9.1 Impulse - 9.2 Momentum and the Impulse Momentum Theorem
... A ball of mass m = 0.25 kg rolling to the right at 1.3 m/s strikes a wall and rebounds to the left at 1.1 m/s. What is the change in the ball’s momentum? What is the impulse delivered to it by the wall? ...
... A ball of mass m = 0.25 kg rolling to the right at 1.3 m/s strikes a wall and rebounds to the left at 1.1 m/s. What is the change in the ball’s momentum? What is the impulse delivered to it by the wall? ...
Optical control of the spin of a magnetic atom in a semiconductor
... first approximation, the hole-Mn exchange interaction reduces to an Ising term J z S z and shifts the emission energy of the QD, depending on the relative orientation of the spin of the Mn (S z ) and hole (J z ) [19–22]. As the spin state of the Mn atom fluctuates during the optical measurements, th ...
... first approximation, the hole-Mn exchange interaction reduces to an Ising term J z S z and shifts the emission energy of the QD, depending on the relative orientation of the spin of the Mn (S z ) and hole (J z ) [19–22]. As the spin state of the Mn atom fluctuates during the optical measurements, th ...
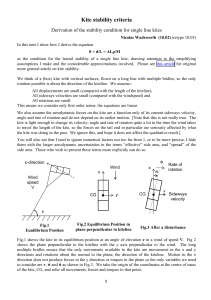
Gaussian to Exponential Crossover in the Attenuation of Polarization
... tings. While in ferrocene and cymantrene systems this was not particularly demanding because of the obvious simple functional dependences they presented, this can be a serious restriction in a more general situation. In such a case, the pulse sequence sketched in Fig. 1b should be used. Here, the am ...
... tings. While in ferrocene and cymantrene systems this was not particularly demanding because of the obvious simple functional dependences they presented, this can be a serious restriction in a more general situation. In such a case, the pulse sequence sketched in Fig. 1b should be used. Here, the am ...
Answer
... light), and the skaters don't lose any mass in the process. Then, the constant mass terms can be put within the derivative. This is good, as it looks like we can now say something about the skaters's velocities. The time rate of change of the sum of each skater's mass times velocity is zero ...
... light), and the skaters don't lose any mass in the process. Then, the constant mass terms can be put within the derivative. This is good, as it looks like we can now say something about the skaters's velocities. The time rate of change of the sum of each skater's mass times velocity is zero ...
Defining and detecting quantum speedup
... classical or quantum hardware unimportant. According to the extended Church-Turing thesis all classical computers are equivalent up to polynomial factors [5]. Similarly, all proposed models of quantum computation are polynomially equivalent, so that a finding of exponential quantum speedup will be m ...
... classical or quantum hardware unimportant. According to the extended Church-Turing thesis all classical computers are equivalent up to polynomial factors [5]. Similarly, all proposed models of quantum computation are polynomially equivalent, so that a finding of exponential quantum speedup will be m ...
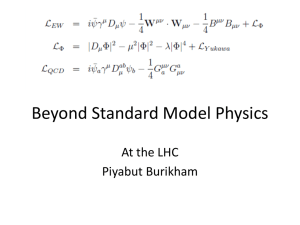
Naturalness via scale invariance and non-trivial UV fixed points in a 4d O(N) scalar field model in the large-N limit
... gaussian one, it will help to have a small parameter to expand in. We investigate whether there is a 4d scale-invariant interacting O(N ) scalar field theory in the 1/N expansion. The case of interest in particle physics is N = 4, since in the absence of gauge and Yukawa couplings, the symmetry grou ...
... gaussian one, it will help to have a small parameter to expand in. We investigate whether there is a 4d scale-invariant interacting O(N ) scalar field theory in the 1/N expansion. The case of interest in particle physics is N = 4, since in the absence of gauge and Yukawa couplings, the symmetry grou ...