100V ...
Physical Science: Ch. 10 - Pleasant Hill Elementary School
... • The electron cloud is a large area, however, the electrons in the electron cloud are not randomly scattered here and there. • If you were to slice an atom in half, there are certain areas surrounding the nucleus where you are more likely to find electrons located. ...
... • The electron cloud is a large area, however, the electrons in the electron cloud are not randomly scattered here and there. • If you were to slice an atom in half, there are certain areas surrounding the nucleus where you are more likely to find electrons located. ...
QCD
... developing – This process depends on the (known) quark distributions and the (unknown) gluon distribution ...
... developing – This process depends on the (known) quark distributions and the (unknown) gluon distribution ...
Bell`s Theorem
... Items other than copying, distributing, and modifying the Content with which this license was distributed (such as using, etc.) are outside the scope of this license. 1. You may copy and distribute exact replicas of the OpenContent (OC) as you receive it, in any medium, provided that you conspicuous ...
... Items other than copying, distributing, and modifying the Content with which this license was distributed (such as using, etc.) are outside the scope of this license. 1. You may copy and distribute exact replicas of the OpenContent (OC) as you receive it, in any medium, provided that you conspicuous ...
Ab initio molecular dynamics: ground and excited states
... Interaction with external potential: nuclei-electrons term Interaction with Hartree potential (Coulomb energy) Usually also the nuclear-nuclear term U {RI } is added in the total energy functional N ...
... Interaction with external potential: nuclei-electrons term Interaction with Hartree potential (Coulomb energy) Usually also the nuclear-nuclear term U {RI } is added in the total energy functional N ...
Electron scattering

Electron scattering occurs when electrons are deviated from their original trajectory. This is due to the electrostatic forces within matter interaction or, if an external magnetic field is present, the electron may be deflected by the Lorentz force. This scattering typically happens with solids such as metals, semiconductors and insulators; and is a limiting factor in integrated circuits and transistors.The application of electron scattering is such that it can be used as a high resolution microscope for hadronic systems, that allows the measurement of the distribution of charges for nucleons and nuclear structure. The scattering of electrons has allowed us to understand that protons and neutrons are made up of the smaller elementary subatomic particles called quarks.Electrons may be scattered through a solid in several ways:Not at all: no electron scattering occurs at all and the beam passes straight through.Single scattering: when an electron is scattered just once.Plural scattering: when electron(s) scatter several times.Multiple scattering: when electron(s) scatter very many times over.The likelihood of an electron scattering and the proliferance of the scattering is a probability function of the specimen thickness to the mean free path.