I II III
... Because of the exponential, small differences in how you round in calculating k2 can make large apparent differences here. ...
... Because of the exponential, small differences in how you round in calculating k2 can make large apparent differences here. ...
Distributed measurement-based quantum computation
... a formal language for distributed quantum computation is lacking. While some endeavors have been made into using techniques from classical process calculi [LJ04, GN04], these have remained rather descriptive and are, to our opinion, not very well-suited to really get a grip on the low-level quantum ...
... a formal language for distributed quantum computation is lacking. While some endeavors have been made into using techniques from classical process calculi [LJ04, GN04], these have remained rather descriptive and are, to our opinion, not very well-suited to really get a grip on the low-level quantum ...
Sri Aurobindo International Centre of Education
... within the content of its consciousness. The result is an effective multitude of individuals perceiving each other from different perspectives. Concomitantly, each self adopts a temporal viewpoint, which is to say that it experiences the world in succession. (Note that all experiential nows are sync ...
... within the content of its consciousness. The result is an effective multitude of individuals perceiving each other from different perspectives. Concomitantly, each self adopts a temporal viewpoint, which is to say that it experiences the world in succession. (Note that all experiential nows are sync ...
CH13 - 3 - F=ma n-t coordinates
... The tangential acceleration, at = dv/dt, represents the time rate of change in the magnitude of the velocity. Depending on the direction of Ft, the particle’s speed will either be increasing or decreasing. The normal acceleration, an = v2/ , represents the time rate of change in the direction of the ...
... The tangential acceleration, at = dv/dt, represents the time rate of change in the magnitude of the velocity. Depending on the direction of Ft, the particle’s speed will either be increasing or decreasing. The normal acceleration, an = v2/ , represents the time rate of change in the direction of the ...
Lecture 5: The Hydrogen Atom (continued). In the previous lecture
... Thus we have n values of ` for a fixed value n of the principal q.n., and for every value of the orbital angular momentum q.n. we have 2` + 1 values of m. Therefore the number of different states with the same n is n2 . When there is more than one wave function at a given energy eigenvalue, then tha ...
... Thus we have n values of ` for a fixed value n of the principal q.n., and for every value of the orbital angular momentum q.n. we have 2` + 1 values of m. Therefore the number of different states with the same n is n2 . When there is more than one wave function at a given energy eigenvalue, then tha ...
Chapter 6. Central Force Motion
... It is to be noted that the centrifugal potential “reduces” the effect of the inverse-squarelaw on the particle. This is because the inverse-square-law force is attractive while the centrifugal force is repulsive. This can be seen in Figure 6-2. It is also possible to guess some characteristics of po ...
... It is to be noted that the centrifugal potential “reduces” the effect of the inverse-squarelaw on the particle. This is because the inverse-square-law force is attractive while the centrifugal force is repulsive. This can be seen in Figure 6-2. It is also possible to guess some characteristics of po ...
Notes #2 Chem 341
... What are the conditions under which the two obsevables may be specified simultaneously with as much precision as desired? ...
... What are the conditions under which the two obsevables may be specified simultaneously with as much precision as desired? ...
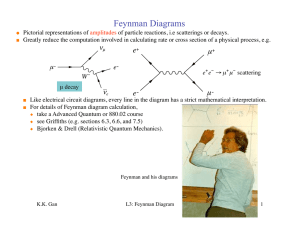
Feynman Diagrams
... Like electrical circuit diagrams, every line in the diagram has€a strict mathematical interpretation. For details of Feynman diagram calculation, ◆ take a Advanced Quantum or 880.02 course ◆ see Griffiths (e.g. sections 6.3, 6.6, and 7.5) ◆ Bjorken & Drell (Relativistic Quantum Mechanics ...
... Like electrical circuit diagrams, every line in the diagram has€a strict mathematical interpretation. For details of Feynman diagram calculation, ◆ take a Advanced Quantum or 880.02 course ◆ see Griffiths (e.g. sections 6.3, 6.6, and 7.5) ◆ Bjorken & Drell (Relativistic Quantum Mechanics ...
Document
... measurements. The probability measure P(ω)=|<ω|Ψ>|2 is not an axiom any more but a consequence of quantum mechanics and the probability theory. λω (A) is interpreted as a value of A in the context of the pre-selected state |Ψ> and the post-selected states {<ω|} of the intended projective measurement ...
... measurements. The probability measure P(ω)=|<ω|Ψ>|2 is not an axiom any more but a consequence of quantum mechanics and the probability theory. λω (A) is interpreted as a value of A in the context of the pre-selected state |Ψ> and the post-selected states {<ω|} of the intended projective measurement ...