Solution
... Solution. If y and z are two inverses of x then in particular y is a left inverse and z is a right inverse. Hence y = z by the previous part of the exercise. Comments. One mistake that occurred a few times was to prove that z −1 = y −1 legitimately but then to conclude immediately from this that z = ...
... Solution. If y and z are two inverses of x then in particular y is a left inverse and z is a right inverse. Hence y = z by the previous part of the exercise. Comments. One mistake that occurred a few times was to prove that z −1 = y −1 legitimately but then to conclude immediately from this that z = ...
general-relativity as an effective-field theory
... generate corrections to c1 , c2 etc. Unless an infinite number of ”accidents” occur at least some of the higher order coefficients will be nonzero. In practice there is no known reason to require that c1 , c2 vanish completely. We can instead view the gravitational action as being organized in an en ...
... generate corrections to c1 , c2 etc. Unless an infinite number of ”accidents” occur at least some of the higher order coefficients will be nonzero. In practice there is no known reason to require that c1 , c2 vanish completely. We can instead view the gravitational action as being organized in an en ...
Some Notes on Field Theory
... number of degrees of freedom. Examples are systems of many interacting particles or critical phenomena like second order phase transitions. Here we will concentrate on the scattering of particles, but the general framework can be applied to any domain in physics. For an introduction, we simplify Nat ...
... number of degrees of freedom. Examples are systems of many interacting particles or critical phenomena like second order phase transitions. Here we will concentrate on the scattering of particles, but the general framework can be applied to any domain in physics. For an introduction, we simplify Nat ...
Rotational Motion Test Review
... 13. A comet orbiting the Sun can be considered an isolated system with no outside forces or torques acting on it. As the comet moves in its highly elliptical orbit, what remains constant? A. Its distant from the Sun B. Its angular speed C. Its linear speed D. Its angular momentum E. The gravitationa ...
... 13. A comet orbiting the Sun can be considered an isolated system with no outside forces or torques acting on it. As the comet moves in its highly elliptical orbit, what remains constant? A. Its distant from the Sun B. Its angular speed C. Its linear speed D. Its angular momentum E. The gravitationa ...
Proton tunneling in hydrogen bonds and its possible implications in
... atoms/groups of the enzyme (C′ ) to the heat bath B. In other words, the conformational motion under interest occurs fast over a time scale that is small compared to the decoherence time enforced by the heat bath B̃. This is quite reasonable as (i) enzymes are usually very large molecules, which imp ...
... atoms/groups of the enzyme (C′ ) to the heat bath B. In other words, the conformational motion under interest occurs fast over a time scale that is small compared to the decoherence time enforced by the heat bath B̃. This is quite reasonable as (i) enzymes are usually very large molecules, which imp ...
Phys.Rev.Lett. 84, 1
... slit and the detector D0 . Detector D0 can be scanned along its x axis by a step motor. The idler photon (photon 2) is sent to an interferometer with equal-path optical arms. The interferometer includes a prism, two 50-50 beam splitters BSA, BSB, two reflecting mirrors MA , MB , and a 50-50 beam spl ...
... slit and the detector D0 . Detector D0 can be scanned along its x axis by a step motor. The idler photon (photon 2) is sent to an interferometer with equal-path optical arms. The interferometer includes a prism, two 50-50 beam splitters BSA, BSB, two reflecting mirrors MA , MB , and a 50-50 beam spl ...
atomic structure
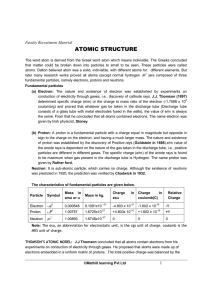
... A (mass number) = Z (Atomic number or Number of protons) + Number of neutrons A-Z = Number of neutrons Note: Mass number is always whole number but mass of proton or a neutron is not a whole number so atomic mass (or) weight is not necessarily a whole number. Atomic mass of an element is not equal t ...
... A (mass number) = Z (Atomic number or Number of protons) + Number of neutrons A-Z = Number of neutrons Note: Mass number is always whole number but mass of proton or a neutron is not a whole number so atomic mass (or) weight is not necessarily a whole number. Atomic mass of an element is not equal t ...