Theoretical Physics (Mathematical and Computitional Physics
... 3.3 Atk79 P.W. Atkins, Quanta, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1979. 3.3 Atk97 P.W. Atkins, R.S. Friedman, Molecular Quantum Mechanics (3rd ed.), Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1997. 3.3 Bro67 G.E. Brown, Lectures on Many-Body Problems, Vol. I & II, Nordita, Copenhagen, 1967. 3.3 Cal58 J. Callaway, Elect ...
... 3.3 Atk79 P.W. Atkins, Quanta, Clarendon Press, Oxford, 1979. 3.3 Atk97 P.W. Atkins, R.S. Friedman, Molecular Quantum Mechanics (3rd ed.), Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1997. 3.3 Bro67 G.E. Brown, Lectures on Many-Body Problems, Vol. I & II, Nordita, Copenhagen, 1967. 3.3 Cal58 J. Callaway, Elect ...
File
... The Quantum World describes the world of … The microscopic world is very __________ and does not follow the same rules as larger objects, what we call ______________ objects. For example: ...
... The Quantum World describes the world of … The microscopic world is very __________ and does not follow the same rules as larger objects, what we call ______________ objects. For example: ...
Holonomic quantum computation with neutral atoms
... [1] is a dynamical one: in order to manipulate the quantum state of systems encoding information, local interactions between low dimensional subsystems (qubits) are switched on and off in such a way to enact a sequence of quantum gates. On the other hand, ever since the discovery of the Berry’s phase ...
... [1] is a dynamical one: in order to manipulate the quantum state of systems encoding information, local interactions between low dimensional subsystems (qubits) are switched on and off in such a way to enact a sequence of quantum gates. On the other hand, ever since the discovery of the Berry’s phase ...
The Learnability of Quantum States
... BQP (Bounded-Error Quantum Polynomial-Time): The class of problems solvable efficiently by aInteresting quantum computer, defined by Bernstein and Vazirani in 1993 ...
... BQP (Bounded-Error Quantum Polynomial-Time): The class of problems solvable efficiently by aInteresting quantum computer, defined by Bernstein and Vazirani in 1993 ...
Pt-Symmetric Scarf-II Potential :an Update
... Renormalization : Sweeping the infinites under the rug. EPR Paradox and Antiparticles. Quantum Mechanics in complex spacetime. The Miracle of creation. Conservation of Angular momentum(a.k.a. ...
... Renormalization : Sweeping the infinites under the rug. EPR Paradox and Antiparticles. Quantum Mechanics in complex spacetime. The Miracle of creation. Conservation of Angular momentum(a.k.a. ...
Titles and Abstracts
... transgression ideas, and provide explicit examples with physical significance. Eyal Subag (Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, Israel) Title: Contraction of so(n) representations via the Gelfand-Tsetlin bases Abstract: We realize any skew-Hermitian integrable representation of iso(n-1) as a con ...
... transgression ideas, and provide explicit examples with physical significance. Eyal Subag (Technion-Israel Institute of Technology, Israel) Title: Contraction of so(n) representations via the Gelfand-Tsetlin bases Abstract: We realize any skew-Hermitian integrable representation of iso(n-1) as a con ...
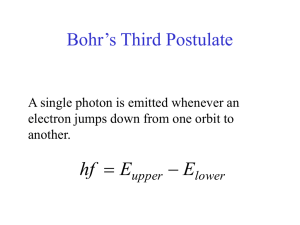
Bohr´s Third Postulate
... At any point the square of the electric field strength is a measure of the probability that a photon will be at that location. ...
... At any point the square of the electric field strength is a measure of the probability that a photon will be at that location. ...
Chapter 1 Statistical Mechanics of Quantum Dots Chapter 2 Artificial
... finite number of electrons usually demonstrate behavior that is called quantum chaos.' This behavior can be caused by disorder, the geometry of a quantum dot, or interactions between electrons. The phenomenon of quantum chaos was intensively studied by Berry for several years.2 However, attention wa ...
... finite number of electrons usually demonstrate behavior that is called quantum chaos.' This behavior can be caused by disorder, the geometry of a quantum dot, or interactions between electrons. The phenomenon of quantum chaos was intensively studied by Berry for several years.2 However, attention wa ...
Computational Complexity and Fundamental Physics
... unwanted interaction between a QC and its external environment, “prematurely measuring” the quantum state A few skeptics, in CS and physics, even argue that building a QC will be fundamentally impossible I don’t expect them to be right, but I hope they are! If so, it would be a revolution in physics ...
... unwanted interaction between a QC and its external environment, “prematurely measuring” the quantum state A few skeptics, in CS and physics, even argue that building a QC will be fundamentally impossible I don’t expect them to be right, but I hope they are! If so, it would be a revolution in physics ...
Atomic Spectroscopy and the Correspondence Principle
... required by classical electromagnetic principles. Initial speculation, however, suggested that the observed line spectrum of the hydrogen atom might be interpeted in terms of electromagnetic emissions related to orbital frequencies of the electron. Subsequently, Bohr achieved agreement with experime ...
... required by classical electromagnetic principles. Initial speculation, however, suggested that the observed line spectrum of the hydrogen atom might be interpeted in terms of electromagnetic emissions related to orbital frequencies of the electron. Subsequently, Bohr achieved agreement with experime ...
Lorentz Invaiance Violation and Granularity of space time
... What is the operational definition of geodesic, when we test the world with extended objects? The path of the center of mass? NO! What are in principle the geodesics of the geometry, or the geometry itself, when all we have to explore it, are quantum particles ( in fact, quantum fields)? There is to ...
... What is the operational definition of geodesic, when we test the world with extended objects? The path of the center of mass? NO! What are in principle the geodesics of the geometry, or the geometry itself, when all we have to explore it, are quantum particles ( in fact, quantum fields)? There is to ...
The Ghost in the Atom, Ed. by P.C.W. Davies and J.R. Brown
... phenomenon, but they have also altered in a profound sense, our view of the natural world. The enviable success of Quantum Mechanics has however been somewhat marred by the deep conceptual problems which it throws up. Of course, for most practicing scientists, the successful explanation of physical ...
... phenomenon, but they have also altered in a profound sense, our view of the natural world. The enviable success of Quantum Mechanics has however been somewhat marred by the deep conceptual problems which it throws up. Of course, for most practicing scientists, the successful explanation of physical ...
Quantum Computing
... A bit of data is represented by a single atom that is in one of two states denoted by |0> and |1>. A single bit of this form is known as a qubit A physical implementation of a qubit could use the two energy levels of an atom. An excited state representing |1> and a ground state representing |0>. Lig ...
... A bit of data is represented by a single atom that is in one of two states denoted by |0> and |1>. A single bit of this form is known as a qubit A physical implementation of a qubit could use the two energy levels of an atom. An excited state representing |1> and a ground state representing |0>. Lig ...
Quantum mechanic and Particle physics
... • Particle like behavior: under some circumstances, quantum objects do things that are similar to ordinary particles. • Wave like behavior: under other circumstances they do thing like ordinary waves. • Indeterminate behavior: some things about quantum particles are indeterminate, but not totally ...
... • Particle like behavior: under some circumstances, quantum objects do things that are similar to ordinary particles. • Wave like behavior: under other circumstances they do thing like ordinary waves. • Indeterminate behavior: some things about quantum particles are indeterminate, but not totally ...
Eighth International Conference on Geometry, Integrability and Quantization
... originating from the works of Witten et al [8–10] may be helpful in searches for the truly fundamental physical theory and in the treatment of important mathematical problems. The main feature of topological theories is the independence of the correlation functions on metrics and coordinates [1]. In ...
... originating from the works of Witten et al [8–10] may be helpful in searches for the truly fundamental physical theory and in the treatment of important mathematical problems. The main feature of topological theories is the independence of the correlation functions on metrics and coordinates [1]. In ...
Wave function collapse
... To be more specific, in the discrete random collapse model, for instance, with a frequency of spontaneous collapses of, e.g., 1017 s−1 the wave function of a microscopic system will collapse about once in 1010 years, the age of the universe, while a macroscopic body with typically 1023 degrees of fr ...
... To be more specific, in the discrete random collapse model, for instance, with a frequency of spontaneous collapses of, e.g., 1017 s−1 the wave function of a microscopic system will collapse about once in 1010 years, the age of the universe, while a macroscopic body with typically 1023 degrees of fr ...
Instructor: Dr. Ju Xin
... References: “Modern Physics for Scientists and Engineers” By Stephen T. Thornton, Andrew F. Rex - Thomson, Brooks/Cole (2006) - Hardback - 672 pages - ISBN 0534417817 Coverage: The first 10 chapters form the core contents of modern and atomic physics. We will selectively cover most of these chapters ...
... References: “Modern Physics for Scientists and Engineers” By Stephen T. Thornton, Andrew F. Rex - Thomson, Brooks/Cole (2006) - Hardback - 672 pages - ISBN 0534417817 Coverage: The first 10 chapters form the core contents of modern and atomic physics. We will selectively cover most of these chapters ...