Analysis of the projected Coupled Cluster Method in Electronic
... actual discretisation, i.e. the underlying (finite) basis set. Consequently, the approximation of the wave function by a Projected Coupled Cluster solution will be considered here in two steps. The first part is the convergence of the Full CI solution towards the exact wave function. Since the Full ...
... actual discretisation, i.e. the underlying (finite) basis set. Consequently, the approximation of the wave function by a Projected Coupled Cluster solution will be considered here in two steps. The first part is the convergence of the Full CI solution towards the exact wave function. Since the Full ...
Slide 1
... • Short, intense pulses – either the atomic evolution is “free” (no coupling) or dominated by the interaction (internal and external components of Hamiltonian ignored) • π-pulses (timed to transfer atoms in state 1 to be in state 2, & ...
... • Short, intense pulses – either the atomic evolution is “free” (no coupling) or dominated by the interaction (internal and external components of Hamiltonian ignored) • π-pulses (timed to transfer atoms in state 1 to be in state 2, & ...
Waveguides, Resonant Cavities, Optical Fibers and
... potentials. The basis of this analogy is the fact that both wave equations for electromagnetic monoenergetic waves (i.e. with well-defined frequency), obtained directly from the Maxwell equations, and the time-independent Schrodinger equation are Helmholtz equations; when specific restrictions - like ...
... potentials. The basis of this analogy is the fact that both wave equations for electromagnetic monoenergetic waves (i.e. with well-defined frequency), obtained directly from the Maxwell equations, and the time-independent Schrodinger equation are Helmholtz equations; when specific restrictions - like ...
Hybrid opto-mechanical systems with nitrogen
... on opto-mechanics. For example, we have transferred the signals from light to mechanical oscillation, and vise versa [15]. We have realized optomechanically induced transparency [16] and generated squeezed lights in opto-mechanical systems [17]. By using mechanical oscillator as an interface, quantu ...
... on opto-mechanics. For example, we have transferred the signals from light to mechanical oscillation, and vise versa [15]. We have realized optomechanically induced transparency [16] and generated squeezed lights in opto-mechanical systems [17]. By using mechanical oscillator as an interface, quantu ...
Haldane charge conjecture in one-dimensional
... D.21 Along the special line V = 2U , the two masses mc,o are equal due to the presence of the extended SU(2) symmetry which rotates the three Majorana fermions ξ 6,7,8 . Within the spin-1 terminology, the interpretation of the phases for U < 0 of Fig. 1 reads as follows: the CDW phase is the Néel p ...
... D.21 Along the special line V = 2U , the two masses mc,o are equal due to the presence of the extended SU(2) symmetry which rotates the three Majorana fermions ξ 6,7,8 . Within the spin-1 terminology, the interpretation of the phases for U < 0 of Fig. 1 reads as follows: the CDW phase is the Néel p ...
Vectors
... Adding perpendicular vectors When two forces act at right angles, you can use the Pythagorean theorem to determine the resultant force. ...
... Adding perpendicular vectors When two forces act at right angles, you can use the Pythagorean theorem to determine the resultant force. ...
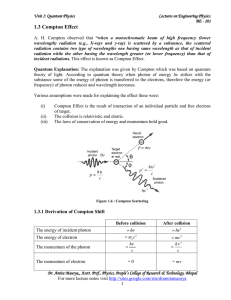
1.3 Compton Effect - IndiaStudyChannel.com
... wavelength) radiation (e.g., X-rays and γ-ray) is scattered by a substance, the scattered radiation contains two type of wavelengths one having same wavelength as that of incident radiation while the other having the wavelength greater (or lower frequency) than that of incident radiations. This effe ...
... wavelength) radiation (e.g., X-rays and γ-ray) is scattered by a substance, the scattered radiation contains two type of wavelengths one having same wavelength as that of incident radiation while the other having the wavelength greater (or lower frequency) than that of incident radiations. This effe ...
Quantum Gaussian Noise - Research Laboratory of Electronics
... frequency ω rad/s, it can then be characterized by a positive-frequency, complex-field envelope E(t) such that P (t) ≡ h̄ω|E(t)|2 is the short-time-average power falling on the sensitive region of the detector at time t. Here, h̄ is Planck’s constant divided by 2π, and so h̄ω is the photon energy at ...
... frequency ω rad/s, it can then be characterized by a positive-frequency, complex-field envelope E(t) such that P (t) ≡ h̄ω|E(t)|2 is the short-time-average power falling on the sensitive region of the detector at time t. Here, h̄ is Planck’s constant divided by 2π, and so h̄ω is the photon energy at ...
Fourier Transform, Period Finding and Factoring in BQP Lecture 4 1
... superposition of states which can be observed, and any measurement can extract at most m = log M bits of information. We now describe a circuit that implements quantum Fourier transform. Step 1: QFTM/2 on the first m − 1 qubits ...
... superposition of states which can be observed, and any measurement can extract at most m = log M bits of information. We now describe a circuit that implements quantum Fourier transform. Step 1: QFTM/2 on the first m − 1 qubits ...