Genes Involved in the Uptake and Catabolism of
... colonies. They were found to be still devoid of PEP-carboxylase activity, and would therefore not grow on any hexose or other substrate which requires this anaplerotic enzyme for catabolism, until theppc+ allele had been introduced. This was done by infecting suspensions of the organisms with phage ...
... colonies. They were found to be still devoid of PEP-carboxylase activity, and would therefore not grow on any hexose or other substrate which requires this anaplerotic enzyme for catabolism, until theppc+ allele had been introduced. This was done by infecting suspensions of the organisms with phage ...
Genes Involved in the Uptake and Catabolism of
... colonies. They were found to be still devoid of PEP-carboxylase activity, and would therefore not grow on any hexose or other substrate which requires this anaplerotic enzyme for catabolism, until theppc+ allele had been introduced. This was done by infecting suspensions of the organisms with phage ...
... colonies. They were found to be still devoid of PEP-carboxylase activity, and would therefore not grow on any hexose or other substrate which requires this anaplerotic enzyme for catabolism, until theppc+ allele had been introduced. This was done by infecting suspensions of the organisms with phage ...
Gene Section WWC1 (WW and C2 domain containing 1)
... kinase aurora and is required for precise mitotic spindle assembly and chromosome alignment (Xiao et al., 2011b; Zhang et al., 2012). Additionally, KIBRA is also regulated by cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) and cell division cycle 14A/B phosphatases (CDC14A, CDC14B) and thus regulates cell-cycle pr ...
... kinase aurora and is required for precise mitotic spindle assembly and chromosome alignment (Xiao et al., 2011b; Zhang et al., 2012). Additionally, KIBRA is also regulated by cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (CDK1) and cell division cycle 14A/B phosphatases (CDC14A, CDC14B) and thus regulates cell-cycle pr ...
The Rad50 Signature Motif: Essential to ATP Binding and
... manganese ions for catalysis and form a DNAbinding groove that can accommodate a doublestranded DNA end.10 In vitro, Mre11 homologs exhibit 30 to 50 exonuclease activity on DNA substrates, as well as endonuclease activity on constrained structures such as hairpin ends.11 – 16 In every organism studi ...
... manganese ions for catalysis and form a DNAbinding groove that can accommodate a doublestranded DNA end.10 In vitro, Mre11 homologs exhibit 30 to 50 exonuclease activity on DNA substrates, as well as endonuclease activity on constrained structures such as hairpin ends.11 – 16 In every organism studi ...
THE ROLE OF THE ret PROTO-ONCOGENE IN HUMAN DISEASE
... As mentioned above, the MEN 2B mutation is present in the catalytic core region of the tyrosine kinase domain. Thus, it is conceivable that the mutation induces a conformational change in this region and activates Ret by an intramolecular mechanism, resulting in an enhancement of its intrinsic tyros ...
... As mentioned above, the MEN 2B mutation is present in the catalytic core region of the tyrosine kinase domain. Thus, it is conceivable that the mutation induces a conformational change in this region and activates Ret by an intramolecular mechanism, resulting in an enhancement of its intrinsic tyros ...
Gene Section ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... NPM1 fused to the 562 C-term aminoacids of ALK (i.e. composed of the oligomerization domain and the metal binding site of NPM1, and the entire cytoplasmic portion of ALK); no apparent expres-sion of the ALK/NPM1 counterpart. Characteristic localisation both in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus, due t ...
... NPM1 fused to the 562 C-term aminoacids of ALK (i.e. composed of the oligomerization domain and the metal binding site of NPM1, and the entire cytoplasmic portion of ALK); no apparent expres-sion of the ALK/NPM1 counterpart. Characteristic localisation both in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus, due t ...
PKB - Friedrich Miescher Institute for Biomedical Research
... Mutations of PI3K pathway genes in colorectal cancer Amino acid changes or amplifications observed for each gene in 146 colorectal cancers. When two mutations in the same gene in a tumor were observed, the mutations are separated by a slash. "Amp" indicates amplification, "wt" indicates wild-type s ...
... Mutations of PI3K pathway genes in colorectal cancer Amino acid changes or amplifications observed for each gene in 146 colorectal cancers. When two mutations in the same gene in a tumor were observed, the mutations are separated by a slash. "Amp" indicates amplification, "wt" indicates wild-type s ...
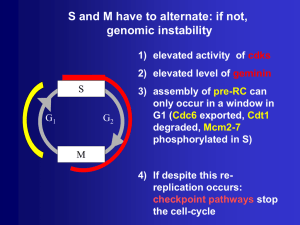
No Slide Title
... tools for cancer screening or detection of relapse • Since the cell-cycle is essential for cell-proliferation, inhibitors of the cell-cycle are anti-proliferative agents useful in a variety of clinical settings (cancer, inflammation, re-stenosis following angioplasty) • Some anomalies in cell-cycle ...
... tools for cancer screening or detection of relapse • Since the cell-cycle is essential for cell-proliferation, inhibitors of the cell-cycle are anti-proliferative agents useful in a variety of clinical settings (cancer, inflammation, re-stenosis following angioplasty) • Some anomalies in cell-cycle ...
Gene Section LIMK1 (LIM domain kinase 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Through cytogenetics method such as CGH and FISH analysis chromosomal gain in 7q11.2 region or entire chromosome 7 including 7q11.23 locus has been reported in some prostate cancer cases. Oncogenesis LIMK1 is overexpressed in prostate cancer cells and tissues compared to benign prostatic hyperplasia ...
... Through cytogenetics method such as CGH and FISH analysis chromosomal gain in 7q11.2 region or entire chromosome 7 including 7q11.23 locus has been reported in some prostate cancer cases. Oncogenesis LIMK1 is overexpressed in prostate cancer cells and tissues compared to benign prostatic hyperplasia ...
Gene Section JAK3 (janus kinase 3 or just another kinase 3)
... heterozygotes, having inherited a distinct mutation from each parent, although some individuals are homozygous for their mutations as a result of parental consanguinity. Most mutations have dramatic effects on protein expression of JAK3, but some missense mutations or small in-frame deletions allow ...
... heterozygotes, having inherited a distinct mutation from each parent, although some individuals are homozygous for their mutations as a result of parental consanguinity. Most mutations have dramatic effects on protein expression of JAK3, but some missense mutations or small in-frame deletions allow ...
Gene Section ALK (anaplastic lymphoma kinase) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... Hybrid/Mutated gene 5' NPM1-3' ALK on the der(5). Abnormal protein 680 amino acids, 80 kDa; N-term 116 amino acids from NPM1 fused to the 563 C-term aminoacids of ALK (i.e. composed of the oligomerization domain and the metal binding site of NPM1, and the entire cytoplasmic portion of ALK); no appar ...
... Hybrid/Mutated gene 5' NPM1-3' ALK on the der(5). Abnormal protein 680 amino acids, 80 kDa; N-term 116 amino acids from NPM1 fused to the 563 C-term aminoacids of ALK (i.e. composed of the oligomerization domain and the metal binding site of NPM1, and the entire cytoplasmic portion of ALK); no appar ...
C-Src Kinase Inhibition: A Promising Route in Kidney Cancer
... C-Src kinase is a non receptor tyrosine kinase, encoded by the c-Src (cellular-Src) gene (Src pronounced “sarc”, which is short for sarcoma, a cancer type which derives from changed connective tissue cells) C-Src protein acts as a signal transduction inhibitor that is a critical component of multipl ...
... C-Src kinase is a non receptor tyrosine kinase, encoded by the c-Src (cellular-Src) gene (Src pronounced “sarc”, which is short for sarcoma, a cancer type which derives from changed connective tissue cells) C-Src protein acts as a signal transduction inhibitor that is a critical component of multipl ...
Activation of the JNK pathway during dorsal closure in Drosophila
... mutant embryos revealed molecular lesions associated with this locus. In fact, cDNA from both slpr alleles harbored a single-point mutation within the MLKcoding region. These lesions were verified to be present in slpr mutant genomic DNA, indicating that slpr encodes Drosophila MLK. Figure 3D shows ...
... mutant embryos revealed molecular lesions associated with this locus. In fact, cDNA from both slpr alleles harbored a single-point mutation within the MLKcoding region. These lesions were verified to be present in slpr mutant genomic DNA, indicating that slpr encodes Drosophila MLK. Figure 3D shows ...
Gene Section JAK2 (janus kinase 2) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... 25 exons spanning roughly 140 kb of genomic DNA; 5402 bp pre-mRNA; 6 different transcripts, putatively encoding 4 different protein isoforms. ...
... 25 exons spanning roughly 140 kb of genomic DNA; 5402 bp pre-mRNA; 6 different transcripts, putatively encoding 4 different protein isoforms. ...
A chimaeric glutamyl:glutaminyl-tRNA synthetase: implications for
... ancestor consisted of only the class-defining catalytic domain. After eubacteria and archaea/eukaryotes split, the two lineages independently acquired two structurally distinct anti-codon binding domains: (1) the bacterial kingdom acquired the helicalcage anti-codon binding domains found in extant e ...
... ancestor consisted of only the class-defining catalytic domain. After eubacteria and archaea/eukaryotes split, the two lineages independently acquired two structurally distinct anti-codon binding domains: (1) the bacterial kingdom acquired the helicalcage anti-codon binding domains found in extant e ...
ALK
... => alterations in drug binding, more so than changes in kinase activity, are probably the primary mechanism underlying resistance of C1156Y–L1198F to lorlatinib and sensitivity to crizotinib ...
... => alterations in drug binding, more so than changes in kinase activity, are probably the primary mechanism underlying resistance of C1156Y–L1198F to lorlatinib and sensitivity to crizotinib ...
Molecular Genetic Testing For BRAF Mutations
... mutation has been reported in approximately 57% of Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) lesions. The high prevalence of BRAF mutations in LCH indicates that LCH is a neoplastic disease that may respond to RAF pathway inhibitors. The presence or absence of the BRAF V600E mutation in a tumor alone does ...
... mutation has been reported in approximately 57% of Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH) lesions. The high prevalence of BRAF mutations in LCH indicates that LCH is a neoplastic disease that may respond to RAF pathway inhibitors. The presence or absence of the BRAF V600E mutation in a tumor alone does ...
Identification of eight novel coagulation factor XIII subunit A
... FXIII deficiency is more common, but usually not associated with severe haemorrhage such as intracranial bleeding and haemarthrosis. In most cases, the disease is caused by F13A gene mutations. Causative mutations associated with the F13B gene are rarer. Design and Methods. We analysed ten index pat ...
... FXIII deficiency is more common, but usually not associated with severe haemorrhage such as intracranial bleeding and haemarthrosis. In most cases, the disease is caused by F13A gene mutations. Causative mutations associated with the F13B gene are rarer. Design and Methods. We analysed ten index pat ...
Gene Section PDGFRA (platelet-derived growth factor receptor, alpha polypeptide)
... Regulation: Function as homo- and/or heterodimers depending on the cell type; activated by ligandinduced dimerization and autophosphorylation on specific tyrosine residues upon binding. Activation of the intracellular kinase activity of the receptor leads to creation of docking sites for signal tran ...
... Regulation: Function as homo- and/or heterodimers depending on the cell type; activated by ligandinduced dimerization and autophosphorylation on specific tyrosine residues upon binding. Activation of the intracellular kinase activity of the receptor leads to creation of docking sites for signal tran ...
AzotoOxidativePhosphorylation
... Our most interesting finding was another operon, Avin19660-Avin19750, that encodes another Ftype ATP synthase distinct from the evolutionarily conserved F-type ATP synthase encoded by Avin52230-52150. This operon’s best hits are to Burkholderia species which are in a different group (Azotobacter a ...
... Our most interesting finding was another operon, Avin19660-Avin19750, that encodes another Ftype ATP synthase distinct from the evolutionarily conserved F-type ATP synthase encoded by Avin52230-52150. This operon’s best hits are to Burkholderia species which are in a different group (Azotobacter a ...
Click
... bonds? (Draw Gleevec and indicate the groups by circling). 12) Looking at the Abl structure, name the residues that appear to hydrogen bond to Gleevec and give the distances between the atoms. Draw these on your Gleevec structure. Hint: there are 4 possible hydrogen bonds within 3.0 Å . Note that on ...
... bonds? (Draw Gleevec and indicate the groups by circling). 12) Looking at the Abl structure, name the residues that appear to hydrogen bond to Gleevec and give the distances between the atoms. Draw these on your Gleevec structure. Hint: there are 4 possible hydrogen bonds within 3.0 Å . Note that on ...
Creatine Kinase Activity in Cultures of Differentiating Myoblasts The
... creatine kinase activity/mg of DNA until 69h in culture, but by 96h the creatine kinase activity/,ug of DNA was 20-fold higher than its initial value at 33h. Creatine kinase activity was assayed by measuring fluorimetrically the creatine produced by the back-reaction of the enzyme (Koedam, 1969). Th ...
... creatine kinase activity/mg of DNA until 69h in culture, but by 96h the creatine kinase activity/,ug of DNA was 20-fold higher than its initial value at 33h. Creatine kinase activity was assayed by measuring fluorimetrically the creatine produced by the back-reaction of the enzyme (Koedam, 1969). Th ...
Gene Section MELK (maternal embryonic leucine zipper kinase) in Oncology and Haematology
... 2007) and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase (ASK1) (Jung et al., 2008) and in inhibition of mRNA splicing during mitosis via its association with NIPP1 (Vulsteke et al., 2004). MELK function is required for mammary tumorigenesis in vivo (Hebbard et al., 2010). ...
... 2007) and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase (ASK1) (Jung et al., 2008) and in inhibition of mRNA splicing during mitosis via its association with NIPP1 (Vulsteke et al., 2004). MELK function is required for mammary tumorigenesis in vivo (Hebbard et al., 2010). ...
Gene Section DUSP1 (dual specificity phosphatase 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... comprising a C-terminal cysteine-dependent protein tyrosine phosphatase active site sequence (Camps et al., 2000). The structure of DUSP proteins confers phosphatase activity for both phospho-serine/threonine and phospho-tyrosine residues. The non-catalytic Nterminal region contains a rhodanese doma ...
... comprising a C-terminal cysteine-dependent protein tyrosine phosphatase active site sequence (Camps et al., 2000). The structure of DUSP proteins confers phosphatase activity for both phospho-serine/threonine and phospho-tyrosine residues. The non-catalytic Nterminal region contains a rhodanese doma ...
BRAF (gene)
BRAF is a human gene that makes a protein called B-Raf. The gene is also referred to as proto-oncogene B-Raf and v-Raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B, while the protein is more formally known as serine/threonine-protein kinase B-Raf.The B-Raf protein is involved in sending signals inside cells, which are involved in directing cell growth. In 2002, it was shown to be faulty (mutated) in some human cancers.Certain other inherited BRAF mutations cause birth defects.Drugs that treat cancers driven by BRAF mutations have been developed. Two of these drugs, vemurafenib and dabrafenib are approved by FDA for treatment of late-stage melanoma. Vemurafenib was the first drug to come out of fragment-based drug discovery.