Guidelines for Evolution Quiz
... Know the “Early” explanations of life and questions that arose from these explanations Know the basic ideas put forth by Lamarck, Malthus, and Lyell. Be able to describe Darwin’s Observations from his trip to the Galapagos Islands Be able to describe the mechanism of natural selection & arti ...
... Know the “Early” explanations of life and questions that arose from these explanations Know the basic ideas put forth by Lamarck, Malthus, and Lyell. Be able to describe Darwin’s Observations from his trip to the Galapagos Islands Be able to describe the mechanism of natural selection & arti ...
Reading 8.2 – Adaptive Radiation
... specific food sources found on different islands). Over time, these differences in variations between populations become more and more pronounced through mutation, genetic drift, and natural selection. And as each population continues to acquire more and more specialized traits for survival in that ...
... specific food sources found on different islands). Over time, these differences in variations between populations become more and more pronounced through mutation, genetic drift, and natural selection. And as each population continues to acquire more and more specialized traits for survival in that ...
Evolution final project
... Types of Selection: Includes a small diagram/graph of the type of selection next to the trait with a brief clear and accurate description. More than 1 type is included. Phylogenetic Tree: Includes a cladogram illustrating the organism’s history of descendants (at least 5) with shared derived charact ...
... Types of Selection: Includes a small diagram/graph of the type of selection next to the trait with a brief clear and accurate description. More than 1 type is included. Phylogenetic Tree: Includes a cladogram illustrating the organism’s history of descendants (at least 5) with shared derived charact ...
Decent With Modification Darwin’s Theory
... all phenomena can be explained in a rational way, in terms of natural causes, without invoking the supernatural ...
... all phenomena can be explained in a rational way, in terms of natural causes, without invoking the supernatural ...
15-3 Darwin Presents His Case
... Homologous structures: structures that have different mature forms but develop from the same embryonic tissues Provides strong evidence that all 4-limbed vertebrates have descended, with modifications, from common ancestors ...
... Homologous structures: structures that have different mature forms but develop from the same embryonic tissues Provides strong evidence that all 4-limbed vertebrates have descended, with modifications, from common ancestors ...
Natural Selection
... • Proposed by Charles Darwin in 1859, based on his observations • Natural selection affects populations, not individuals • Natural selection produces change in populations due to genetic variations present • Ex) Leopard frogs • Populations in genetic equilibrium do not change or evolve • Natural sel ...
... • Proposed by Charles Darwin in 1859, based on his observations • Natural selection affects populations, not individuals • Natural selection produces change in populations due to genetic variations present • Ex) Leopard frogs • Populations in genetic equilibrium do not change or evolve • Natural sel ...
Chapter 16 Evolution and Adapations
... that share a common origin but may serve different functions in modern species. • These structures are evidence that organisms with similar structure evolved from a common ancestor. ...
... that share a common origin but may serve different functions in modern species. • These structures are evidence that organisms with similar structure evolved from a common ancestor. ...
Evolution and the History of Life
... Darwin Does Some Thinking • Darwin wonders how did the finches become so different. He thought maybe there was a storm that separated the original population resulting in geographic isolation (one of the ways that speciation can occur) • Darwin’s hypothesis was that the Galápagos finches were desce ...
... Darwin Does Some Thinking • Darwin wonders how did the finches become so different. He thought maybe there was a storm that separated the original population resulting in geographic isolation (one of the ways that speciation can occur) • Darwin’s hypothesis was that the Galápagos finches were desce ...
EEB 245/Spring 2004 C. Simon First Study Guide, second
... If the frequency of the common allele in a population was .7 and there were only two alleles at that locus, what would be the expected proportions of each genotype in the next generation, assuming that the population was in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? List four factors that can cause a heterozygote ...
... If the frequency of the common allele in a population was .7 and there were only two alleles at that locus, what would be the expected proportions of each genotype in the next generation, assuming that the population was in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? List four factors that can cause a heterozygote ...
2-3-16 Evolution Outline Packet 1
... 2. Domestic animals (Which ones are the most valuable in terms of food or other characteristics.) B. Man can “erase” what Nature took thousands of years to “create” (gradualism) by controlling which organisms get to reproduce and which don’t. C. This is not always the best outcome for that environme ...
... 2. Domestic animals (Which ones are the most valuable in terms of food or other characteristics.) B. Man can “erase” what Nature took thousands of years to “create” (gradualism) by controlling which organisms get to reproduce and which don’t. C. This is not always the best outcome for that environme ...
a17 HowPopEvolve
... Darwin was intrigued by he fact that Galápagos Island organisms resembled those in South America. ...
... Darwin was intrigued by he fact that Galápagos Island organisms resembled those in South America. ...
AP Biology TEST #5 – EVOLUTION REVIEW SHEET
... 31. Which of the following statements about gene families is false? A) Gene families evolve via gene duplication. B) Pseudogenes are quickly removed from gene families by deletion. C) Members of a gene family can include several functional genes. D) Examples of gene families include the engrailed a ...
... 31. Which of the following statements about gene families is false? A) Gene families evolve via gene duplication. B) Pseudogenes are quickly removed from gene families by deletion. C) Members of a gene family can include several functional genes. D) Examples of gene families include the engrailed a ...
Evidence of Evolution2013
... Evidence of Evolution Background When Charles Darwin first proposed the idea that all new species descend from an ancestor, he performed an exhaustive amount of research to provide as much evidence as possible. Today, the major pieces of evidence for this theory can be broken down into the fossil re ...
... Evidence of Evolution Background When Charles Darwin first proposed the idea that all new species descend from an ancestor, he performed an exhaustive amount of research to provide as much evidence as possible. Today, the major pieces of evidence for this theory can be broken down into the fossil re ...
HS-LS4 Biological Evolution: Unity and Diversity
... and reproduce in their altered environment. If members cannot adjust to change that is too fast or drastic, the opportunity for the species’ evolution is lost. (HS-LS4-5) LS4.D: Biodiversity and Humans Humans depend on the living world for the resources and other benefits provided by biodiversity. ...
... and reproduce in their altered environment. If members cannot adjust to change that is too fast or drastic, the opportunity for the species’ evolution is lost. (HS-LS4-5) LS4.D: Biodiversity and Humans Humans depend on the living world for the resources and other benefits provided by biodiversity. ...
ARTICLE- Lamarck vs. Darwin
... did not accept an arrow of complexity driving through the history of life. He argued that complexity evolved simply as a result of life adapting to its local conditions from one generation to the next. He also argued that species could go extinct rather than change into new forms. But Darwin also re ...
... did not accept an arrow of complexity driving through the history of life. He argued that complexity evolved simply as a result of life adapting to its local conditions from one generation to the next. He also argued that species could go extinct rather than change into new forms. But Darwin also re ...
Diversity of life Notes: WAP 111
... Consider characteristics that are common to all living organisms and develop an operational definition of life. Become familiar with the microscope as a tool used by scientists to study organisms in detail. Discover cells and begin to understand their importance as the basic units of life. Appreciat ...
... Consider characteristics that are common to all living organisms and develop an operational definition of life. Become familiar with the microscope as a tool used by scientists to study organisms in detail. Discover cells and begin to understand their importance as the basic units of life. Appreciat ...
Chapter 15 notes I. Darwin`s Voyage and Discovery A. 1809 Charles
... a. Example: Rainbow trout spawn in the spring. Brook trout spawn in the fall. These two species are isolated reproductively by time. ...
... a. Example: Rainbow trout spawn in the spring. Brook trout spawn in the fall. These two species are isolated reproductively by time. ...
"evolution" is best described as
... 2. Different species evolved because of inbreeding 3. There were no new species evolving at this time. 4. Changes in the environment caused some different species to develop. ...
... 2. Different species evolved because of inbreeding 3. There were no new species evolving at this time. 4. Changes in the environment caused some different species to develop. ...
evolution by natural selection
... individuals with one version of the trait have greater reproductive success than individuals with a different version of the trait. It can also be thought of as the elimination of alleles from a population that reduce the reproductive rate of individuals carrying them relative to the reproductive ra ...
... individuals with one version of the trait have greater reproductive success than individuals with a different version of the trait. It can also be thought of as the elimination of alleles from a population that reduce the reproductive rate of individuals carrying them relative to the reproductive ra ...
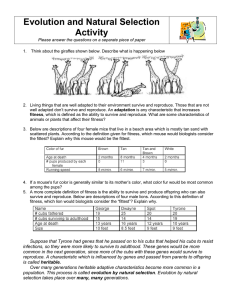
Evolution and Natural Selection Activity
... 6. Why would a deer be more likely to eat the left front cactus than the other two shown? 7. In figure 3, two of the cacti have flowers, but the cactus that has been eaten by the deer is too damaged to make flowers. Figure 4 shows the situation several months later. What has happened? Do you think t ...
... 6. Why would a deer be more likely to eat the left front cactus than the other two shown? 7. In figure 3, two of the cacti have flowers, but the cactus that has been eaten by the deer is too damaged to make flowers. Figure 4 shows the situation several months later. What has happened? Do you think t ...
Giants of Evolution - York College of Pennsylvania
... but constant diversity of circumstances, she has gradually brought about in this respect the state of things which we now observe. How grand is this consideration, and especially how remote is it from all that is generally thought on this subject!" Text of a lecture given by Lamarck at the Musée Nat ...
... but constant diversity of circumstances, she has gradually brought about in this respect the state of things which we now observe. How grand is this consideration, and especially how remote is it from all that is generally thought on this subject!" Text of a lecture given by Lamarck at the Musée Nat ...
ch4 - Otterville R-VI School District
... genetic variability Mutations: random changes in the structure or number of DNA molecules in a cell that can be inherited by offspring. ...
... genetic variability Mutations: random changes in the structure or number of DNA molecules in a cell that can be inherited by offspring. ...
Evolution: Exhibition Notes 1
... Charles Darwin In 1831, the idea of change through evolution was not new and scientific thought was ripe for advancement in this field. A 22 year old Charles Darwin joined a 5-year expedition on HMS Beagle as the ship’s naturalist. The voyage covered 64,000 kilometres charting the South American coa ...
... Charles Darwin In 1831, the idea of change through evolution was not new and scientific thought was ripe for advancement in this field. A 22 year old Charles Darwin joined a 5-year expedition on HMS Beagle as the ship’s naturalist. The voyage covered 64,000 kilometres charting the South American coa ...