Neural Correlates of Selection
... • Question: does attention modulate spike rate of neurons that respond to visual stimuli? ...
... • Question: does attention modulate spike rate of neurons that respond to visual stimuli? ...
مواصفات مقرر الأصول الفلسفية للتربية
... - Distinguish between the gene pool of a population and the genotype of an individual. - Discuss the factors that can alter the gene frequencies in populations. - Distinguish between stabilizing selection, directional selection, and disruptive selection. ...
... - Distinguish between the gene pool of a population and the genotype of an individual. - Discuss the factors that can alter the gene frequencies in populations. - Distinguish between stabilizing selection, directional selection, and disruptive selection. ...
Theory of Evolution and its Impact
... In his Autobiography, written towards the end of his life, Darwin wrote of the Origin as containing “one long argument” ([6], p. 140). But what was this argument? Actually it came in several (at least three) parts. In a letter written a year or two after the Origin was first published, Darwin made e ...
... In his Autobiography, written towards the end of his life, Darwin wrote of the Origin as containing “one long argument” ([6], p. 140). But what was this argument? Actually it came in several (at least three) parts. In a letter written a year or two after the Origin was first published, Darwin made e ...
Evolutionary rescue and the limits of adaptation
... inadequate to fuel appreciable change in the short term of a few dozen generations. Any species can then be regarded as having a fixed set of attributes during the period of an ecological study. At the same time, evolutionary theory was often almost devoid of ecological context. In particular, the d ...
... inadequate to fuel appreciable change in the short term of a few dozen generations. Any species can then be regarded as having a fixed set of attributes during the period of an ecological study. At the same time, evolutionary theory was often almost devoid of ecological context. In particular, the d ...
- Philsci-Archive
... work.7 But again the myth covers up the different theoretical and methodological approaches of these ‘re-discoverers’, as well as their differences with Mendel--different experimental methods, different mathematical techniques, different theoretical presuppositions and conclusions drawn. In this cas ...
... work.7 But again the myth covers up the different theoretical and methodological approaches of these ‘re-discoverers’, as well as their differences with Mendel--different experimental methods, different mathematical techniques, different theoretical presuppositions and conclusions drawn. In this cas ...
Natural Selection and Developmental Constraints in the Evolution of
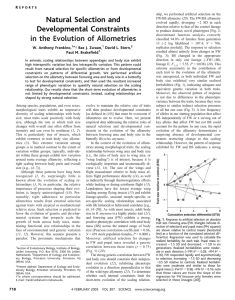
... these traits respond indirectly to direct selection on their scaling relationship. Hence, the allometry itself is not developmentally constrained; what does appear to be constrained is the way in which the individual components contribute to the evolution of this complex phenotype. Our results, toge ...
... these traits respond indirectly to direct selection on their scaling relationship. Hence, the allometry itself is not developmentally constrained; what does appear to be constrained is the way in which the individual components contribute to the evolution of this complex phenotype. Our results, toge ...
Mendelian Inheritance
... do the poets of the present not speak of it? What men are poets who can speak of Jupiter if he were a man, but if he is an immense spinning sphere of methane and ammonia must be silent? -Richard Feynman ...
... do the poets of the present not speak of it? What men are poets who can speak of Jupiter if he were a man, but if he is an immense spinning sphere of methane and ammonia must be silent? -Richard Feynman ...
18 Return of the Hopeful Monster
... grooves in burrowing animals to transport soil, for example) and rejected them all in favor of discontinuous transition. These tales, in the "just-so story" tradition of evolutionary natural history, do not prove anything. But the weight of these, and many similar cases, wore down my faith in gradua ...
... grooves in burrowing animals to transport soil, for example) and rejected them all in favor of discontinuous transition. These tales, in the "just-so story" tradition of evolutionary natural history, do not prove anything. But the weight of these, and many similar cases, wore down my faith in gradua ...
Darwin`s Theory of Evolution
... Before Darwin’s time, most Europeans believed that Earth and all life forms: 1. were created only a few 1000 years ago 2. had not changed since creation During Darwin’s life, a lot of evidence was discovered to change this way of thought This made Darwin dramatically change his way of thinking. ...
... Before Darwin’s time, most Europeans believed that Earth and all life forms: 1. were created only a few 1000 years ago 2. had not changed since creation During Darwin’s life, a lot of evidence was discovered to change this way of thought This made Darwin dramatically change his way of thinking. ...
Evolution - Auburn University
... heritable (this was expanded by others later, as genetics came to be understood) ...
... heritable (this was expanded by others later, as genetics came to be understood) ...
Chapter 7
... think that species could evolve over time. It became clear to Darwin that Earth was much older than anyone had imagined. ...
... think that species could evolve over time. It became clear to Darwin that Earth was much older than anyone had imagined. ...
Hardy-Weinberg Theorem Charles Darwin`s unique contribution to
... Hardy-Weinberg Theorem Charles Darwin’s unique contribution to biology was not that he “discovered evolution”, but rather, that he proposed a mechanism for evolutionary change ….natural selection, the differential survival and reproduction of the individuals in a population. In On the Origin of Spec ...
... Hardy-Weinberg Theorem Charles Darwin’s unique contribution to biology was not that he “discovered evolution”, but rather, that he proposed a mechanism for evolutionary change ….natural selection, the differential survival and reproduction of the individuals in a population. In On the Origin of Spec ...
less would have been more1 - Stephen Stearns
... their chromosomal genes, do not easily cause genomic conflicts. Replicating units that occur in many copies and whose replication and segregation are not strictly controlled, such as cytoplasmic genetic elements, more easily cause genomic conflict. Sexual organisms are more prone to experience genom ...
... their chromosomal genes, do not easily cause genomic conflicts. Replicating units that occur in many copies and whose replication and segregation are not strictly controlled, such as cytoplasmic genetic elements, more easily cause genomic conflict. Sexual organisms are more prone to experience genom ...
EVOLUTION - Cloudfront.net
... Darwin’s Theory Darwin didn’t publish his ideas for 20 years! Darwin published On the Origins of Species in 1859. It provides evidence that evolution has occurred by NATURAL SELECTION. ...
... Darwin’s Theory Darwin didn’t publish his ideas for 20 years! Darwin published On the Origins of Species in 1859. It provides evidence that evolution has occurred by NATURAL SELECTION. ...
File
... members of the same species. Mutation, meiosis and sexual reproduction cause variation between individuals in a species. Adaptations are characteristics that make an individual suited to its environment and way of life. Species tend to produce more offspring than the environment can support. Individ ...
... members of the same species. Mutation, meiosis and sexual reproduction cause variation between individuals in a species. Adaptations are characteristics that make an individual suited to its environment and way of life. Species tend to produce more offspring than the environment can support. Individ ...
Study Guide for Exam 2 – Biol-1, C. Briggs, revised Fall 2015 Test
... - why does DNA replication come before the chromosomes condense in prophase? 4. explain how the following contribute to genetic variation in sexual reproduction: independent assortment of chromosomes, random fertilization, crossing over. 5. Other big questions: These are beyond the scope of our text ...
... - why does DNA replication come before the chromosomes condense in prophase? 4. explain how the following contribute to genetic variation in sexual reproduction: independent assortment of chromosomes, random fertilization, crossing over. 5. Other big questions: These are beyond the scope of our text ...
Study Guide for Exam 2 – Biol-1, C. Briggs, revised Fall 2015 Test
... - why does DNA replication come before the chromosomes condense in prophase? 4. explain how the following contribute to genetic variation in sexual reproduction: independent assortment of chromosomes, random fertilization, crossing over. 5. Other big questions: These are beyond the scope of our text ...
... - why does DNA replication come before the chromosomes condense in prophase? 4. explain how the following contribute to genetic variation in sexual reproduction: independent assortment of chromosomes, random fertilization, crossing over. 5. Other big questions: These are beyond the scope of our text ...
Aspects of unconscious selection and the evolution of domesticated
... Unconscious selection did not operate in the evolution of the domesticates until man deliberately planted seeds . This was a conscious act on the part of man to secure more plants - either directly, or indirectly as an appeasement to the gods to ensure bountiful harvests in the future (Heiser, 1985) ...
... Unconscious selection did not operate in the evolution of the domesticates until man deliberately planted seeds . This was a conscious act on the part of man to secure more plants - either directly, or indirectly as an appeasement to the gods to ensure bountiful harvests in the future (Heiser, 1985) ...
Hindu Paradigm of Evolution
... The integration of holistic cosmic thought with the theory of evolution is important not just for biology but also for all branches of humanities and social sciences. Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection has been used to justify models of individualistic growth whether of an individual or of a c ...
... The integration of holistic cosmic thought with the theory of evolution is important not just for biology but also for all branches of humanities and social sciences. Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection has been used to justify models of individualistic growth whether of an individual or of a c ...
Experimentally assessing the relative
... but predation treatments did not alter selection on phenotypic traits. By contrast, experimentally increasing population density dramatically increased the strength of viability selection favouring large body size, long relative limb length and high running stamina. Our results from A. sagrei are co ...
... but predation treatments did not alter selection on phenotypic traits. By contrast, experimentally increasing population density dramatically increased the strength of viability selection favouring large body size, long relative limb length and high running stamina. Our results from A. sagrei are co ...
Natural Selection and Evolution
... Theory of Natural Selection Those individuals with the traits most suitable to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce and pass those traits on to the next generation. Thursday, January 17, 2013 ...
... Theory of Natural Selection Those individuals with the traits most suitable to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce and pass those traits on to the next generation. Thursday, January 17, 2013 ...
evol-art
... benefits and pitfalls of creative evolutionary computation. Evolution can find solutions that disregard our conventions and theories. Efficient new designs have been evolved, and unusual art. ...
... benefits and pitfalls of creative evolutionary computation. Evolution can find solutions that disregard our conventions and theories. Efficient new designs have been evolved, and unusual art. ...
Influences on Darwin
... 1. Jean Baptiste Lamarck (1744–1829) was an important French naturalist. He was one of the first scientists to propose that species change over time. However, Lamarck was wrong about how species change. His idea of the inheritance of acquired characteristics is incorrect. Traits an organism develops ...
... 1. Jean Baptiste Lamarck (1744–1829) was an important French naturalist. He was one of the first scientists to propose that species change over time. However, Lamarck was wrong about how species change. His idea of the inheritance of acquired characteristics is incorrect. Traits an organism develops ...
Natural selection

Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype; it is a key mechanism of evolution. The term ""natural selection"" was popularised by Charles Darwin, who intended it to be compared with artificial selection, now more commonly referred to as selective breeding.Variation exists within all populations of organisms. This occurs partly because random mutations arise in the genome of an individual organism, and these mutations can be passed to offspring. Throughout the individuals’ lives, their genomes interact with their environments to cause variations in traits. (The environment of a genome includes the molecular biology in the cell, other cells, other individuals, populations, species, as well as the abiotic environment.) Individuals with certain variants of the trait may survive and reproduce more than individuals with other, less successful, variants. Therefore, the population evolves. Factors that affect reproductive success are also important, an issue that Darwin developed in his ideas on sexual selection, which was redefined as being included in natural selection in the 1930s when biologists considered it not to be very important, and fecundity selection, for example.Natural selection acts on the phenotype, or the observable characteristics of an organism, but the genetic (heritable) basis of any phenotype that gives a reproductive advantage may become more common in a population (see allele frequency). Over time, this process can result in populations that specialise for particular ecological niches (microevolution) and may eventually result in the emergence of new species (macroevolution). In other words, natural selection is an important process (though not the only process) by which evolution takes place within a population of organisms. Natural selection can be contrasted with artificial selection, in which humans intentionally choose specific traits (although they may not always get what they want). In natural selection there is no intentional choice. In other words, artificial selection is teleological and natural selection is not teleological.Natural selection is one of the cornerstones of modern biology. The concept was published by Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace in a joint presentation of papers in 1858, and set out in Darwin's influential 1859 book On the Origin of Species, in which natural selection was described as analogous to artificial selection, a process by which animals and plants with traits considered desirable by human breeders are systematically favoured for reproduction. The concept of natural selection was originally developed in the absence of a valid theory of heredity; at the time of Darwin's writing, nothing was known of modern genetics. The union of traditional Darwinian evolution with subsequent discoveries in classical and molecular genetics is termed the modern evolutionary synthesis. Natural selection remains the primary explanation for adaptive evolution.