EVALUATION OF A NEW APPROACH IN QUANTUM ATOMIC
... A new approach to teach quantum atomic physics in upper high school has been transmitted to three teachers of ordinary high school with partial success. In one of the three classes all but one objective have been reached by many students. Only the mathematical understanding of the Schrödinger equati ...
... A new approach to teach quantum atomic physics in upper high school has been transmitted to three teachers of ordinary high school with partial success. In one of the three classes all but one objective have been reached by many students. Only the mathematical understanding of the Schrödinger equati ...
Spectrum of quasistable states in a strong infrared
... /4ωIR − F9I2 /4ωIR . This phenomenon can be understood if one imagines that the energy levels of high-lying states are shifted by the ponderomotive energy, thus the resonance is also shifted [17]. The peaks, respectively, are shifted by a different amount because electrons in the IR field with bigge ...
... /4ωIR − F9I2 /4ωIR . This phenomenon can be understood if one imagines that the energy levels of high-lying states are shifted by the ponderomotive energy, thus the resonance is also shifted [17]. The peaks, respectively, are shifted by a different amount because electrons in the IR field with bigge ...
Nuclear and Particle Physics
... Rutherford: Atoms revealed as consisting of electrons orbiting an incredibly dense positively charged nucleus Nucleus comprised of protons (charged) and neutrons (uncharged) - mn~mp ...
... Rutherford: Atoms revealed as consisting of electrons orbiting an incredibly dense positively charged nucleus Nucleus comprised of protons (charged) and neutrons (uncharged) - mn~mp ...
Document
... It is important for you to come to class prepared, i.e. be familiar with the material to be presented. To test your preparedness, a simple five-minute quiz, testing your qualitative familiarity with the material to be discussed in class, will be given at the beginning of some of the classes. No make ...
... It is important for you to come to class prepared, i.e. be familiar with the material to be presented. To test your preparedness, a simple five-minute quiz, testing your qualitative familiarity with the material to be discussed in class, will be given at the beginning of some of the classes. No make ...
ISSN : 2347-7385 Energy Levels Calculations of
... shell with the inclusion of the 0h11/2 intruder state as well. It is now therefore fully possible to work to large-scale shellmodel examinations and study the excitation levels for large systems. In these systems, inter core is assumed and space is determined by considering shell gaps. Figure 1 show ...
... shell with the inclusion of the 0h11/2 intruder state as well. It is now therefore fully possible to work to large-scale shellmodel examinations and study the excitation levels for large systems. In these systems, inter core is assumed and space is determined by considering shell gaps. Figure 1 show ...
Inorganic Chemistry A Self-study exercises Chapters 1,2 and 3 1
... 13.Write down two possible sets of quantum numbers that describe an electron in a 2s atomic orbital. What is the physical significance of these unique sets? 14.Write down two possible sets of quantum numbers to describe an electron in a 3s atomic orbital. 15.If an electron has the quantum numbers n ...
... 13.Write down two possible sets of quantum numbers that describe an electron in a 2s atomic orbital. What is the physical significance of these unique sets? 14.Write down two possible sets of quantum numbers to describe an electron in a 3s atomic orbital. 15.If an electron has the quantum numbers n ...
Theory of Chemical Bonds
... the wave function of the atomic orbitals. During the calculation of the eigenvalues of the Schrödinger equation with equ. 4.15, we get integrals which contain the square of the wave function of an atomic orbital (∫ψ1*H ψ1dτ). These integral represent the Coulomb interaction energy between the electr ...
... the wave function of the atomic orbitals. During the calculation of the eigenvalues of the Schrödinger equation with equ. 4.15, we get integrals which contain the square of the wave function of an atomic orbital (∫ψ1*H ψ1dτ). These integral represent the Coulomb interaction energy between the electr ...
chapter 7 - atomic structure
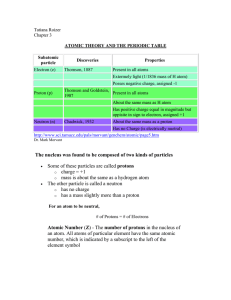
... the space outside the nucleus. The number of protons (referred to as the atomic number) determines the identity of the atom; neutrons provide nuclear stability and together with protons, they account for most of the atomic mass. The atom contains a vast empty space where electrons are supposed to be ...
... the space outside the nucleus. The number of protons (referred to as the atomic number) determines the identity of the atom; neutrons provide nuclear stability and together with protons, they account for most of the atomic mass. The atom contains a vast empty space where electrons are supposed to be ...
Types of Measurement
... 3 Phases (States) of Matter The balance between the attractive forces between the particles and the kinetic energy of the particles determines the phase of matter. 1. High KE of the particles and low attractive forces between the particles = gas. 2. Low KE of the particles and high attractive force ...
... 3 Phases (States) of Matter The balance between the attractive forces between the particles and the kinetic energy of the particles determines the phase of matter. 1. High KE of the particles and low attractive forces between the particles = gas. 2. Low KE of the particles and high attractive force ...
douglas c. giancoli
... the flashes would seem random. Indeed, there is no way to predict just where any one electron would hit the screen. If we let the experiment run for a long time, and kept track of where each electron hit the screen, we would soon see a pattern emerging—the interference pattern predicted by the wave ...
... the flashes would seem random. Indeed, there is no way to predict just where any one electron would hit the screen. If we let the experiment run for a long time, and kept track of where each electron hit the screen, we would soon see a pattern emerging—the interference pattern predicted by the wave ...
Electronic Structure Calculations of InP
... model has been used [10, 11]. It has several functionalities necessary for a proper calculation of this rather complicated quantum structure. The program is able to calculate the energy levels of a QW in a 3D geometric numerical box and it can simultaneously handle QDs of even large sizes, with diff ...
... model has been used [10, 11]. It has several functionalities necessary for a proper calculation of this rather complicated quantum structure. The program is able to calculate the energy levels of a QW in a 3D geometric numerical box and it can simultaneously handle QDs of even large sizes, with diff ...
Word - The Chemistry Book
... three types of radioactivity: alpha particles (+), beta particles (-) and gamma rays (neutral). By performing other experiments and using this information, Rutherford created an atomic model different from Thomson's. Rutherford believed that the atom was mostly empty space. It contains an extremely ...
... three types of radioactivity: alpha particles (+), beta particles (-) and gamma rays (neutral). By performing other experiments and using this information, Rutherford created an atomic model different from Thomson's. Rutherford believed that the atom was mostly empty space. It contains an extremely ...
Lecture 24 (Slides) October 18
... electrons. These atoms are usually chemically unstable. Two such atoms can come together to form a molecule with no unpaired electrons. This process can involve the formation of covalent chemical bonds and is highly exothermic. ...
... electrons. These atoms are usually chemically unstable. Two such atoms can come together to form a molecule with no unpaired electrons. This process can involve the formation of covalent chemical bonds and is highly exothermic. ...
atomic theory and the periodic table
... Each orbital has a name. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. The "1" represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. The "s" tells you about the shape of the orbital. s orbitals are spherically symmetric around the nucleus - in e ...
... Each orbital has a name. The orbital occupied by the hydrogen electron is called a 1s orbital. The "1" represents the fact that the orbital is in the energy level closest to the nucleus. The "s" tells you about the shape of the orbital. s orbitals are spherically symmetric around the nucleus - in e ...
atom a very small particle that makes up most kinds of matters and
... transfer of (heat) energy from one object to another due to a difference in ...
... transfer of (heat) energy from one object to another due to a difference in ...
LCAO Method: H2+ Molecule
... The description of the electronic behavior of atoms and molecules as pertains to their reactivity is an application of quantum chemistry. Since quantum-mechanical studies on atoms are considered to be on the borderline between chemistry and physics, and not always included in quantum chemistry, what ...
... The description of the electronic behavior of atoms and molecules as pertains to their reactivity is an application of quantum chemistry. Since quantum-mechanical studies on atoms are considered to be on the borderline between chemistry and physics, and not always included in quantum chemistry, what ...
Band theory of bonding in metals
... Electromagnetic theory is required to give a more detailed account of the optical properties of metals. Malleability: Moving atoms relative to each other still leaves each atom surrounded by a sea of electrons, so there is little difference in energy on deformation, and thus little resistance to def ...
... Electromagnetic theory is required to give a more detailed account of the optical properties of metals. Malleability: Moving atoms relative to each other still leaves each atom surrounded by a sea of electrons, so there is little difference in energy on deformation, and thus little resistance to def ...
Bohr model
In atomic physics, the Rutherford–Bohr model or Bohr model, introduced by Niels Bohr in 1913, depicts the atom as a small, positively charged nucleus surrounded by electrons that travel in circular orbits around the nucleus—similar in structure to the solar system, but with attraction provided by electrostatic forces rather than gravity. After the cubic model (1902), the plum-pudding model (1904), the Saturnian model (1904), and the Rutherford model (1911) came the Rutherford–Bohr model or just Bohr model for short (1913). The improvement to the Rutherford model is mostly a quantum physical interpretation of it. The Bohr model has been superseded, but the quantum theory remains sound.The model's key success lay in explaining the Rydberg formula for the spectral emission lines of atomic hydrogen. While the Rydberg formula had been known experimentally, it did not gain a theoretical underpinning until the Bohr model was introduced. Not only did the Bohr model explain the reason for the structure of the Rydberg formula, it also provided a justification for its empirical results in terms of fundamental physical constants.The Bohr model is a relatively primitive model of the hydrogen atom, compared to the valence shell atom. As a theory, it can be derived as a first-order approximation of the hydrogen atom using the broader and much more accurate quantum mechanics and thus may be considered to be an obsolete scientific theory. However, because of its simplicity, and its correct results for selected systems (see below for application), the Bohr model is still commonly taught to introduce students to quantum mechanics or energy level diagrams before moving on to the more accurate, but more complex, valence shell atom. A related model was originally proposed by Arthur Erich Haas in 1910, but was rejected. The quantum theory of the period between Planck's discovery of the quantum (1900) and the advent of a full-blown quantum mechanics (1925) is often referred to as the old quantum theory.