Late Proterozoic – Paleozoic Tectonostratigraphic Development and
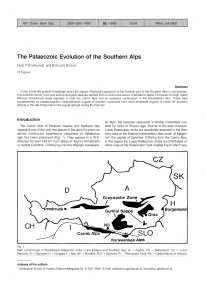
... et al. 1997). The supposed Panafrican provenance of some crustal elements thus requires careful scrutiny before an interpretation of their affinity. The present paper builds on the work of the authors in Moravia where the best data on the Cadomian basement and DevonianCarboniferous sediments and pa ...
... et al. 1997). The supposed Panafrican provenance of some crustal elements thus requires careful scrutiny before an interpretation of their affinity. The present paper builds on the work of the authors in Moravia where the best data on the Cadomian basement and DevonianCarboniferous sediments and pa ...
Evolution of the Paleo-Asian Ocean (Altai−Sayan Region, Central
... been integrated after Dobretsov et al. (1995). Fragments detached from Gondwanaland in Early Paleozoic have been postulated not only in Central Asia but also in the Middle East (Cocks, 2001 and the references). However, the breakup processes of Gondwana as well as those of Rodinia are still hypothet ...
... been integrated after Dobretsov et al. (1995). Fragments detached from Gondwanaland in Early Paleozoic have been postulated not only in Central Asia but also in the Middle East (Cocks, 2001 and the references). However, the breakup processes of Gondwana as well as those of Rodinia are still hypothet ...
as a PDF - University of Innsbruck
... quartzites and greywackes. They are overlain by more than 300 m thick acidic volcanites and volcaniclastic rocks named the "Comelico Porphyroid" and "Fleons Formation" respectively (Fig. 3), and their lateral equivalents comprising the Himmelberg Sandstone and the Uggwa Shale. Locally, the latter co ...
... quartzites and greywackes. They are overlain by more than 300 m thick acidic volcanites and volcaniclastic rocks named the "Comelico Porphyroid" and "Fleons Formation" respectively (Fig. 3), and their lateral equivalents comprising the Himmelberg Sandstone and the Uggwa Shale. Locally, the latter co ...
The Geology How old are the rocks?
... www.lancashire-geologists.co.uk The Geologists’ Association (GA) was formed in 1858, and actively promotes the study of geology to all who are interested in Earth Sciences. The Lancashire Group is a local branch of the GA which meets monthly in Clitheroe. It is an informal, friendly and inclusive or ...
... www.lancashire-geologists.co.uk The Geologists’ Association (GA) was formed in 1858, and actively promotes the study of geology to all who are interested in Earth Sciences. The Lancashire Group is a local branch of the GA which meets monthly in Clitheroe. It is an informal, friendly and inclusive or ...
Chapter 11—Late Paleozoic Events
... C. Metallic Ores (ores that accompany volcanism) 1. Hercynian-Alleghenian ores: Sn, Cu, Ag, Au, An, Pb, Pt 2. Uralian ores 3. Asian orogenic ores: China, Burma, Japan, Malaya Answers to Discussion Questions 1. The southern Appalachians (Alleghenian orogeny) and the Ouachita Mountains were built duri ...
... C. Metallic Ores (ores that accompany volcanism) 1. Hercynian-Alleghenian ores: Sn, Cu, Ag, Au, An, Pb, Pt 2. Uralian ores 3. Asian orogenic ores: China, Burma, Japan, Malaya Answers to Discussion Questions 1. The southern Appalachians (Alleghenian orogeny) and the Ouachita Mountains were built duri ...
Pangaea - SD43 Teacher Sites
... similarly, the freshwater reptile Mesosaurus has only been found in localized regions of the coasts of Brazil and West Africa.[5] Additional evidence for Pangaea is found in the geology of adjacent continents, including matching geological trends between the eastern coast of South America and the we ...
... similarly, the freshwater reptile Mesosaurus has only been found in localized regions of the coasts of Brazil and West Africa.[5] Additional evidence for Pangaea is found in the geology of adjacent continents, including matching geological trends between the eastern coast of South America and the we ...
The Variscides
... Shan in Asia, and the Lachland Fold Belt in Australia, the Variscan Belt is a segment of a mountain system that has existed all around the world during the Paleozoic, as the Alpine mountain system encircles the globe today. ...
... Shan in Asia, and the Lachland Fold Belt in Australia, the Variscan Belt is a segment of a mountain system that has existed all around the world during the Paleozoic, as the Alpine mountain system encircles the globe today. ...
Take a closer look at... FERNS
... Some ferns are tiny, with mossy leaves just 1 cm long, but rare tropical tree ferns can grow up to 25 m tall. Ferns can absorb heavy metals from the air and soil. They can be used to clean up polluted areas. One species of fern - bracken - can smother hillsides. Now bracken is being turned into comp ...
... Some ferns are tiny, with mossy leaves just 1 cm long, but rare tropical tree ferns can grow up to 25 m tall. Ferns can absorb heavy metals from the air and soil. They can be used to clean up polluted areas. One species of fern - bracken - can smother hillsides. Now bracken is being turned into comp ...
responses to questions accompanying selected figures
... What shape was the Pangea landmass at the end of the Paleozoic? a. the land mass stretched out in a east-west orientation b. the land mass stretched out in a north-south orientation c. the land mass stretched out in a northeast-southwest orientation ...
... What shape was the Pangea landmass at the end of the Paleozoic? a. the land mass stretched out in a east-west orientation b. the land mass stretched out in a north-south orientation c. the land mass stretched out in a northeast-southwest orientation ...
Settle-Carlisle booklet
... As the train pulls out of Settle, Sugar Loaf hill is to the east. It is formed of Carboniferous Limestone and along the bottom of the hill lies the South Craven fault. This fault is part of the system of faults (including the North Craven Fault) which form the boundary between the Pennine basin to t ...
... As the train pulls out of Settle, Sugar Loaf hill is to the east. It is formed of Carboniferous Limestone and along the bottom of the hill lies the South Craven fault. This fault is part of the system of faults (including the North Craven Fault) which form the boundary between the Pennine basin to t ...
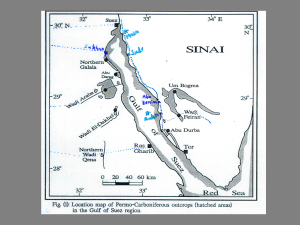
Abu Darag Formation
... about 10 kms south of Ain Sukhna. This formation could be subdivided into three members as follows (KORA & MANSOUR 1992). ...
... about 10 kms south of Ain Sukhna. This formation could be subdivided into three members as follows (KORA & MANSOUR 1992). ...
Coal Measures
... In the United Kingdom, ‘Coal Measures’ refer to layers of rock specifically from a time that geologists call the Upper Carboniferous period. The Coal Measures were deposited about 310 million years ago, and these layers of rock contain many coal seams. At this time in the Earth’s history, the rocks ...
... In the United Kingdom, ‘Coal Measures’ refer to layers of rock specifically from a time that geologists call the Upper Carboniferous period. The Coal Measures were deposited about 310 million years ago, and these layers of rock contain many coal seams. At this time in the Earth’s history, the rocks ...
Carboniferous

The Carboniferous is a geologic period and system that extends from the end of the Devonian Period, at 358.9 ± 0.4 million years ago, to the beginning of the Permian Period, at 298.9 ± 0.15 Ma. The name Carboniferous means ""coal-bearing"" and derives from the Latin words carbō (“coal”) and ferō (“I bear, I carry”), and was coined by geologists William Conybeare and William Phillips in 1822. Based on a study of the British rock succession, it was the first of the modern 'system' names to be employed, and reflects the fact that many coal beds were formed globally during this time. The Carboniferous is often treated in North America as two geological periods, the earlier Mississippian and the later Pennsylvanian.Terrestrial life was well established by the Carboniferous period. Amphibians were the dominant land vertebrates, of which one branch would eventually evolve into reptiles, the first fully terrestrial vertebrates. Arthropods were also very common, and many (such as Meganeura), were much larger than those of today. Vast swaths of forest covered the land, which would eventually be laid down and become the coal beds characteristic of the Carboniferous system. The atmospheric content of oxygen also reached their highest levels in history during the period, 35% compared with 21% today. This increased the atmospheric density by a third over today’s value. A minor marine and terrestrial extinction event occurred in the middle of the period, caused by a change in climate. The later half of the period experienced glaciations, low sea level, and mountain building as the continents collided to form Pangaea.