Teacher notes and student sheets
... Scientists and other thinkers don’t come up with ideas/theories in isolation. They are influenced by other ideas from people who came before them or are publishing ideas at the same time. Sometimes one idea builds on another to develop a theory. In other cases, disagreement over the best theory (ie ...
... Scientists and other thinkers don’t come up with ideas/theories in isolation. They are influenced by other ideas from people who came before them or are publishing ideas at the same time. Sometimes one idea builds on another to develop a theory. In other cases, disagreement over the best theory (ie ...
Teacher notes and student sheets
... Scientists and other thinkers don’t come up with ideas/theories in isolation. They are influenced by other ideas from people who came before them or are publishing ideas at the same time. Sometimes one idea builds on another to develop a theory. In other cases, disagreement over the best theory (ie ...
... Scientists and other thinkers don’t come up with ideas/theories in isolation. They are influenced by other ideas from people who came before them or are publishing ideas at the same time. Sometimes one idea builds on another to develop a theory. In other cases, disagreement over the best theory (ie ...
Evolution is
... Tortoises- noticed different shaped shells which allowed for different neck movement based on the environment ...
... Tortoises- noticed different shaped shells which allowed for different neck movement based on the environment ...
B. Inference 1
... 1. Increases the number of homozygotes and decreases number of heterozygotes a) With random mating you might expect 1:2:1 ratio of genotypes, but with nonrandom mating you might get a 1:1:1 ratio b) AA x AA = AA + AA; aa x aa = aa + aa; Aa x Aa = AA + Aa + Aa + aa 2. Allelic frequency does not chang ...
... 1. Increases the number of homozygotes and decreases number of heterozygotes a) With random mating you might expect 1:2:1 ratio of genotypes, but with nonrandom mating you might get a 1:1:1 ratio b) AA x AA = AA + AA; aa x aa = aa + aa; Aa x Aa = AA + Aa + Aa + aa 2. Allelic frequency does not chang ...
Evolutionary Theory, according to Darwin
... • Culture change is not linear or progressive. Change is locally determined by the setting and the essential features that relate folks to that setting. • Technology does not drive culture change… interaction between organisms and their setting drive change. ...
... • Culture change is not linear or progressive. Change is locally determined by the setting and the essential features that relate folks to that setting. • Technology does not drive culture change… interaction between organisms and their setting drive change. ...
Evolution
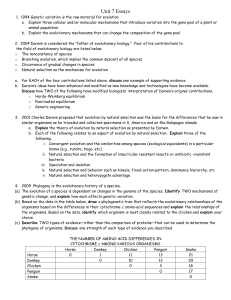
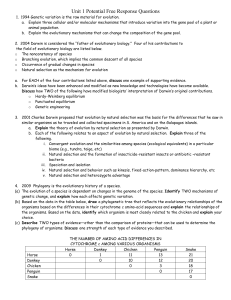
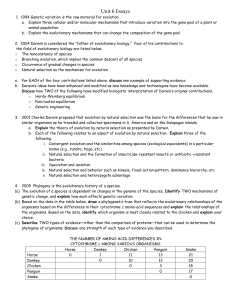
... 1. 1994 Genetic variation is the raw material for evolution. a. Explain three cellular and/or molecular mechanisms that introduce variation into the gene pool of a plant or animal population. b. Explain the evolutionary mechanisms that can change the composition of the gene pool. 2. 2004 Darwin is c ...
... 1. 1994 Genetic variation is the raw material for evolution. a. Explain three cellular and/or molecular mechanisms that introduce variation into the gene pool of a plant or animal population. b. Explain the evolutionary mechanisms that can change the composition of the gene pool. 2. 2004 Darwin is c ...
Unit 6 Essays
... 1. 1994 Genetic variation is the raw material for evolution. a. Explain three cellular and/or molecular mechanisms that introduce variation into the gene pool of a plant or animal population. b. Explain the evolutionary mechanisms that can change the composition of the gene pool. 2. 2004 Darwin is c ...
... 1. 1994 Genetic variation is the raw material for evolution. a. Explain three cellular and/or molecular mechanisms that introduce variation into the gene pool of a plant or animal population. b. Explain the evolutionary mechanisms that can change the composition of the gene pool. 2. 2004 Darwin is c ...
Unit 6 Essays
... 1. 1994 Genetic variation is the raw material for evolution. a. Explain three cellular and/or molecular mechanisms that introduce variation into the gene pool of a plant or animal population. b. Explain the evolutionary mechanisms that can change the composition of the gene pool. 2. 2004 Darwin is c ...
... 1. 1994 Genetic variation is the raw material for evolution. a. Explain three cellular and/or molecular mechanisms that introduce variation into the gene pool of a plant or animal population. b. Explain the evolutionary mechanisms that can change the composition of the gene pool. 2. 2004 Darwin is c ...
Chapter 15 - Western High School
... • Individuals in a population show variations among others in the same species • Variations are inherited • Animals have more young than can survive on the available resources • Variations that increase reproductive success will be more common in the next generation ...
... • Individuals in a population show variations among others in the same species • Variations are inherited • Animals have more young than can survive on the available resources • Variations that increase reproductive success will be more common in the next generation ...
The puzzle of ultrasociality
... (e.g., Bellah 2011). Other key innovations include literacy and record keeping, formal legal systems, bureaucracies, organized religion, urbanization, and states. The primary mode of evolution during this stage was clearly cultural, although recent analyses indicate that genetic evolution did not ce ...
... (e.g., Bellah 2011). Other key innovations include literacy and record keeping, formal legal systems, bureaucracies, organized religion, urbanization, and states. The primary mode of evolution during this stage was clearly cultural, although recent analyses indicate that genetic evolution did not ce ...
Ecology Unit Outline - nnhsbiology
... 2. We often discuss “life” and assume that we collectively know what the term “life” means. a. To a biologist such as yourself (yes you are) how do you determine that something is alive? b. How did “life” come into being on earth? c. How did first life alter the planet’s landscape and atmosphere an ...
... 2. We often discuss “life” and assume that we collectively know what the term “life” means. a. To a biologist such as yourself (yes you are) how do you determine that something is alive? b. How did “life” come into being on earth? c. How did first life alter the planet’s landscape and atmosphere an ...
12_biology_impQ_CH07_evolution
... Speciation : It is the formation of new species from the pre-existing ones. Organic (Biological) Evolution : Changes in the characteristics/features of organisms or groups of such populations over a number of generations. Homologous organs : These have same basic structure and embryonic origin but p ...
... Speciation : It is the formation of new species from the pre-existing ones. Organic (Biological) Evolution : Changes in the characteristics/features of organisms or groups of such populations over a number of generations. Homologous organs : These have same basic structure and embryonic origin but p ...
AP Biology - Naber Biology
... 5. Explain the role of fossils in rock strata as a window to life in earlier times. ...
... 5. Explain the role of fossils in rock strata as a window to life in earlier times. ...
Theory
... No new species originated; species could only be lost over time. Result - No evolution. ...
... No new species originated; species could only be lost over time. Result - No evolution. ...
An Introduction to Evolution
... The Importance of Understanding Evolution Understanding evolution you will give you a greater appreciation for… -the way plants and animals survive -why plants and animals look the way the do -why species are found only in certain areas -the natural world!!! ...
... The Importance of Understanding Evolution Understanding evolution you will give you a greater appreciation for… -the way plants and animals survive -why plants and animals look the way the do -why species are found only in certain areas -the natural world!!! ...
Natural selection and adaptation
... Scoville,H.”What is Evolution?”History and Definitions.2015. 21 August 2015..
http://evolution.about.com/od/scientists/p/Georges-Cuvier.htm
http://evolution.about.com/od/evidence/a/Fossil-Record.htm
...
... Scoville,H.”What is Evolution?”History and Definitions.2015. 21 August 2015.
Evolution Study Guide 2 - OG
... C. adaptation B. fossil evidence D. none of the above 3. Darwin realized that members of populations compete for food, living space, and other necessities. This is known as A. struggle for existence. C. survival of the fittest. B. variation and adaptations. D. natural selection. 4. Both bats and mos ...
... C. adaptation B. fossil evidence D. none of the above 3. Darwin realized that members of populations compete for food, living space, and other necessities. This is known as A. struggle for existence. C. survival of the fittest. B. variation and adaptations. D. natural selection. 4. Both bats and mos ...
Consolidation
... the LAW in order to enforce and impose ORDER. This order was an artificial not a natural order. It required power and authority to enforce the rules that were themselves merely human creations created to deal with human egoism (which was on Hobbes account) the only permanent or eternal reality. ...
... the LAW in order to enforce and impose ORDER. This order was an artificial not a natural order. It required power and authority to enforce the rules that were themselves merely human creations created to deal with human egoism (which was on Hobbes account) the only permanent or eternal reality. ...