quantum paradox - Brian Whitworth
... over any distance ignore speed of light limits; and superposed states can co-exist in physically opposite ways that should cancel, like opposite spin. In sum, the quantum world described by quantum theory cannot possibly be physical. For example, an electron’s quantum wave can spread across a galaxy ...
... over any distance ignore speed of light limits; and superposed states can co-exist in physically opposite ways that should cancel, like opposite spin. In sum, the quantum world described by quantum theory cannot possibly be physical. For example, an electron’s quantum wave can spread across a galaxy ...
The Hydrogen Atom
... Summary of Early Atomic Models The Thomson Model Description: Electrons are embedded in a wide positively charged area, like raisins in a cookie. Problem: Does not agree with the Rutherford particles experiment. The Rutherford Model Description: Miniature Solar system with electrons orbiting the n ...
... Summary of Early Atomic Models The Thomson Model Description: Electrons are embedded in a wide positively charged area, like raisins in a cookie. Problem: Does not agree with the Rutherford particles experiment. The Rutherford Model Description: Miniature Solar system with electrons orbiting the n ...
chapter 7 part 2
... single values.” electron is considered to be a point charge that goes around the nucleus, which is also considered to be a point charge and assumed to be stationary, the great distance between electron and proton with respect to their actual size and the 1836 times larger mass of the ...
... single values.” electron is considered to be a point charge that goes around the nucleus, which is also considered to be a point charge and assumed to be stationary, the great distance between electron and proton with respect to their actual size and the 1836 times larger mass of the ...
Quantum gravity
... For about 70 years, this wave-particle duality was explained by another unsettling tenet of quantum theory - the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. Formulated by Werner Heisenberg in 1927 and recently made more precise, the theory puts an upper limit on knowledge. It says one can never know both the ...
... For about 70 years, this wave-particle duality was explained by another unsettling tenet of quantum theory - the Heisenberg uncertainty principle. Formulated by Werner Heisenberg in 1927 and recently made more precise, the theory puts an upper limit on knowledge. It says one can never know both the ...
quantum mechanics and real events - Heriot
... takes a dualistic view, dividing the world into two parts, often called the system and the environment, or the quantum part and the classical part. The classical part is described in terms of the familar ideas of everyday life, according to which the world consists of objects which have definite po ...
... takes a dualistic view, dividing the world into two parts, often called the system and the environment, or the quantum part and the classical part. The classical part is described in terms of the familar ideas of everyday life, according to which the world consists of objects which have definite po ...
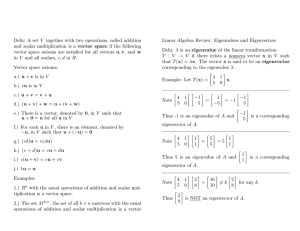
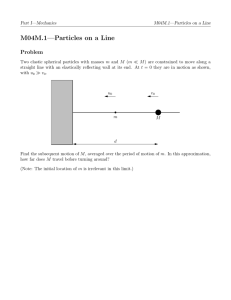
Rotational Motion Practice MC Answers
... shown above, and sticks to dle satellite. \'\'lllch of the following is erue of dle isolated asteroid-satellite system in tllls collision? a. Kinetic energy K is conserved b. Total Energy E is conserved, but angular momenmm L is not conserved c. Angular momentum L is conserved, but linear momenrtun ...
... shown above, and sticks to dle satellite. \'\'lllch of the following is erue of dle isolated asteroid-satellite system in tllls collision? a. Kinetic energy K is conserved b. Total Energy E is conserved, but angular momenmm L is not conserved c. Angular momentum L is conserved, but linear momenrtun ...