* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download - Smart Science
Survey
Document related concepts
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Embryonic stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Stem-cell therapy wikipedia , lookup
Dictyostelium discoideum wikipedia , lookup
Chimera (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Induced pluripotent stem cell wikipedia , lookup
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
State switching wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
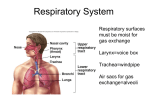
Biology Term 1 B1.7 Unit 1 – Cells B1.1 Unit 2 – Size matters B2.1 Each side is a square so: B1.1 TB The largest known living single-celled organisms are sponge-like creatures called xenophyophores that live on the ocean floor. They can reach a size of up to 20 cm across. Surface area of each square = 4 cm 4 cm = 16 cm2 Total surface area of cube = 16 6 = 96 cm2 Volume of cube = 4 cm 4 cm 4 cm = 64 cm3 The biggest egg ever laid was about 30 cm in length and was laid by an animal that is now extinct: the Elephant Bird of Madagascar. So the surface area to volume ratio = 96/64 = 1.5 B1.3 B2.2 Eyepiece Objective Magnification A mouse has fur over its body and face to keep heat in. It also sits very close to the ground and can roll up into a ball to keep heat in. 10 10 100 B2.3 15 100 1500 5 20 100 10 40 400 Large organisms need much more energy to live than small organisms, so they have larger and more complicated digestive systems. They need big, powerful hearts to pump the blood around their circulatory systems. B1.5 B2.3 TB Specialised human cells include red blood cells, white blood cells, muscle cells, brain cells, sex cells (gametes), liver cells, skin cells. A small bird such as a hummingbird has feathers to keep warm and to help it fly. It flies short distances and has to flap its wings very fast. Its heart is small and beats very fast to keep circulating its blood. It spends most of the daytime finding food, and eats higher energy food such as nectar. Many small birds huddle together in groups at night to share warmth. In a flowering plant, specialised cells include root hair cells, leaf cells, gametes (sex cells) and palisade cells. B1.6 Excretory system: liver, kidneys Nervous system: brain Digestive system: stomach, intestines A small mammal such as a bat lives and sleeps during the day huddled together with many other bats to keep warm. It lives in warmer, sheltered, dark places out of reach of predators. Its wings are made of skin that it wan wrap around itself to keep warm; its body is covered in fur. It spends most of the night flying fast and catching and © Smart Learning Ltd 2014 – Copying permitted for purchasing institution only. SMART SCIENCE 1 Biology Term 1 – Answers to Student’s Book questions Answers: Student’s Book questions Biology Term 1 – Answers to Student’s Book questions Answers: Student’s Book questions eating insects. Bats hibernate over the winter to avoid cold temperatures and lack of food. Unit 9 – Movement A small reptile such as a lizard seeks out warm, sunny places in which to spend the day. Lizards are cold-blooded, meaning they need external warmth such as from the Sun in order to live. When they need to move they do so quickly, in order to catch prey such as insects. B9.1 B2.4 TB (1) B9.2 Total volume of lungs is about 6000 cm3. There are 10 mm in every 1 cm, so there are 1000 mm3 in every 1 cm3. So the total volume of lungs is about 6000 1000 = 6000 000 mm3 Bones have blood vessels because the living cells in bone need a supply of nutrients. Also, the new blood cells formed in the bone marrow need to be carried away to join the rest of the blood in the body. A sensitive plant detects an object nearby by a change in the electrical charge on the leaves. The leaves then fold up, and the leaf stalks droop down, because the plant withdraws water from the leaves and stalk. B2.4 TB (2) Number of alveoli volume of lungs volume of one alveolus 6000 000 750 million 0.008 B2.4 TB (3) Total surface area = area of one alveolus number of alveoli = 0.2 mm2 750 000 000 = 150 000 000 mm2 = 1500 000 cm2 B2.4 TB (4) Total surface area of lungs if they were simple spheres = 2000 cm3. So by having millions of alveoli inside the lungs, the total surface area = 1500 000 = 750 times larger than simple spheres. 2000 B2.4 TB (5) Surface area of tennis court = 23.2 8.2 = just over 190 m2 = 1900 000 cm2. So the surface area of the alveoli in our lungs is not much smaller than the area of a tennis court! B2.5 A blue whale’s brain is the largest brain known. It has a mass of about 6.0 kg, which is slightly more than four times more massive than a human brain. This might mean blue whales are very intelligent, but we know that the size of an animal’s brain does not necessarily relate to the animal’s intelligence. (We know that whales communicate through complex sounds and show intelligent behaviour, but we cannot tell how intelligent they may be from the size of their brains.) 2 TEACHER’S HANDBOOK 1 B9.5 The thigh contains an antagonistic pair of muscles, one in the front and one behind the bone. (There are more muscles than this in the thigh, but this explains the basic principle.) To lift the leg up, the front muscle contracts while the back muscle relaxes; to push the leg back down, the front muscle relaxes and the back muscle contracts. B9.5 TB What appears to be a ‘knee’ on a flamingo is in fact the equivalent of a human ankle. The flamingo’s knee is hidden under its feathers, higher up near the top of its leg. B9.6 (1) Bones help protect your organs from damage, as well as hold the parts of our body in place and make blood. If you are playing sports, you can protect your bones from damage by wearing protective clothing and being careful. If you are unlucky enough to break a bone, if it did not repair itself you would lose protection of your organs in that part of your body, and you might not be able to walk (if, for example, a leg bone stays broken). B9.6 (2) Fruit and vegetables provide minerals and vitamins. We can get minerals and some vitamins from dairy products too such as milk. © Smart Learning Ltd 2014 – Copying permitted for purchasing institution only.