* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AP_Physics_B_-_Planck_s_Constant_lab
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Mercury-arc valve wikipedia , lookup
Topology (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Stepper motor wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Signal-flow graph wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Current mirror wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
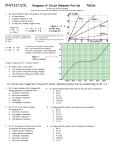
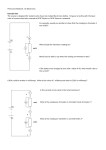
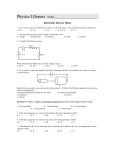
Name_________________________Box #_____ Date_____________________per____________ AP Physics B – Planck’s Constant Purpose: To use an LED to measure the threshold voltage in efforts to graphically determine the value for Planck’s Constant. Materials: Pasco Circuit board, voltmeter, ammeter, various LEDS In this lab we will be introduced to TWO new schematic symbols, This is called a variable resistance, also known as a dimmer switch. There are THREE connections, one on each end and one in the middle. This is called an LED, light emitting diode. This is a great example to illustrate the photoelectric effect due to the GAP in between the terminals. The LED has two leads, one longer than the other. The short lead is the negative terminal and the long lead is the positive. Construct a series circuit with a 3Volt DC power source, a variable resistor, a voltmeter, an ammeter, and an LED. Draw the circuit below and get it checked by your instructor. Hint: The LED must be attached to the middle and one of the outside leads of the variable resistor. Procedure: 1. Record the color and wavelength of the LED you are using. 2. Measure and record the current (A) and the voltage (V) as you turn the dimmer switch. You may have to record the same current over and over. This is normal. Do this until you cannot turn the switch any farther. 3. Plot a graph of current ( y-axis) and voltage ( x-axis). 4. Measure and record the STOPPING VOLTAGE of the LED, which will be the KNEE of the graph. (see picture for reference). 5. Repeat this procedure for four different colors. LED 1 Volts Current LED 2 Volts Current LED 3 Volts Current LED 4 Volts Current LED COLOR Wavelength Frequency Stopping Potential Using the stopping potential and the charge of an electron, calculate the maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons for each LED below. Make a graph of kinetic energy ( y-axis) and frequency (x-axis) . Find the slope and y-intercept of this graph. Slope _____________________ Y-intercept____________________ What does the slope and y-intercept represent? Determine the % error between the experimental value for Planck’s Constant and the actual value.